Brief overview of Bio backgound
... Polymer, genotype, phenotype, conformation Inheritance, homology, phylogenetic trees ...
... Polymer, genotype, phenotype, conformation Inheritance, homology, phylogenetic trees ...
2-Familial adenomatous polyposis coli
... Most common polymorphisms are neutral, but some cause subtle changes in gene expression or in protein structure and function .It is thought that these polymorphisms lead to variations in phenotype within the general population, including variations in susceptibility to common diseases. An example is ...
... Most common polymorphisms are neutral, but some cause subtle changes in gene expression or in protein structure and function .It is thought that these polymorphisms lead to variations in phenotype within the general population, including variations in susceptibility to common diseases. An example is ...
Inheritance - World of Teaching
... which make up chromosomes. Responsible for inheritance of specific characteristics ...
... which make up chromosomes. Responsible for inheritance of specific characteristics ...
Mutations - year13bio
... to a stop codon resulting in a shorter, usually nonfunctional protein. ...
... to a stop codon resulting in a shorter, usually nonfunctional protein. ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... Gregor Mendel was the first to suggest that heritable factors were passed from parent to offspring, determining characteristics Genomics is the study of an organism’s genome (its entire hereditary content) Humans have the most complex genome of any living organism The wheat genome (Triticum aestivum ...
... Gregor Mendel was the first to suggest that heritable factors were passed from parent to offspring, determining characteristics Genomics is the study of an organism’s genome (its entire hereditary content) Humans have the most complex genome of any living organism The wheat genome (Triticum aestivum ...
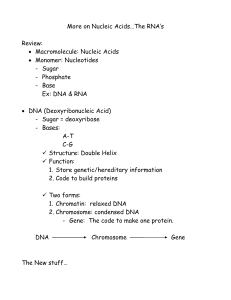
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... Function: 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
... Function: 1. Store genetic/hereditary information 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
History of Genetics
... – the genetic code is a list of which 3 base DNA or RNA sequence (codon) encodes which amino acid. The same genetic code is used in (almost) all organisms. ...
... – the genetic code is a list of which 3 base DNA or RNA sequence (codon) encodes which amino acid. The same genetic code is used in (almost) all organisms. ...
History of Genetics - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... – the genetic code is a list of which 3 base DNA or RNA sequence (codon) encodes which amino acid. The same genetic code is used in (almost) all organisms. ...
... – the genetic code is a list of which 3 base DNA or RNA sequence (codon) encodes which amino acid. The same genetic code is used in (almost) all organisms. ...
1 Biology 20 Protein Synthesis DNA: How is this linear information
... If mutations occur in the gametes (sperm or ovum), then they can be transferred to offspring Gene mutation: Point mutations: 2 types of mutations: 1) Base substitution: a) could make no difference at all, why? GGC Æ GGU in mRNA; still codes for glycine b) could be: c) could be detrimental (useless p ...
... If mutations occur in the gametes (sperm or ovum), then they can be transferred to offspring Gene mutation: Point mutations: 2 types of mutations: 1) Base substitution: a) could make no difference at all, why? GGC Æ GGU in mRNA; still codes for glycine b) could be: c) could be detrimental (useless p ...
Codons and Amino Acids
... Mutated Hemoglobin Sequence: GTG CAC CTG ACT CCT GTG GAG DNA Amino Acid Where is the location of the mutation that produced hemoglobin-s? What kind of a mutation is it (substitution, deletion, or insertion)? How does this mutation affect the amino acid sequence as compared to a normal hemoglobin mol ...
... Mutated Hemoglobin Sequence: GTG CAC CTG ACT CCT GTG GAG DNA Amino Acid Where is the location of the mutation that produced hemoglobin-s? What kind of a mutation is it (substitution, deletion, or insertion)? How does this mutation affect the amino acid sequence as compared to a normal hemoglobin mol ...
Lecture#31 – Evolution and cis
... –> just instructions are different (Hox genes - page 421-426 in text) Vertebrate on average ~20K genes The same set of genes has been relatively stable for ~100M years The real change is in the regulation of those genes -> altered expression Analogy: same bricks and cement to build a doghouse and a ...
... –> just instructions are different (Hox genes - page 421-426 in text) Vertebrate on average ~20K genes The same set of genes has been relatively stable for ~100M years The real change is in the regulation of those genes -> altered expression Analogy: same bricks and cement to build a doghouse and a ...
History of Genetics
... – the genetic code is a list of which 3 base DNA or RNA sequence (codon) encodes which amino acid. The same genetic code is used in (almost) all organisms. ...
... – the genetic code is a list of which 3 base DNA or RNA sequence (codon) encodes which amino acid. The same genetic code is used in (almost) all organisms. ...
Daily Learning Targets
... 12. I can describe the processes of replication, transcription, and translation. (C.1.a) ...
... 12. I can describe the processes of replication, transcription, and translation. (C.1.a) ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? ...
Mutations & DNA Technology Worksheet
... http://www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~mcclean/plsc431/chromnumber/number3.htm ...
... http://www.ndsu.edu/pubweb/~mcclean/plsc431/chromnumber/number3.htm ...
Genetics Unit Test
... c. mRNA going to ribosome. b. tRNA matching mRNA d. amino acids linked together. 35. An added gene is what type of mutation? a. deletion c. insertion b. substitution d. ultraviolet 36. Using DNA to identify who committed a crime is a. genetic engineering. c. genetic disease. b. DNA fingerprinting. d ...
... c. mRNA going to ribosome. b. tRNA matching mRNA d. amino acids linked together. 35. An added gene is what type of mutation? a. deletion c. insertion b. substitution d. ultraviolet 36. Using DNA to identify who committed a crime is a. genetic engineering. c. genetic disease. b. DNA fingerprinting. d ...
genetics - Yazscience10
... Genetic Code (2) • Human DNA contains enough information necessary to assemble about 100 000 different kinds of proteins • All known life forms use the same genetic code and same cellular mechanism to produce proteins • Humans share many genes with organisms that appear vastly different from us ...
... Genetic Code (2) • Human DNA contains enough information necessary to assemble about 100 000 different kinds of proteins • All known life forms use the same genetic code and same cellular mechanism to produce proteins • Humans share many genes with organisms that appear vastly different from us ...
Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) is an autosomal recessive
... Homolog of the Human Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome Gene. KATHARINA HOPP, Department of Biology, Brescia University, Owensboro, KY 42301. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes bone marrow failure, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, and congenital anomalies. SDS ...
... Homolog of the Human Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome Gene. KATHARINA HOPP, Department of Biology, Brescia University, Owensboro, KY 42301. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes bone marrow failure, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, and congenital anomalies. SDS ...
F4-6 Gene Regulation and Mutation Ch12,13
... particular proteins b. Operon responds to changes in environment 3. Parts of an operon a. Operator – segment of DNA that acts as on/off switch for transcription b. Promotor – section of DNA where RNA 1st binds c. Regulatory gene – makes repressor proteins to prevent or allow transcription d. Genes c ...
... particular proteins b. Operon responds to changes in environment 3. Parts of an operon a. Operator – segment of DNA that acts as on/off switch for transcription b. Promotor – section of DNA where RNA 1st binds c. Regulatory gene – makes repressor proteins to prevent or allow transcription d. Genes c ...
11.4.14 KEY - Iowa State University
... 5. LacI+ is (dominant/recessive) to LacI-. This is because LacI acts (cis/trans). 6. Explain why mutations in the lacO gene are cis in their effects. 7. Describe the three different types of mutations that are possible in structural genes. 1. gene product is present and inactive due to mutation, su ...
... 5. LacI+ is (dominant/recessive) to LacI-. This is because LacI acts (cis/trans). 6. Explain why mutations in the lacO gene are cis in their effects. 7. Describe the three different types of mutations that are possible in structural genes. 1. gene product is present and inactive due to mutation, su ...
Slide 1
... • What form does DNA take in the nucleus? • chromosome • How do the 150 million base pairs that make up the human genome fit into the nucleus? • wrapped around histones • coiled and supercoiled chromatin condenses into chromosomes ...
... • What form does DNA take in the nucleus? • chromosome • How do the 150 million base pairs that make up the human genome fit into the nucleus? • wrapped around histones • coiled and supercoiled chromatin condenses into chromosomes ...
Student Name: Teacher
... 13. It is often more difficult to improve polygenic traits than those controlled by simple inheritance because polygenic traits are controlled by: A. ...
... 13. It is often more difficult to improve polygenic traits than those controlled by simple inheritance because polygenic traits are controlled by: A. ...
Learning Guide:
... 3. Create a graphic organizer that illustrates the differences between the processes of transcription and translation, including how they operate in prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. 4. Create a diagram illustrating the following mutations: a. Silent mutation b. Missense mutation c. Nonsense mutation d. F ...
... 3. Create a graphic organizer that illustrates the differences between the processes of transcription and translation, including how they operate in prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. 4. Create a diagram illustrating the following mutations: a. Silent mutation b. Missense mutation c. Nonsense mutation d. F ...
Biology EOC One Page Quick Review Prokaryote – a unicellular
... Cell differentiation - a process that occurs in which cells and tissues become specialized Nucleotide – phosphate , sugar, base subunit of DNA, RNA Nitrogen bases – A, T, C, G, sequence of these determine amino acids that make proteins that give organisms traits Transcription – process of making mRN ...
... Cell differentiation - a process that occurs in which cells and tissues become specialized Nucleotide – phosphate , sugar, base subunit of DNA, RNA Nitrogen bases – A, T, C, G, sequence of these determine amino acids that make proteins that give organisms traits Transcription – process of making mRN ...
Recombinant DNA
... genome into bacterial episomes and create a library of bacterial colonies that can be used to replicate DNA ...
... genome into bacterial episomes and create a library of bacterial colonies that can be used to replicate DNA ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.