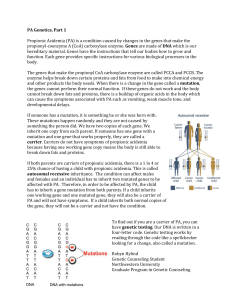
Mutation
... • 2. missense mutations. Missense mutations substitute one amino acid for another. Some missense mutations have very large effects, while others have minimal or no effect. It depends on where the mutation occurs in the protein’s structure, and how big a change in the type of amino acid it is. – Exam ...
... • 2. missense mutations. Missense mutations substitute one amino acid for another. Some missense mutations have very large effects, while others have minimal or no effect. It depends on where the mutation occurs in the protein’s structure, and how big a change in the type of amino acid it is. – Exam ...
Genetics - Bill Nye ANSWERS
... RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a specific amino acid? 3 Bacteria resistant to ...
... RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a specific amino acid? 3 Bacteria resistant to ...
ACTA2 - Cincinnati Children`s Hospital Medical Center
... All 9 exons of the ACTA2 gene, as well as the exon/intron boundaries and portion of untranslated regions of the gene are amplified by PCR. Genomic DNA sequences from both forward and reverse directions are obtained by automatic fluorescent detection using an ABI PRISM® 3730 DNA Analyzer. Sequence va ...
... All 9 exons of the ACTA2 gene, as well as the exon/intron boundaries and portion of untranslated regions of the gene are amplified by PCR. Genomic DNA sequences from both forward and reverse directions are obtained by automatic fluorescent detection using an ABI PRISM® 3730 DNA Analyzer. Sequence va ...
GENETIC MUTATIONS - Manning's Science
... Aneuploidy = incorrect number of chromosomes Trisomy = extra chromosome (2n +1) Monosomy = missing chromosome (2n -1) Triploid = 3n, Tetraploid = 4n ...
... Aneuploidy = incorrect number of chromosomes Trisomy = extra chromosome (2n +1) Monosomy = missing chromosome (2n -1) Triploid = 3n, Tetraploid = 4n ...
Principles of Genetics, A BRIEF INTRODUCTION
... material that occurs between adjacent chromatids during meiosis. Deme: An independent subpopulation. Diploid: In diploid organisms, each body cell carries two sets of chromosomes; each chromosome exists in two homolohous forms, one of which is phenotypically realized. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, a d ...
... material that occurs between adjacent chromatids during meiosis. Deme: An independent subpopulation. Diploid: In diploid organisms, each body cell carries two sets of chromosomes; each chromosome exists in two homolohous forms, one of which is phenotypically realized. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, a d ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
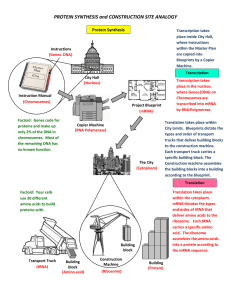
... within the Master Plan are copied into Blueprints by a Copier Machine. ...
... within the Master Plan are copied into Blueprints by a Copier Machine. ...
level two biology: genetic variation
... Naming and describing types of point mutations (insertion, elimination and substitution). Writing examples of insertion, elimination and substitution mutations (by writing out a sequence of bases – A, T, C and G). Defining the term ‘frame shift’ and describing which types of point mutation ...
... Naming and describing types of point mutations (insertion, elimination and substitution). Writing examples of insertion, elimination and substitution mutations (by writing out a sequence of bases – A, T, C and G). Defining the term ‘frame shift’ and describing which types of point mutation ...
Allele: One of the variant forms of the DNA sequence at a particular
... form (the recessive one). Some alleles may have no direct affect (silent) but may tag genes or other nearby alleles that are causative or contribute to a genetic characteristic, such as a disease or disease susceptibility. Chromosome: A compact, threadlike organization in the nucleus of human cells ...
... form (the recessive one). Some alleles may have no direct affect (silent) but may tag genes or other nearby alleles that are causative or contribute to a genetic characteristic, such as a disease or disease susceptibility. Chromosome: A compact, threadlike organization in the nucleus of human cells ...
06.Variation in human beings as a quality of life and a genetic
... The effects of chromosome and gene mutations are very variable. In many cases the mutations are lethal and prevent development of the organism. Some forms of chromosomal mutation may bring certain gene sequences together, and that combined effect may produce a «beneficial» characteristic. Another si ...
... The effects of chromosome and gene mutations are very variable. In many cases the mutations are lethal and prevent development of the organism. Some forms of chromosomal mutation may bring certain gene sequences together, and that combined effect may produce a «beneficial» characteristic. Another si ...
Example of selective breeding in cats
... collards and kale are have all originated from the same wild mustard plant. ...
... collards and kale are have all originated from the same wild mustard plant. ...
Human Genetics
... As the complementary strand is formed, the DNA and the new strand are “zipped” together, creating two separate strands of the same DNA. ...
... As the complementary strand is formed, the DNA and the new strand are “zipped” together, creating two separate strands of the same DNA. ...
I. Mutations: primary tools of genetic analysis
... of DNA ð one way geneticists classify mutations is by their effect on the DNA molecule B. Spontaneous mutations affecting genes occur at a very low rate 1. The mutation rate varies from gene to gene 2. Forward mutations occur more often than reverse mutations C. Mutations arise from many kinds of ra ...
... of DNA ð one way geneticists classify mutations is by their effect on the DNA molecule B. Spontaneous mutations affecting genes occur at a very low rate 1. The mutation rate varies from gene to gene 2. Forward mutations occur more often than reverse mutations C. Mutations arise from many kinds of ra ...
mutations
... 33 cell division (in egg cells). • with thirteen times as many errata in his DNA, about 185 of the 200 copying mistakes in each human conception may come from the sperm. • however, a woman’s eggs are more likely to carry serious errors in chromosome numbers, and these errors increase with maternal a ...
... 33 cell division (in egg cells). • with thirteen times as many errata in his DNA, about 185 of the 200 copying mistakes in each human conception may come from the sperm. • however, a woman’s eggs are more likely to carry serious errors in chromosome numbers, and these errors increase with maternal a ...
Ch9outline
... the amino acid sequence of a protein The Genetic Message Expressed I: Protein Form 9.12: Proteins are polyamides 9.13: Polypeptides are short chains of amino acids 9.14: Protein shapes are determined by interactions *9.15: Your hair curls due to disulfide bridges and hydrogen bonds The Genetic Messa ...
... the amino acid sequence of a protein The Genetic Message Expressed I: Protein Form 9.12: Proteins are polyamides 9.13: Polypeptides are short chains of amino acids 9.14: Protein shapes are determined by interactions *9.15: Your hair curls due to disulfide bridges and hydrogen bonds The Genetic Messa ...
Biology Final Exam
... 5. What would be the complementary sequence of nucleotides for an mRNA molecule on the original DNA strand above? 6. In RNA, thymine is replaced by ________________. 7. What would be the amino acid sequence translated from the following mRNA sequence: CCAGUUAGG? 8. What is a point mutation? 9. The H ...
... 5. What would be the complementary sequence of nucleotides for an mRNA molecule on the original DNA strand above? 6. In RNA, thymine is replaced by ________________. 7. What would be the amino acid sequence translated from the following mRNA sequence: CCAGUUAGG? 8. What is a point mutation? 9. The H ...
Propionic-Acidemia-G.. - Propionic Acidemia Foundation
... something the person did. We have two copies of each gene. We inherit one copy from each parent. If someone has one gene with a mutation and one gene that works properly, they are called a carrier. Carriers do not have symptoms of propionic acidemia because having one working gene copy means the bod ...
... something the person did. We have two copies of each gene. We inherit one copy from each parent. If someone has one gene with a mutation and one gene that works properly, they are called a carrier. Carriers do not have symptoms of propionic acidemia because having one working gene copy means the bod ...
If you have BRCA in the family (Scotland)
... been passed on to me. According to SIGN Guideline 3.2.2: “BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation analysis should be considered in a family where there is a 10% or greater risk of mutations present” I am therefore I may be eligible for genetic testing to find out whether or not I am a carrier. I’m aware that havin ...
... been passed on to me. According to SIGN Guideline 3.2.2: “BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation analysis should be considered in a family where there is a 10% or greater risk of mutations present” I am therefore I may be eligible for genetic testing to find out whether or not I am a carrier. I’m aware that havin ...
notes for mondays lab
... 2. Proteinase K: an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of cellular proteins by splitting them into smaller peptides and amino acids 3. Buffer AL: a cell lysis solution that breaks open cell and nuclear membranes 4. Ethanol: used to precipitate DNA from the extracted material 5. Buffer AW1 and AW2: ...
... 2. Proteinase K: an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of cellular proteins by splitting them into smaller peptides and amino acids 3. Buffer AL: a cell lysis solution that breaks open cell and nuclear membranes 4. Ethanol: used to precipitate DNA from the extracted material 5. Buffer AW1 and AW2: ...
Evolution, part 2
... Embryology These drawings are now known to be completely “fudged” to create similarities that do not exist. Even Richard Dawkins thinks that they should not be used. ...
... Embryology These drawings are now known to be completely “fudged” to create similarities that do not exist. Even Richard Dawkins thinks that they should not be used. ...
Introduction to Protein Science Architecture, Function
... Chapter2: Genomics and Proteomics - Protein evolution How do proteins develop new functions? (1) Divergence – progressive localized changes in sequence and structure -> initially to change in specificity -> ultimately to changes in the nature of the reaction catalysed (2) Recruitment – one protein ...
... Chapter2: Genomics and Proteomics - Protein evolution How do proteins develop new functions? (1) Divergence – progressive localized changes in sequence and structure -> initially to change in specificity -> ultimately to changes in the nature of the reaction catalysed (2) Recruitment – one protein ...
Chapter 6 Advanced Genetics
... Changes affecting # of Chromosomes A genome is a complete haploid set of its chromosomes. A diploid cell has two complete genomes. Review haploid and diploid cells if this is confusing. Diploid organisms, like us, have to go through meiosis to produce haploid gametes (either sperm or eggs). ...
... Changes affecting # of Chromosomes A genome is a complete haploid set of its chromosomes. A diploid cell has two complete genomes. Review haploid and diploid cells if this is confusing. Diploid organisms, like us, have to go through meiosis to produce haploid gametes (either sperm or eggs). ...
Genes: Structure, Replication, & Mutation
... loss of protein activity to no change in the level of activity at all, depending on the amino acid substitution. ...
... loss of protein activity to no change in the level of activity at all, depending on the amino acid substitution. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.