STUDY GUIDE
... 4. Rings of DNA found in bacteria are responsible for a great deal of the exchange of genetic information that occurs in nature. What are these rings? A. enzymes C. strands B. plasmids D. viruses 5. What is the large molecule found inside a cell that contains all of the information needed for the ce ...
... 4. Rings of DNA found in bacteria are responsible for a great deal of the exchange of genetic information that occurs in nature. What are these rings? A. enzymes C. strands B. plasmids D. viruses 5. What is the large molecule found inside a cell that contains all of the information needed for the ce ...
sex
... TRANSLOCATION: breaks off a segment from one chromosome and attaches it to another gain-of-function mutation: increases the activity of the gene or makes it active in inappropriate circumstances; these mutations are usually dominant. dominant-negative mutation: dominant-acting mutation that blocks g ...
... TRANSLOCATION: breaks off a segment from one chromosome and attaches it to another gain-of-function mutation: increases the activity of the gene or makes it active in inappropriate circumstances; these mutations are usually dominant. dominant-negative mutation: dominant-acting mutation that blocks g ...
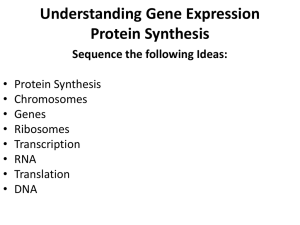
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations
... have on genes. If these mutagens interact with DNA, they can produce mutations at high rates: Some compounds interfere with base-pairing, increasing the error rate of DNA replication. • Others weaken the DNA strand, causing breaks and inversions that produce chromosomal mutations. • Cells can someti ...
... have on genes. If these mutagens interact with DNA, they can produce mutations at high rates: Some compounds interfere with base-pairing, increasing the error rate of DNA replication. • Others weaken the DNA strand, causing breaks and inversions that produce chromosomal mutations. • Cells can someti ...
Domain Genetics - preassessment questions
... 10. Why is it important for the cells of multicellular organisms to undergo mitosis? A. Mitosis allows for reproduction with male and female gametes. B. Mitosis increases variation within an ...
... 10. Why is it important for the cells of multicellular organisms to undergo mitosis? A. Mitosis allows for reproduction with male and female gametes. B. Mitosis increases variation within an ...
iiiliiiltiiliiiitii lilliitlii$itttit ffffli|tiiiiiiHii.
... cells and can causemutations to arise as these cells divide. Manv chemicalsalso can interfere with DNA replication and lead to mutation. Whenever a cell copiesits DNA, there is a small chance it may misread the sequenceand add the wrong nucleotide. Our cells have proofreading proteins that can fix m ...
... cells and can causemutations to arise as these cells divide. Manv chemicalsalso can interfere with DNA replication and lead to mutation. Whenever a cell copiesits DNA, there is a small chance it may misread the sequenceand add the wrong nucleotide. Our cells have proofreading proteins that can fix m ...
No Slide Title
... was induced in BL2 cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Single cells were either analyzed for mutations in the V4-39 gene after 90 min of stimulation or isolated in single wells and left for 24 or 48 h (one or two divisions) before analysis. (a) Three representative mutations in the V4-39 gene, ...
... was induced in BL2 cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Single cells were either analyzed for mutations in the V4-39 gene after 90 min of stimulation or isolated in single wells and left for 24 or 48 h (one or two divisions) before analysis. (a) Three representative mutations in the V4-39 gene, ...
Final
... Which of the following is characteristic of a plasmid? Circle all that apply a. b. c. d. ...
... Which of the following is characteristic of a plasmid? Circle all that apply a. b. c. d. ...
AS 90715 version 2 Describe the role of DNA in relation to gene
... Concepts and processes relating to gene expression include: the role of DNA in gene expression: selected from o nucleic acid structure and function o protein structure and function o the genetic code o DNA replication o protein synthesis (transcription, translation) allele interactions: selected ...
... Concepts and processes relating to gene expression include: the role of DNA in gene expression: selected from o nucleic acid structure and function o protein structure and function o the genetic code o DNA replication o protein synthesis (transcription, translation) allele interactions: selected ...
Molecular and Biochemical Basis of genetic Disorder
... mutation active in the absence of the ligand). ...
... mutation active in the absence of the ligand). ...
Mutation - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... proteins are often relatively unimportant to function. However, often nonsense mutations result in completely non-functional proteins. 4. Sense mutations are the opposite of nonsense mutations. Here, a stop codon is converted into an amino acid codon. Since DNA outside of protein-coding regions cont ...
... proteins are often relatively unimportant to function. However, often nonsense mutations result in completely non-functional proteins. 4. Sense mutations are the opposite of nonsense mutations. Here, a stop codon is converted into an amino acid codon. Since DNA outside of protein-coding regions cont ...
G 10 20 30 40 50 40 30 20 10 G
... amino acids that the bacterium uses as food. This process is a natural example of what genetic phenomenon? 41. Genetic engineering has produced goats whose milk contains proteins that can be used as medicines. This effect was produced by what means? 42. Scientists found that, over a period of 200 ye ...
... amino acids that the bacterium uses as food. This process is a natural example of what genetic phenomenon? 41. Genetic engineering has produced goats whose milk contains proteins that can be used as medicines. This effect was produced by what means? 42. Scientists found that, over a period of 200 ye ...
Unit 1: Cells, Cell Reproduction, and Development
... In what type of cells does mitosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What are the four phases of mitosis, and in what order do they occur in? What happens during each phase of mitosis? In what type of cells does meiosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What happens during each division of meiosis? ...
... In what type of cells does mitosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What are the four phases of mitosis, and in what order do they occur in? What happens during each phase of mitosis? In what type of cells does meiosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What happens during each division of meiosis? ...
Opportunities for Theory in Biological Physics. 1) Chromosome
... How is the “open” architecture of the nucleus maintained and controlled under the osmotic pressure of de-condensed, active DNA sections. Equation of State of DNA bundles is known. Dynamics: Chromosome dynamics driven by DNA condensation/de-condensation events triggered by local gene expression:”gene ...
... How is the “open” architecture of the nucleus maintained and controlled under the osmotic pressure of de-condensed, active DNA sections. Equation of State of DNA bundles is known. Dynamics: Chromosome dynamics driven by DNA condensation/de-condensation events triggered by local gene expression:”gene ...
Final Exam Review Study the following terms and concepts to
... • What would happen if you removed any of the reactants? • Why cellular respiration is considered an opposite process of Photosynthesis? Who do they relate? • Aerobic – • Anaerobic• Lactic acid fermentation• Alcoholic fermentationChapter 10 10.2—Cell division • Cell regulation• What controls cell re ...
... • What would happen if you removed any of the reactants? • Why cellular respiration is considered an opposite process of Photosynthesis? Who do they relate? • Aerobic – • Anaerobic• Lactic acid fermentation• Alcoholic fermentationChapter 10 10.2—Cell division • Cell regulation• What controls cell re ...
Paradigm Shifts in Biomedical Research
... Cell Cycle Checkpoints and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
... Cell Cycle Checkpoints and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
File - Wildcat Biology Review
... If a corn plant has a genotype of Ttyy, what are the possible genetic combinations that could be present in a single grain of pollen from this plant? A. B. C. D. ...
... If a corn plant has a genotype of Ttyy, what are the possible genetic combinations that could be present in a single grain of pollen from this plant? A. B. C. D. ...
2-3 DNA to Proteins - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... chromosome so that a copy of the needed gene can be made. This is copy is called RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is similar to DNA except it is only one strand. o RNA to Ribosome – The RNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome which “reads” the code on the ...
... chromosome so that a copy of the needed gene can be made. This is copy is called RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA is similar to DNA except it is only one strand. o RNA to Ribosome – The RNA then leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome which “reads” the code on the ...
Study guideCh8
... wrong base pair, instead of the base substation happening randomly). Base analogs can be introduced into the cells, which bind to the wrong base pair. How is this similar in resulting mutation to the presence of methylguanine? Is this another form of base substitution? What kind of mutation do inter ...
... wrong base pair, instead of the base substation happening randomly). Base analogs can be introduced into the cells, which bind to the wrong base pair. How is this similar in resulting mutation to the presence of methylguanine? Is this another form of base substitution? What kind of mutation do inter ...
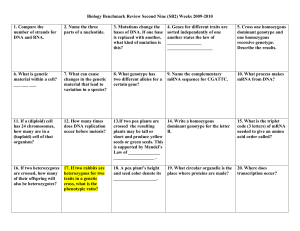
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... 4. Genes for different traits are sorted independently of one another states the law of ...
... 4. Genes for different traits are sorted independently of one another states the law of ...
Leaving Cert Biology Notes - Genetics Definitions
... Manipulation or alteration / of genes or of genotypes ...
... Manipulation or alteration / of genes or of genotypes ...
classes of mutation
... mutation alters a protein that plays a critical role in the body, a medical condition can result. A condition caused by mutations in one or more genes is called a genetic disorder. Some mutations alter a gene's DNA base sequence but do not change the function of the protein made by the gene. One stu ...
... mutation alters a protein that plays a critical role in the body, a medical condition can result. A condition caused by mutations in one or more genes is called a genetic disorder. Some mutations alter a gene's DNA base sequence but do not change the function of the protein made by the gene. One stu ...
mutation
... Alter the bonding structure (base pairing) and therefore can induce changes in sequence during replication. ...
... Alter the bonding structure (base pairing) and therefore can induce changes in sequence during replication. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.