Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... What is the name of the fivecarbon monosaccharide sugar found in the nucleotides of DNA? Deoxyribose ...
... What is the name of the fivecarbon monosaccharide sugar found in the nucleotides of DNA? Deoxyribose ...
NOVA Online Cancer Tutorial
... 1. What is the role of DNA in cells? 2. Why is it important that the DNA be the same in all the cells? C.)Mutation of DNA: 1. How is the mutated DNA different than the “normal” DNA? 2. How can mutations be caused? D.)Genetically Altered Cell/First Mutation: 1. Which process do body cells use to repl ...
... 1. What is the role of DNA in cells? 2. Why is it important that the DNA be the same in all the cells? C.)Mutation of DNA: 1. How is the mutated DNA different than the “normal” DNA? 2. How can mutations be caused? D.)Genetically Altered Cell/First Mutation: 1. Which process do body cells use to repl ...
-body stores fat in special cells filled with fat globules.
... There are 20 different amino acids found in our food Only four are made by your body! ...
... There are 20 different amino acids found in our food Only four are made by your body! ...
1 - gcisd
... d. Know a few examples of genetic disorders Tay-Sach’s, Sickle-Cell Anemia, Huntington’s disease, Albinism, Hemophilia 9. HOW A GENOTYPE LEADS TO A PHENOTYPE a. Find the definition of both and then explain how they are related to each other 10. KNOW ABOUT MRNA’S ROLE IN REPRODUCTION a. Where is it g ...
... d. Know a few examples of genetic disorders Tay-Sach’s, Sickle-Cell Anemia, Huntington’s disease, Albinism, Hemophilia 9. HOW A GENOTYPE LEADS TO A PHENOTYPE a. Find the definition of both and then explain how they are related to each other 10. KNOW ABOUT MRNA’S ROLE IN REPRODUCTION a. Where is it g ...
History of Genetics
... – the genetic code is a list of which 3 base DNA or RNA sequence (codon) encodes which amino acid. The same genetic code is used in (almost) all organisms. ...
... – the genetic code is a list of which 3 base DNA or RNA sequence (codon) encodes which amino acid. The same genetic code is used in (almost) all organisms. ...
BIOL 311 Human Genetics
... Alter regulatory elements that regulate splicing (splicing enhancers or silencers) Usually loss of function mutations are recessive, however some show incomplete dominance or "haploinsufficiency"--where one good copy is not sufficient to restore function. Dominant negative effect--when a mutant po ...
... Alter regulatory elements that regulate splicing (splicing enhancers or silencers) Usually loss of function mutations are recessive, however some show incomplete dominance or "haploinsufficiency"--where one good copy is not sufficient to restore function. Dominant negative effect--when a mutant po ...
Genetic Disorders
... body. Each cell, however, has the remarkable ability to recognize mistakes and fix them before it passes them along to its descendants. But a cell's DNA repair mechanisms can fail, or be overwhelmed, or become less efficient with age. ...
... body. Each cell, however, has the remarkable ability to recognize mistakes and fix them before it passes them along to its descendants. But a cell's DNA repair mechanisms can fail, or be overwhelmed, or become less efficient with age. ...
Chapter 6 Review Terms: Somatic Cell, Game - District 196 e
... A pairs with _____, C pairs with _____, G pairs with _____, and T pairs with _____ ...
... A pairs with _____, C pairs with _____, G pairs with _____, and T pairs with _____ ...
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis
... reading frame of the genetic code. Which of these 3 mutations is a frameshift mutation? ...
... reading frame of the genetic code. Which of these 3 mutations is a frameshift mutation? ...
ANNEX B: Selected Biotechnology Terms
... Antibody – an immunoglobulin that specifically recognizes and binds to an antigenic determinant on an antigen. Antibodies destroy or weaken bacteria and neutralize organic poisons, thus forming the basis of immunity. Bioregulators – chemicals or enzymes that control physiological functions, such as ...
... Antibody – an immunoglobulin that specifically recognizes and binds to an antigenic determinant on an antigen. Antibodies destroy or weaken bacteria and neutralize organic poisons, thus forming the basis of immunity. Bioregulators – chemicals or enzymes that control physiological functions, such as ...
DNA Personal Ads
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
PBI 3 Student Handout 2
... The human β-globin protein functions in transporting oxygen throughout our bodies. The sequence of the 147 amino acids that comprise the precursor protein is encoded in a sequence of nucleotides that make up the β-Globin Gene. The first amino acid (Met) is later removed to produce a 146 amino acid p ...
... The human β-globin protein functions in transporting oxygen throughout our bodies. The sequence of the 147 amino acids that comprise the precursor protein is encoded in a sequence of nucleotides that make up the β-Globin Gene. The first amino acid (Met) is later removed to produce a 146 amino acid p ...
Practicing Protein Synthesis
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases. Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person (or a cow) cannot digest ...
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases. Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person (or a cow) cannot digest ...
Congenital Bilateral Absence of the Vas Deferens – an Overview
... Initial genetic testing is typically based on screening for 23 of the most common mutations as recommended by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) (4). These mutations account for 55% to 97% of CFTR-related disease, depend ...
... Initial genetic testing is typically based on screening for 23 of the most common mutations as recommended by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) (4). These mutations account for 55% to 97% of CFTR-related disease, depend ...
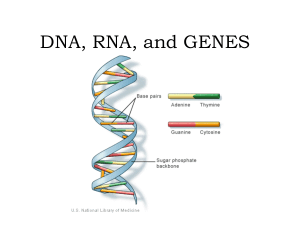
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... are built. • Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the proteins. ...
... are built. • Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the proteins. ...
Experience 2 Follow-up 1. Answer the following
... 3. Please tell me the type of point mutation being described (be specific!) and describe the result of that mutation on the amino acid sequence AND polypeptide that is made from the mutated DNA. ...
... 3. Please tell me the type of point mutation being described (be specific!) and describe the result of that mutation on the amino acid sequence AND polypeptide that is made from the mutated DNA. ...
Standard Genetic Code
... DNA/RNA – for storing information about how to make proteins The building blocks for proteins are 20 different types of amino acids, and these amino acids are strung together one after another when a protein is built. The instructions for building each particular protein is encoded in DNA in the c ...
... DNA/RNA – for storing information about how to make proteins The building blocks for proteins are 20 different types of amino acids, and these amino acids are strung together one after another when a protein is built. The instructions for building each particular protein is encoded in DNA in the c ...
Review Guide Genetics
... The genetic code for all organisms is the same – meaning that in ALL organisms the same mRNA code will code for the same amino acids. An organism’s proteins are different because the DNA specifies a different number, order and type of amino acids for each protein to be made. ...
... The genetic code for all organisms is the same – meaning that in ALL organisms the same mRNA code will code for the same amino acids. An organism’s proteins are different because the DNA specifies a different number, order and type of amino acids for each protein to be made. ...
Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication
... The genetic code for all organisms is the same – meaning that in ALL organisms the same mRNA code will code for the same amino acids. An organism’s proteins are different because the DNA specifies a different number, order and type of amino acids for each protein to be made. ...
... The genetic code for all organisms is the same – meaning that in ALL organisms the same mRNA code will code for the same amino acids. An organism’s proteins are different because the DNA specifies a different number, order and type of amino acids for each protein to be made. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.