5. Common and rare alleles
... Mutation means 1. the process by which a gene undergoes a structural change, 2. a modified gene resulting from mutation Mutations: -gene mutations -„point“ mutation – only one nucleotide qualitative change -in regulatory sequences quantitative change -compound mutations -chromosomal mutations -n ...
... Mutation means 1. the process by which a gene undergoes a structural change, 2. a modified gene resulting from mutation Mutations: -gene mutations -„point“ mutation – only one nucleotide qualitative change -in regulatory sequences quantitative change -compound mutations -chromosomal mutations -n ...
NEWS W Einstein Cancer Center
... usually come to mind. But mutations are not the only culprits in cancer. Scientists now know that gene expression—whether a gene turns on or stays silent—is directed by chemicals that latch onto genes. These chemical alterations are referred to as “epigenetic” changes because—unlike mutations— they ...
... usually come to mind. But mutations are not the only culprits in cancer. Scientists now know that gene expression—whether a gene turns on or stays silent—is directed by chemicals that latch onto genes. These chemical alterations are referred to as “epigenetic” changes because—unlike mutations— they ...
Chapter 7: Getting into genes Name
... Which one of the following statements about mutations is not correct? A Mutations can be caused by radiation. B A mutation is a change in a gene or chromosome. C All mutations are harmful. D Mutations can occur as DNA is being copied. E Mutations can occur by pure chance. F Mutations can be inherite ...
... Which one of the following statements about mutations is not correct? A Mutations can be caused by radiation. B A mutation is a change in a gene or chromosome. C All mutations are harmful. D Mutations can occur as DNA is being copied. E Mutations can occur by pure chance. F Mutations can be inherite ...
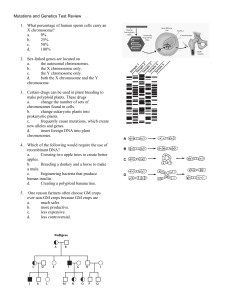
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
... 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA - Northwestern High School
... amylase, that help break down starches. Expression of this genes allows it to function. Our marrow cells would not need to have this protein produced. – Morphogenesis (cell differentiation, cell ...
... amylase, that help break down starches. Expression of this genes allows it to function. Our marrow cells would not need to have this protein produced. – Morphogenesis (cell differentiation, cell ...
Protein Synthesis Review
... 13. For the DNA triplet CGT, write the complementary mRNA codon and the tRNA anticodon. 14. What amino acid does the triplet GCA represent? 15. Explain the functions of start and stop codons. 16. What would be the effect on translation if the termination codon were changed by mutation? If the start ...
... 13. For the DNA triplet CGT, write the complementary mRNA codon and the tRNA anticodon. 14. What amino acid does the triplet GCA represent? 15. Explain the functions of start and stop codons. 16. What would be the effect on translation if the termination codon were changed by mutation? If the start ...
Study Guide
... 2. A, T, C, and G are the letters of the genetic alphabet. In different sequences or order, these four letters create the codes that spell out the 20 different amino acids that serve as the building blocks for all of the proteins that are needed for the functioning of a living organism. 3. DNA conta ...
... 2. A, T, C, and G are the letters of the genetic alphabet. In different sequences or order, these four letters create the codes that spell out the 20 different amino acids that serve as the building blocks for all of the proteins that are needed for the functioning of a living organism. 3. DNA conta ...
Term
... Permanent Loss of (enzyme) function (or activity) This is the pH at which an enzyme works best at. [The concept that]An enzyme will combine (usually) with only one substrate to form a product. Cells which have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. The way organisms change genetically from p ...
... Permanent Loss of (enzyme) function (or activity) This is the pH at which an enzyme works best at. [The concept that]An enzyme will combine (usually) with only one substrate to form a product. Cells which have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. The way organisms change genetically from p ...
Mutation
... • Silent mutations have no effect on the amino acid produced by a codon because of redundancy in the genetic code • Missense mutations still code for an amino acid, but not the correct amino acid • Nonsense mutations change an amino acid codon into a stop codon, nearly always leading to a nonfuncti ...
... • Silent mutations have no effect on the amino acid produced by a codon because of redundancy in the genetic code • Missense mutations still code for an amino acid, but not the correct amino acid • Nonsense mutations change an amino acid codon into a stop codon, nearly always leading to a nonfuncti ...
Types of mutation
... broken. But mutation is not always bad. Most DNA changes fall in the large areas of the genome that sit between genes, and usually they have no effect. When variations occur within genes, there is more often a consequence, but even then mutation only rarely causes death or disease. Mutation also gen ...
... broken. But mutation is not always bad. Most DNA changes fall in the large areas of the genome that sit between genes, and usually they have no effect. When variations occur within genes, there is more often a consequence, but even then mutation only rarely causes death or disease. Mutation also gen ...
5. Protein Synthesis
... 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it found? 10. Briefly describe transcription. 11. Briefly describe translation. ...
... 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it found? 10. Briefly describe transcription. 11. Briefly describe translation. ...
013368718X_CH04_047
... In a substitution, one base is changed to a different base, which may affect only a single amino acid and have no effect at all. In insertions and deletions, one base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. Insertions and deletions are called frameshift mutations because they shift the “re ...
... In a substitution, one base is changed to a different base, which may affect only a single amino acid and have no effect at all. In insertions and deletions, one base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. Insertions and deletions are called frameshift mutations because they shift the “re ...
Name - PSUSDscienceresources
... and put in their place the genes for hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Mulligan hoped that the genetically modified virus would no longer tell the cell it had entered to make more virus particles. It would just order hemoglobin proteins. Mulligan assembled his fleet of ...
... and put in their place the genes for hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Mulligan hoped that the genetically modified virus would no longer tell the cell it had entered to make more virus particles. It would just order hemoglobin proteins. Mulligan assembled his fleet of ...
Lecture 6 S - BEHESHTI MAAL
... Spontaneous Mutations: Base substitutions Most common type of substitution Mistake during DNA replication, incorrect base incorporated into DNA Three types: 1. Silent mutation: no effect on protein (remember- several codons code for the same amino acid) 2. Missense mutation: codon has changed and d ...
... Spontaneous Mutations: Base substitutions Most common type of substitution Mistake during DNA replication, incorrect base incorporated into DNA Three types: 1. Silent mutation: no effect on protein (remember- several codons code for the same amino acid) 2. Missense mutation: codon has changed and d ...
MUTATION, DNA REPAIR AND CANCER
... Bind to cell surface and initiate cascade leading to cell division which includes activating specific genes Mutations in genes producing cell growth signaling proteins can change them into oncogenes producing abnormally high level of activity in some proteins An oncogene may promote cancer by keepin ...
... Bind to cell surface and initiate cascade leading to cell division which includes activating specific genes Mutations in genes producing cell growth signaling proteins can change them into oncogenes producing abnormally high level of activity in some proteins An oncogene may promote cancer by keepin ...
Study guide
... about the genetic basis of cancer (see figure 11.17). Ch. 12: DNA technology (Study for this chapter along with the lab exercise from this week and last) In class we used a template strand of DNA and made the complementary strand, using a made-up plasmid. We then created a restriction enzyme cut of ...
... about the genetic basis of cancer (see figure 11.17). Ch. 12: DNA technology (Study for this chapter along with the lab exercise from this week and last) In class we used a template strand of DNA and made the complementary strand, using a made-up plasmid. We then created a restriction enzyme cut of ...
Robust systems persist in response to mutations
... one binding site. Payne and Wagner found that the more sites a transcription factor can bind to—and the more one can "hop" from one compatible site to the next through single mutations—the more robust the transcription factor's function. What's more, that robustness makes it easier for a population ...
... one binding site. Payne and Wagner found that the more sites a transcription factor can bind to—and the more one can "hop" from one compatible site to the next through single mutations—the more robust the transcription factor's function. What's more, that robustness makes it easier for a population ...
Morgan and Sex Linkage / Mutations
... Types of Mutations 1. Germ Cell Mutation – mutation that occurs in the gametes. 2. Somatic Cell Mutation – mutation that occurs in the somatic cells. All mutations fall under the 2 above: - Lethal Mutations – causes death - Silent Mutations – not on a gene – does not harm the organism - Nonsense Mu ...
... Types of Mutations 1. Germ Cell Mutation – mutation that occurs in the gametes. 2. Somatic Cell Mutation – mutation that occurs in the somatic cells. All mutations fall under the 2 above: - Lethal Mutations – causes death - Silent Mutations – not on a gene – does not harm the organism - Nonsense Mu ...
Control of Gene Expression
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
Mutations and Cancer Review Sheet Key
... Change in the sequence of the base pairs of DNA. 2. During which of the 4 stage cell cycle do most mutations occur and why? (G1 S G2 Cell Division) S (synthesis) because the DNA is being unzipped and rebuilt during DNA replication. 3. List the 3 types of mutations. single base substitutions, inserti ...
... Change in the sequence of the base pairs of DNA. 2. During which of the 4 stage cell cycle do most mutations occur and why? (G1 S G2 Cell Division) S (synthesis) because the DNA is being unzipped and rebuilt during DNA replication. 3. List the 3 types of mutations. single base substitutions, inserti ...
Mapping Mutations in the HIV RNA
... The HIV protease protein, is required to process other HIV proteins into their functional forms. Protease inhibitors medicines, act by blocking this critical maturation step. ...
... The HIV protease protein, is required to process other HIV proteins into their functional forms. Protease inhibitors medicines, act by blocking this critical maturation step. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.