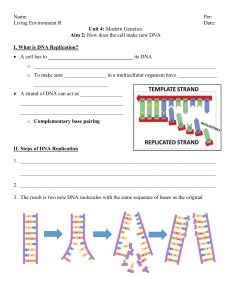
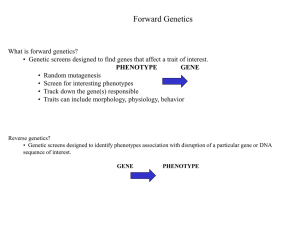
fix my dna text
... Protein structure is determined by the DNA base code. Proteins are made from lots of amino acids joined together. Each amino acid is coded by the sequence (order) of three bases. For example, GGT codes are found in glycine but TCA codes are found in serine, a different amino acid. The sequence of ba ...
... Protein structure is determined by the DNA base code. Proteins are made from lots of amino acids joined together. Each amino acid is coded by the sequence (order) of three bases. For example, GGT codes are found in glycine but TCA codes are found in serine, a different amino acid. The sequence of ba ...
Gene Section PMS1 (PMS1 postmeiotic segregation increased 1 (S. cerevisiae))
... Raschle M, Marra G, Nystrom-Lahti M, Schar P, Jiricny J. Identification of hMutLbeta, a heterodimer of hMLH1 and hPMS1. J Biol Chem 1999;274:32368-32375. Kondo E, Horii A, Fukushige S. The interacting domains of three MutL heterodimers in man: hMLH1 interacts with 36 homologous amino acid residues w ...
... Raschle M, Marra G, Nystrom-Lahti M, Schar P, Jiricny J. Identification of hMutLbeta, a heterodimer of hMLH1 and hPMS1. J Biol Chem 1999;274:32368-32375. Kondo E, Horii A, Fukushige S. The interacting domains of three MutL heterodimers in man: hMLH1 interacts with 36 homologous amino acid residues w ...
Variation and Selection
... Chromosome mutations in humans usually result in spontaneous abortion of the foetus But a proportion survive e.g. Downs syndrome. The affected person has one extra chromosome in their genome (i.e. 47 instead of 46 chromosomes) This happens during meiosis when an egg cell is formed .In egg the 21st c ...
... Chromosome mutations in humans usually result in spontaneous abortion of the foetus But a proportion survive e.g. Downs syndrome. The affected person has one extra chromosome in their genome (i.e. 47 instead of 46 chromosomes) This happens during meiosis when an egg cell is formed .In egg the 21st c ...
Table 3.
... Multiples melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
... Multiples melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
Answers to Exam Practice Questions 1. Mitosis produces two
... through a secretory vesicle with then goes to the cell membrane to be released. ...
... through a secretory vesicle with then goes to the cell membrane to be released. ...
Complementation
... • novel function (usually dominant) • Examples include chimeric proteins due to translocations • genetic definition: additional alleles (+ or Df) don’t affect the ...
... • novel function (usually dominant) • Examples include chimeric proteins due to translocations • genetic definition: additional alleles (+ or Df) don’t affect the ...
Lecture 10
... Related and structurally similar species may have variation in the amount of their total DNA by a factor of 100 In humans: ~5% of DNA is transcribed and 1.5% represents coding regions (exons). The rest is made of repeats with no obvious function. ...
... Related and structurally similar species may have variation in the amount of their total DNA by a factor of 100 In humans: ~5% of DNA is transcribed and 1.5% represents coding regions (exons). The rest is made of repeats with no obvious function. ...
Game 2
... Why has DNA become the genetic material of cells when RNA was considered the first form? ...
... Why has DNA become the genetic material of cells when RNA was considered the first form? ...
Lecture 5 Mutation and Genetic Variation
... b. Silent site substitution (synonymous) – a base substitution that does not cause a change in the amino acid due to codon redundancy. 2. In general, most replacement mutations will have relatively little +/- effect on fitness. ...
... b. Silent site substitution (synonymous) – a base substitution that does not cause a change in the amino acid due to codon redundancy. 2. In general, most replacement mutations will have relatively little +/- effect on fitness. ...
Document
... 1. DNA structure (and RNA structure) (Figures 5.26, 16.5, 16.6, 16.7, 16.8, 16.X-pg. 310) 2. DNA structure provides a mechanism for DNA replication 3. Steps in DNA replication (16.9, 16.12, 16.13, 16.14, 16.15, 16.16, 16.17) 4. DNA replication involves many enzymes (gene products): (Table 16.1) 5. D ...
... 1. DNA structure (and RNA structure) (Figures 5.26, 16.5, 16.6, 16.7, 16.8, 16.X-pg. 310) 2. DNA structure provides a mechanism for DNA replication 3. Steps in DNA replication (16.9, 16.12, 16.13, 16.14, 16.15, 16.16, 16.17) 4. DNA replication involves many enzymes (gene products): (Table 16.1) 5. D ...
Chapter 12 “DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis” Reading/Study Guide
... 2. The following scientists all contributed to solving the mystery of heredity and the double helix. Describe what each did, and if given, what experiment they used: a. Frederick Griffith ...
... 2. The following scientists all contributed to solving the mystery of heredity and the double helix. Describe what each did, and if given, what experiment they used: a. Frederick Griffith ...
Stg Chp 11 - Edublogs @ Macomb ISD
... In your textbook, read about the genetic code. Complete each statement. 4. Proteins are made up of 5. There are twenty different types of _ 6. The message of the DNA code is information for building. 7. Each set of three nitrogenous bases that codes for an amino acid is known as a ...
... In your textbook, read about the genetic code. Complete each statement. 4. Proteins are made up of 5. There are twenty different types of _ 6. The message of the DNA code is information for building. 7. Each set of three nitrogenous bases that codes for an amino acid is known as a ...
E1. If the physiological adaptation theory had been correct
... E1. If the physiological adaptation theory had been correct, mutations should have occurred after the cells were plated on the media containing T1 bacteriophages. Since the same numbers of bacteria were streaked on each plate, we would have expected to see roughly the same number of resistant coloni ...
... E1. If the physiological adaptation theory had been correct, mutations should have occurred after the cells were plated on the media containing T1 bacteriophages. Since the same numbers of bacteria were streaked on each plate, we would have expected to see roughly the same number of resistant coloni ...
Mutations II
... • These evolved beta-galactosidase (ebg) genes didn’t “just appear out of nowhere”. . . – The ebg genes are mutated versions of genes elsewhere in the genome, used for other functions (exactly what is still uncertain) – The “wild” ebg enzyme has almost no ability to catalyze lactose—but a singl ...
... • These evolved beta-galactosidase (ebg) genes didn’t “just appear out of nowhere”. . . – The ebg genes are mutated versions of genes elsewhere in the genome, used for other functions (exactly what is still uncertain) – The “wild” ebg enzyme has almost no ability to catalyze lactose—but a singl ...
Genetic Analysis Problem Set
... wrinkled seeds. This phenotype is found to be heritable and segregate like a single recessive nuclear mutation. You hypothesize that this phenotype is due to a mutation in the R gene. Briefly describe 3 experiments you could do to test your hypothesis indicating the result that would support it. ...
... wrinkled seeds. This phenotype is found to be heritable and segregate like a single recessive nuclear mutation. You hypothesize that this phenotype is due to a mutation in the R gene. Briefly describe 3 experiments you could do to test your hypothesis indicating the result that would support it. ...
Protein Synthesis
... beads and pipe cleaners. When you have your protein completed, have your teacher check it. If there are any errors, please go back and find your mistakes. 8. Did you have any “mutations” during the process? ____________ ...
... beads and pipe cleaners. When you have your protein completed, have your teacher check it. If there are any errors, please go back and find your mistakes. 8. Did you have any “mutations” during the process? ____________ ...
a10c Biotechnology
... 1. What are some applications of biotechnology in the fields of medicine, food production, agriculture, criminal investigation, and genetic research? 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an ex ...
... 1. What are some applications of biotechnology in the fields of medicine, food production, agriculture, criminal investigation, and genetic research? 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they "look for"? Name an ex ...
Genetics
... • Adenine and thymine make a lovely pair • Cytosine without guanine would seem very bare • Oh, de-ox-y-ri-bo-nu-cleic acid • RNA is ri-bo-nu-cleic acid ...
... • Adenine and thymine make a lovely pair • Cytosine without guanine would seem very bare • Oh, de-ox-y-ri-bo-nu-cleic acid • RNA is ri-bo-nu-cleic acid ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.