Causes
... • A human has 1014 nucleated cells each with 3x 109 base pairs of DNA. If about 1016 cell divisions occur in a lifetime and • 10−10 mutations per base pair per cell generation escape repair, • there may eventually be as many as one mutation per 106 bp in the genome. • Fortunately,most of these will ...
... • A human has 1014 nucleated cells each with 3x 109 base pairs of DNA. If about 1016 cell divisions occur in a lifetime and • 10−10 mutations per base pair per cell generation escape repair, • there may eventually be as many as one mutation per 106 bp in the genome. • Fortunately,most of these will ...
This is to serve as a general overview of important topics. I highly
... conservative and dispersive models. The two complementary strands are held together ______________________ bonds. Within the DNA there bonds are __________________ ...
... conservative and dispersive models. The two complementary strands are held together ______________________ bonds. Within the DNA there bonds are __________________ ...
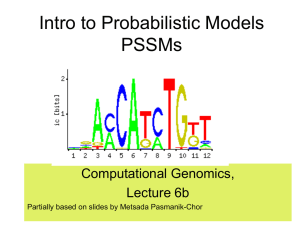
CG7b-PSSM
... Computational Genomics, Lecture 6b Partially based on slides by Metsada Pasmanik-Chor ...
... Computational Genomics, Lecture 6b Partially based on slides by Metsada Pasmanik-Chor ...
8 How Cellular Information is Altered
... consortium of an organism Phenotype: the characteristics expressed by a cell ...
... consortium of an organism Phenotype: the characteristics expressed by a cell ...
dna_notes - KScience
... Mutations are more often deleterious because selection in a species has selected for the genome it now has and changes are therefore more likely to be less useful. Mutations can lead to severe loss of function e.g. Thalassaemia. Many cancers are due to mutations in genes that regulate cells. There i ...
... Mutations are more often deleterious because selection in a species has selected for the genome it now has and changes are therefore more likely to be less useful. Mutations can lead to severe loss of function e.g. Thalassaemia. Many cancers are due to mutations in genes that regulate cells. There i ...
Learning Goals Chapter 13
... 5. To analyze the differences between the sequences and conclude why there are more differences in introns than in exons Text Section 13.2 Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis 1. Identify the universal genetic code and explain how it is read. 2. Describe the steps in the process of transcribing DNA into ...
... 5. To analyze the differences between the sequences and conclude why there are more differences in introns than in exons Text Section 13.2 Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis 1. Identify the universal genetic code and explain how it is read. 2. Describe the steps in the process of transcribing DNA into ...
Transcription and Translation Exercise
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
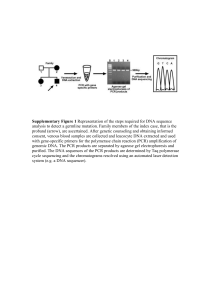
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
The 2 alleles on chromosome 13q14 must be inactivated
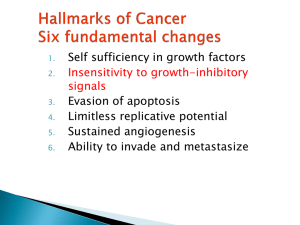
... differentiated pool & lose replicative potential The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by Rb gene ...
... differentiated pool & lose replicative potential The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by Rb gene ...
(pt=4) Label the following diagram with the following terms: ATP
... In fermentation, which chemical compound is used to accept electrons so that glycolysis ...
... In fermentation, which chemical compound is used to accept electrons so that glycolysis ...
Sources of Genetic Variation - University of Evansville Faculty Web
... – Assume that there are at least 100,000 pairs of genes in humans, and that the average mutation rate/gene/generation is 10-5 – The average number of mutations arising per generation would then be estimated as at least: 2 X 105 X 10-5 mutations/gene = 2 mutations for a human zygote – There are about ...
... – Assume that there are at least 100,000 pairs of genes in humans, and that the average mutation rate/gene/generation is 10-5 – The average number of mutations arising per generation would then be estimated as at least: 2 X 105 X 10-5 mutations/gene = 2 mutations for a human zygote – There are about ...
Chromosomes and Inertitance
... substitution, addition or removal of a single nucleotide in DNA ...
... substitution, addition or removal of a single nucleotide in DNA ...
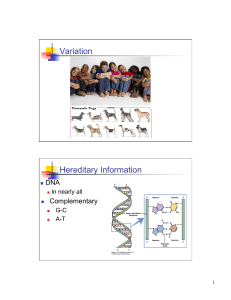
Variation Hereditary Information
... As the source of adaptive variability, then, mutations (and orthodox evolution theories) fail completely. As a source of "negative variability," however, mutations serve only too well. Basing their thinking on what we observe of mutations and their net effect (genetic burden), creationists use mutat ...
... As the source of adaptive variability, then, mutations (and orthodox evolution theories) fail completely. As a source of "negative variability," however, mutations serve only too well. Basing their thinking on what we observe of mutations and their net effect (genetic burden), creationists use mutat ...
Name of structure?
... shared by all organisms? All 20 amino acids are common to all living systems ...
... shared by all organisms? All 20 amino acids are common to all living systems ...
Assessment Specifications
... Candidates may be required to draw and / or interpret a Punnett square for any of the specified monohybrid or dihybrid inheritance patterns, and calculate the expected proportions of genotype and phenotype (expressed as a ratio, fraction, percentage, or decimal). Understanding of genetic drift is co ...
... Candidates may be required to draw and / or interpret a Punnett square for any of the specified monohybrid or dihybrid inheritance patterns, and calculate the expected proportions of genotype and phenotype (expressed as a ratio, fraction, percentage, or decimal). Understanding of genetic drift is co ...
Honors Biology Final Outline
... DNA structure and function is essential to understanding genetics Chargaff’s Rules & the relationship to Watson & Crick’s proposed base-pairs The central dogma for biological information: DNA, RNA, & Protein The DNA of a gene serves as a template for transcribing this information into RNA (b ...
... DNA structure and function is essential to understanding genetics Chargaff’s Rules & the relationship to Watson & Crick’s proposed base-pairs The central dogma for biological information: DNA, RNA, & Protein The DNA of a gene serves as a template for transcribing this information into RNA (b ...
Chapter 13 Mutation, DNA Repair, and Recombination
... Mutations alter the nucleotide sequences of genes in several ways, for example the substitution of one base pair for another or the deletion or addition or one or a few base pairs. ...
... Mutations alter the nucleotide sequences of genes in several ways, for example the substitution of one base pair for another or the deletion or addition or one or a few base pairs. ...
Document
... • Information passed on in the sexual reproduction • Needed for new characteristics to develop • Offspring recieve genes by inheriting chromosomes ...
... • Information passed on in the sexual reproduction • Needed for new characteristics to develop • Offspring recieve genes by inheriting chromosomes ...
Molecular Basis of Lung Disease
... • One in 10 people of European descent is a carrier of one of two mutations in alpha1-antitrypsin that result in a partial deficiency of the inhibitor • S mutation (Glu264Val), which in homozygotes results in a 40 percent decrease in plasma alpha1-antitrypsin concentrations. This by itself poses a n ...
... • One in 10 people of European descent is a carrier of one of two mutations in alpha1-antitrypsin that result in a partial deficiency of the inhibitor • S mutation (Glu264Val), which in homozygotes results in a 40 percent decrease in plasma alpha1-antitrypsin concentrations. This by itself poses a n ...
Protein Synthesis Review Sheet
... 2. What are the 4 bases of RNA and how do they pair up? a. b. c. d. 3. Name the two types of RNA and the basic function of each. II. Protein Synthesis List the 5 steps of protein synthesis here (use separate notes handout): ...
... 2. What are the 4 bases of RNA and how do they pair up? a. b. c. d. 3. Name the two types of RNA and the basic function of each. II. Protein Synthesis List the 5 steps of protein synthesis here (use separate notes handout): ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.