Document
... having evolved one from another through gene duplication. Paralogs are separated by a gene duplication event. • Each specific gene family member (e.g. a specific gene in human) is an ortholog of the same family member in another species (e.g. mouse). Both evolved from an ancestral globin gene. Ortho ...
... having evolved one from another through gene duplication. Paralogs are separated by a gene duplication event. • Each specific gene family member (e.g. a specific gene in human) is an ortholog of the same family member in another species (e.g. mouse). Both evolved from an ancestral globin gene. Ortho ...
Worksheet for 4/16
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
Jasmonic acid (JA) is a plant hormone that plays an important role in
... stress hormone ethylene. ORA59, belonging to the plant‐specific class of AP2‐domain transcription factors, is the main regulator of JA/ethylene‐ responsive defense gene expression in the model plant species Arabidopsis thaliana. The aim of the research described in this thesis was to study how th ...
... stress hormone ethylene. ORA59, belonging to the plant‐specific class of AP2‐domain transcription factors, is the main regulator of JA/ethylene‐ responsive defense gene expression in the model plant species Arabidopsis thaliana. The aim of the research described in this thesis was to study how th ...
Curtis, MD and Grossniklaus, U. (2003) A gateway cloning vector set
... DNA isolation and Southern blot analysis. DNA isolation was carried out as previously described (Keb-Llanes et al. 2002) with some modifications. A mid-log phase culture (15 mL) was harvested by centrifugation at 3,000 X g for 5 min. The pellet was resuspended in 400 μL extraction buffer A without p ...
... DNA isolation and Southern blot analysis. DNA isolation was carried out as previously described (Keb-Llanes et al. 2002) with some modifications. A mid-log phase culture (15 mL) was harvested by centrifugation at 3,000 X g for 5 min. The pellet was resuspended in 400 μL extraction buffer A without p ...
A) Describe and/or predict observed patterns of
... they change the codon reading frame. Other mutation vocabulary Silent Mutation - the mutation goes unnoticed – it does not change the amino acid sequence or is not in a coding region Missense – an insertion, deletion, or substitution that would make the message different Nonsense – really bad; ...
... they change the codon reading frame. Other mutation vocabulary Silent Mutation - the mutation goes unnoticed – it does not change the amino acid sequence or is not in a coding region Missense – an insertion, deletion, or substitution that would make the message different Nonsense – really bad; ...
I. Natural selection and human evolution
... a. Specific proteins perform many functions in cells. b. The Central Dogma (DNA to RNA to protein) represents a major framework for understanding how genotype determines phenotype. c. A change in the nucleotide sequence (mutation) of a gene may cause a change in the function of a protein, thereby ch ...
... a. Specific proteins perform many functions in cells. b. The Central Dogma (DNA to RNA to protein) represents a major framework for understanding how genotype determines phenotype. c. A change in the nucleotide sequence (mutation) of a gene may cause a change in the function of a protein, thereby ch ...
Application of Algorithm Research to Molecular Biology
... different kinds of cells. For instance, in human beings, we have muscle cells, blood cells, neural cells etc. • How can different cells perform different functions? ...
... different kinds of cells. For instance, in human beings, we have muscle cells, blood cells, neural cells etc. • How can different cells perform different functions? ...
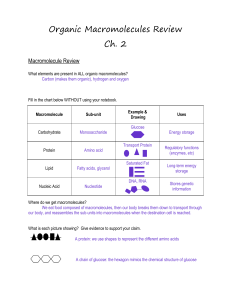
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
Inheritance and Genetic Diseases
... Men only have one X chromosome so will have one of each sex linked allele, this is why certain genetic diseases are present more in males than females - If gene on X chromosome mutates/gene for disease male will express it, female only express it if gene is recessive on both X chromosomes ...
... Men only have one X chromosome so will have one of each sex linked allele, this is why certain genetic diseases are present more in males than females - If gene on X chromosome mutates/gene for disease male will express it, female only express it if gene is recessive on both X chromosomes ...
Genetics - Region 11 Math And Science Teacher Partnership
... Transcriptional control that prevents mRNA from being synthesized: Heterochromatin vs. Euchromatin, acetylation/deacetylation of DNA, DNA methylation, transcription factors (activators and ...
... Transcriptional control that prevents mRNA from being synthesized: Heterochromatin vs. Euchromatin, acetylation/deacetylation of DNA, DNA methylation, transcription factors (activators and ...
01 - Educator Pages
... A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for RNA and protein. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes lined up like the cars of a train. When genes are being used, the strand of DNA is stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of proteins ...
... A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for RNA and protein. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes lined up like the cars of a train. When genes are being used, the strand of DNA is stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of proteins ...
Cell Cycle SG
... 5. Describe the process of cytokinesis and its end products. 6. Explain why a chromosome does not have sister chromatids during G1. ...
... 5. Describe the process of cytokinesis and its end products. 6. Explain why a chromosome does not have sister chromatids during G1. ...
Quiz 2 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... a. carbohydrates b. cholesterol c. phospholipids d. proteins e. ATP ...
... a. carbohydrates b. cholesterol c. phospholipids d. proteins e. ATP ...
DNA and RNA Notes
... Replication of DNA Why does DNA replicate itself? DNA must make an exact copy of itself in order to pass on its _____________ to the ...
... Replication of DNA Why does DNA replicate itself? DNA must make an exact copy of itself in order to pass on its _____________ to the ...
gene control regions?
... What is the structure of a chromosome and how does that relate to function? ...
... What is the structure of a chromosome and how does that relate to function? ...
fall final study guide
... develop a genetic disorder called _____________. 21. Males are much more likely to develop hemophilia and other sex-linked disorders than ___________. 22. By constructing a human _______________, genetic counselors can study how a trait was inherited over several generations in a single family. 23. ...
... develop a genetic disorder called _____________. 21. Males are much more likely to develop hemophilia and other sex-linked disorders than ___________. 22. By constructing a human _______________, genetic counselors can study how a trait was inherited over several generations in a single family. 23. ...
PP-Protein Synthesis
... Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read. Summarize the process of translation. ...
... Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read. Summarize the process of translation. ...
doc Summer 2010 Lecture 4
... If you have t/t, e.g., will have function, but not if have T/t or T/T LOF for all but homozygous recessive o Sometimes need proteins to work as dimers Homo/heterodimers If have protein that functions as dimer, and mutation alters one of the proteins’ shape, could screw up the function Bein ...
... If you have t/t, e.g., will have function, but not if have T/t or T/T LOF for all but homozygous recessive o Sometimes need proteins to work as dimers Homo/heterodimers If have protein that functions as dimer, and mutation alters one of the proteins’ shape, could screw up the function Bein ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.