Thomas Hunt Morgan, 1933
... One evening in 1913 one of Morgan’s students, Alfred Sturtevant took home some of Morgan’s breeding records. Reasoning that the closer genes are on the chromosome the less likely they are to cross over with the homologous chromosome, he worked all night and the next morning presented Morgan with a ...
... One evening in 1913 one of Morgan’s students, Alfred Sturtevant took home some of Morgan’s breeding records. Reasoning that the closer genes are on the chromosome the less likely they are to cross over with the homologous chromosome, he worked all night and the next morning presented Morgan with a ...
Assessment Schedule – 2007 Biology: Describe the role of DNA in
... because both types of haemoglobin / red blood cell are present. ...
... because both types of haemoglobin / red blood cell are present. ...
Mosaicism adds to challenge in molecular diagnostics
... loss-of-function mutations in the PIGA gene, germline in the first condition and mosaic in the second. “Does the clinician think those two patients have the same disease?” Dr. Biesecker asked. “Mosaicism makes everything in genetics more challenging and more interesting,” he concluded. “It also make ...
... loss-of-function mutations in the PIGA gene, germline in the first condition and mosaic in the second. “Does the clinician think those two patients have the same disease?” Dr. Biesecker asked. “Mosaicism makes everything in genetics more challenging and more interesting,” he concluded. “It also make ...
Cells - Troup County High School
... • aids in protein synthesis in the ribosome • 3 types: • messenger RNA: mRNA carries the DNA nucleotide sequence for a protein from the nucleus to the ribosome • transfer RNA: tRNA transports amino acids (building blocks of proteins) to the ribosome • ribosomal RNA: rRNA makes up the structure of th ...
... • aids in protein synthesis in the ribosome • 3 types: • messenger RNA: mRNA carries the DNA nucleotide sequence for a protein from the nucleus to the ribosome • transfer RNA: tRNA transports amino acids (building blocks of proteins) to the ribosome • ribosomal RNA: rRNA makes up the structure of th ...
Determination
... We have identified 15 CYP1B1 mutations, five of which have not been previously reported: E173K, D291G, G329V, R368C, I399V. We used bioinformatics tools and did protein homology modeling of the CYP1B1 protein using information at databases and located our mutations and other known CYP1B1 mutations i ...
... We have identified 15 CYP1B1 mutations, five of which have not been previously reported: E173K, D291G, G329V, R368C, I399V. We used bioinformatics tools and did protein homology modeling of the CYP1B1 protein using information at databases and located our mutations and other known CYP1B1 mutations i ...
CA Breast cancer
... The function of these genes was not clear until studies on a related protein in yeast revealed their normal role: they participate in repairing radiation-induced breaks in double-stranded DNA. This means that mutations might disable this mechanism leading to more errors in DNA replication. ...
... The function of these genes was not clear until studies on a related protein in yeast revealed their normal role: they participate in repairing radiation-induced breaks in double-stranded DNA. This means that mutations might disable this mechanism leading to more errors in DNA replication. ...
Mutations and Disorders worksheet-ANS
... KS 9. male, possible poor sexual development SC10. heterozygotes have advantage against malaria PT 11. Trisomy 13 HD 12. every child of affected parent has 50% chance of getting it TS 13. lack an enzyme that breaks down lipids TS 14. high incidence in Jewish people CF 15. most prevalent recessive le ...
... KS 9. male, possible poor sexual development SC10. heterozygotes have advantage against malaria PT 11. Trisomy 13 HD 12. every child of affected parent has 50% chance of getting it TS 13. lack an enzyme that breaks down lipids TS 14. high incidence in Jewish people CF 15. most prevalent recessive le ...
learning objectives
... 1. Prokaryotic DNA is made up of a continuous sequence of genes with no interruptions. 2. Eukaryotic DNA is constructed differently because it possesses gene sequences that code for amino acids, called exons, plus intervening, nonusable sequences of nucleotides, called introns. 3. Intron sequences m ...
... 1. Prokaryotic DNA is made up of a continuous sequence of genes with no interruptions. 2. Eukaryotic DNA is constructed differently because it possesses gene sequences that code for amino acids, called exons, plus intervening, nonusable sequences of nucleotides, called introns. 3. Intron sequences m ...
DNA to Protein - Duplin County Schools
... 1. After watching the animation, what is the correct sequence of the following statements? ___________ A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 1. After watching the animation, what is the correct sequence of the following statements? ___________ A. B. C. D. E. ...
DNA NOTES
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
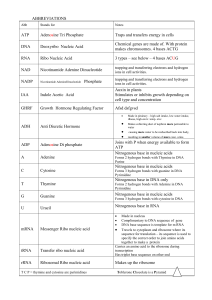
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
Essays for Chapters 16, 17, and 18
... a. Describe the four main types of genetic material (six classes) found in viruses and their mode of replication (focus mainly on those described in class.) b. Explain how each of the four main types of genetic material code for making proteins necessary for viral coats or metabolism. c. Explain the ...
... a. Describe the four main types of genetic material (six classes) found in viruses and their mode of replication (focus mainly on those described in class.) b. Explain how each of the four main types of genetic material code for making proteins necessary for viral coats or metabolism. c. Explain the ...
Test Review on DNA Structure, DNA Replication
... Be able to explain the process of translation including: The purpose of translation The site of translation Structure of a tRNA molecule. Be able to compare and contrast the structure and function of mRNA molecules and tRNA molecules. Be able to explain what a codon is in mRNA and an anticod ...
... Be able to explain the process of translation including: The purpose of translation The site of translation Structure of a tRNA molecule. Be able to compare and contrast the structure and function of mRNA molecules and tRNA molecules. Be able to explain what a codon is in mRNA and an anticod ...
DNA replication.
... When DNA is copied, the two strands of the old DNA are pulled apart by enzymes that move along each of the two single strands pairing up new nucleotide units and then zipping the strands closed. This produces two new pieces of DNA, each containing one strand from the old DNA and one newly made stran ...
... When DNA is copied, the two strands of the old DNA are pulled apart by enzymes that move along each of the two single strands pairing up new nucleotide units and then zipping the strands closed. This produces two new pieces of DNA, each containing one strand from the old DNA and one newly made stran ...
Wearing Your Genes
... (nurture) are complex and not well understood. 13. Explain what is meant by the “nature vs. nurture” debate. ...
... (nurture) are complex and not well understood. 13. Explain what is meant by the “nature vs. nurture” debate. ...
Pleiotropy - MACscience
... ability to hear • Pigmentation may play a role in maintaining fluid in ear canals ...
... ability to hear • Pigmentation may play a role in maintaining fluid in ear canals ...
DNA Sequencing
... 6. As part of a routine medical procedure, your doctor discovers that you have a rare, beneficial variant of a protein that protects you from heart disease. Should your doctor be able to patent the protein? 7. Should you be entitled to any money from the ...
... 6. As part of a routine medical procedure, your doctor discovers that you have a rare, beneficial variant of a protein that protects you from heart disease. Should your doctor be able to patent the protein? 7. Should you be entitled to any money from the ...
Chapter 2- Genetics
... Free-floating nucleotides in cells are derived from the food one eats. ____ new strands of DNA are formed into the double helix. f) The genetic code With only 4 bases, billions of genes can be coded. Proteins are made from specific _______ __________________ called genes. A protein is a ch ...
... Free-floating nucleotides in cells are derived from the food one eats. ____ new strands of DNA are formed into the double helix. f) The genetic code With only 4 bases, billions of genes can be coded. Proteins are made from specific _______ __________________ called genes. A protein is a ch ...
GENETICS VOCABULARY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 – section 3 1
... 22. A number that describes how likely it is that an event will occur. 23. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. 24. The offspring of many ...
... 22. A number that describes how likely it is that an event will occur. 23. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. 24. The offspring of many ...
Criteria for gene mutations to be used in genetic testing of Malignant
... in microsomal SR preparations from muscle biopsies (Richter et al. 1997), and in lymphoblasts (Girard et al. 2001, Tilgen et al. 2001). Read-out parameters were Ca2+ flux and resting [Ca2+] or ryanodine binding to SRRYR1 preparations. Myotubes and lymphoblasts were derived from individual patients a ...
... in microsomal SR preparations from muscle biopsies (Richter et al. 1997), and in lymphoblasts (Girard et al. 2001, Tilgen et al. 2001). Read-out parameters were Ca2+ flux and resting [Ca2+] or ryanodine binding to SRRYR1 preparations. Myotubes and lymphoblasts were derived from individual patients a ...
Glossary of Terms – Molecular Biology, Genetics, Clinical Neurology
... neurobiology. Much of it is jargon and will probably not be encountered in daily life, but nevertheless it will be found in the literature. It is by no means complete, however it should help in finding explanations for most puzzling terms! Alleles: Alternate forms of a gene at a specific location or ...
... neurobiology. Much of it is jargon and will probably not be encountered in daily life, but nevertheless it will be found in the literature. It is by no means complete, however it should help in finding explanations for most puzzling terms! Alleles: Alternate forms of a gene at a specific location or ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.