Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
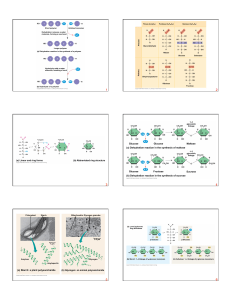
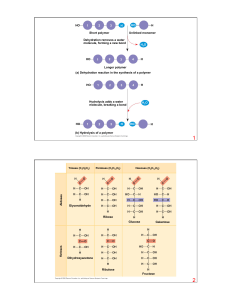
... (b) Cellulose: 1–4 linkage of β glucose monomers ...
... (b) Cellulose: 1–4 linkage of β glucose monomers ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... o Hydrophobic side chains orient themselves so that they are minimally exposed to water in the protein’s interior ...
... o Hydrophobic side chains orient themselves so that they are minimally exposed to water in the protein’s interior ...
Molecular Diagnosis I: Methods in Molecular Medicine 张咸宁
... incorporating them into the primers •PCR product can be sequenced •Sizing of repeated regions-microsatellite •Detecting infectious diseases (viral genomes) ...
... incorporating them into the primers •PCR product can be sequenced •Sizing of repeated regions-microsatellite •Detecting infectious diseases (viral genomes) ...
dna testing workshop 2005
... b. Give at least two critical functions for normal p53 in the cell. c. Which regions of the p53 gene are the most likely to be mutated in human cancers? d. How does this information help us to design treatments for cancers in which p53 plays a critical role? 4. Answer the following questions for one ...
... b. Give at least two critical functions for normal p53 in the cell. c. Which regions of the p53 gene are the most likely to be mutated in human cancers? d. How does this information help us to design treatments for cancers in which p53 plays a critical role? 4. Answer the following questions for one ...
Additional Slides Ch Biotech Dr Violet
... • Restriction endonucleases (restriction enzymes): Bacterial enzymes that cleave double-stranded DNA into smaller, more manageable fragments • Each enzyme cleaves DNA at a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence (4-6bp), producing restriction fragments. • DNA sequence that is recognized by a restri ...
... • Restriction endonucleases (restriction enzymes): Bacterial enzymes that cleave double-stranded DNA into smaller, more manageable fragments • Each enzyme cleaves DNA at a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence (4-6bp), producing restriction fragments. • DNA sequence that is recognized by a restri ...
What is Cloning?
... seemed to indicate that, other than her cancer and arthritis, she appeared to be quite normal. The unnamed sheep from which Dolly was cloned had died several years prior to her creation. Dolly was a mother to six lambs, bred the old-fashioned way. ...
... seemed to indicate that, other than her cancer and arthritis, she appeared to be quite normal. The unnamed sheep from which Dolly was cloned had died several years prior to her creation. Dolly was a mother to six lambs, bred the old-fashioned way. ...
CST Review
... BI1. d. The central dogma-Genetic instructions are transcribed (copied) into mRNA in the nucleus, then the genetic instructions are translated into proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Meiosis produces sex cells, chromosomes pairs are separated randomly during this process, producing game ...
... BI1. d. The central dogma-Genetic instructions are transcribed (copied) into mRNA in the nucleus, then the genetic instructions are translated into proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Meiosis produces sex cells, chromosomes pairs are separated randomly during this process, producing game ...
CST Review
... BI1. d. The central dogma-Genetic instructions are transcribed (copied) into mRNA in the nucleus, then the genetic instructions are translated into proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Meiosis produces sex cells, chromosomes pairs are separated randomly during this process, producing game ...
... BI1. d. The central dogma-Genetic instructions are transcribed (copied) into mRNA in the nucleus, then the genetic instructions are translated into proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. BI2. a. Meiosis produces sex cells, chromosomes pairs are separated randomly during this process, producing game ...
Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 2
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
... 1. Go to the Apple Genomics website at www.four-h.purdue.edu/apple_genomics 2. Click on the link Apple Molecular Biology. 3. Click on the link Cloning. 4. After reading the introduction click on the third and fourth animation to learn more about cloning. 5. Then complete the review questions on this ...
PowerPoint Slides for *The Mystery Disease* Lab
... Recessive: conditions are only revealed in individuals who have two copies of the mutant allele (are homozygous). ...
... Recessive: conditions are only revealed in individuals who have two copies of the mutant allele (are homozygous). ...
View PowerPoint Presentation of High School Guided Inquiry
... Recessive: conditions are only revealed in individuals who have two copies of the mutant allele (are homozygous). ...
... Recessive: conditions are only revealed in individuals who have two copies of the mutant allele (are homozygous). ...
Lecture 1 - Graham Ellis
... 1. DNA contains the instructions needed to construct other components of cells such as protein and RNA. 2. There are 20 different kinds of amino acid that combine to make proteins. There are many possible combinations, resulting in many different types of protein. 3. The cell DNA tells a cell the or ...
... 1. DNA contains the instructions needed to construct other components of cells such as protein and RNA. 2. There are 20 different kinds of amino acid that combine to make proteins. There are many possible combinations, resulting in many different types of protein. 3. The cell DNA tells a cell the or ...
Fall 2009
... 90) The process in which DNA is copied and what does it assure? 91) What are the roles of proteins verses enzymes in the process of replication? 92) What are the names of the enzymes used in replication (_____ __________) and in transcription (______ ______________). 93) What feature is built in to ...
... 90) The process in which DNA is copied and what does it assure? 91) What are the roles of proteins verses enzymes in the process of replication? 92) What are the names of the enzymes used in replication (_____ __________) and in transcription (______ ______________). 93) What feature is built in to ...
Fall 2009
... 90) The process in which DNA is copied and what does it assure? 91) What are the roles of proteins verses enzymes in the process of replication? 92) What are the names of the enzymes used in replication (_____ __________) and in transcription (______ ______________). 93) What feature is built in to ...
... 90) The process in which DNA is copied and what does it assure? 91) What are the roles of proteins verses enzymes in the process of replication? 92) What are the names of the enzymes used in replication (_____ __________) and in transcription (______ ______________). 93) What feature is built in to ...
DNA
... • A gene is a unit of DNA that codes for a polypeptide (protein chain). • Genes can have several parts: –Promoter: controls where and when the gene is expressed –Open Reading Frame: coding sequence of the gene –Terminator Sequence: ends transcription –Enhancer: areas other than promoter than can ‘up ...
... • A gene is a unit of DNA that codes for a polypeptide (protein chain). • Genes can have several parts: –Promoter: controls where and when the gene is expressed –Open Reading Frame: coding sequence of the gene –Terminator Sequence: ends transcription –Enhancer: areas other than promoter than can ‘up ...
Techniques
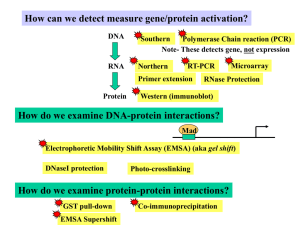
... _________________________ used for RNA and DNA separation ________________________ gel electrophoresis is used for protein separation ...
... _________________________ used for RNA and DNA separation ________________________ gel electrophoresis is used for protein separation ...
Fanconi Anemia Panel by next-generation sequencing (NGS)
... indicated as a follow-up test in symptomatic patients with a normal sequencing result or a single (heterozygous) mutation in one of the genes on the panel. Analytical Sensitivity: The sensitivity of DNA sequencing is over 99% for the detection of nucleotide base changes, small deletions (<10 bp) and ...
... indicated as a follow-up test in symptomatic patients with a normal sequencing result or a single (heterozygous) mutation in one of the genes on the panel. Analytical Sensitivity: The sensitivity of DNA sequencing is over 99% for the detection of nucleotide base changes, small deletions (<10 bp) and ...
Karotype Chromosomal Abnormalities
... In your groups, brainstorm 3 reasons why genetic diversity can be beneficial ...
... In your groups, brainstorm 3 reasons why genetic diversity can be beneficial ...
African Regional Training of Trainers workshop on the Identification and
... Genes are the unit of Heredity • Genetic material is like a Recipe Book • Chromosomes are Chapters in the Book • Genes are like Individual Recipes • Genes act as the Blue Print for Life ...
... Genes are the unit of Heredity • Genetic material is like a Recipe Book • Chromosomes are Chapters in the Book • Genes are like Individual Recipes • Genes act as the Blue Print for Life ...
Slide 1
... it first binds to one strand of the DNA at a site called the promoter and then moves down the DNA molecule and assembles a complementary copy of RNA transcription ends when the RNA polymerase reaches a certain nucleotide sequence that signals it stop ...
... it first binds to one strand of the DNA at a site called the promoter and then moves down the DNA molecule and assembles a complementary copy of RNA transcription ends when the RNA polymerase reaches a certain nucleotide sequence that signals it stop ...
Biology Vocabulary
... A monk who, while working with pea plants, discovered that traits in organisms are due to paired factors. He is called the “Father of Genetics.” ...
... A monk who, while working with pea plants, discovered that traits in organisms are due to paired factors. He is called the “Father of Genetics.” ...
Exam 3 Review B - Iowa State University
... 3. If you have 4 exons, how many lariats would form? What is responsible for the lariat? a. 3, splicesome b. 3, mRNA c. 6, splicesome d. 6, mRNA 4. How many amino acids would be expressed if the mRNA sequence is 54 bases long? a. 20 b. 16 c. 12 d. 18 5. All are true about alternative splicing except ...
... 3. If you have 4 exons, how many lariats would form? What is responsible for the lariat? a. 3, splicesome b. 3, mRNA c. 6, splicesome d. 6, mRNA 4. How many amino acids would be expressed if the mRNA sequence is 54 bases long? a. 20 b. 16 c. 12 d. 18 5. All are true about alternative splicing except ...
DNA Structure, Replication and Translation Review
... 3. What type of bond holds the sugar and phosphate together? Is this bond strong or weak? What is the significance of this? They are joined by covalent bonds called phosphodiester linkages. These are strong bonds that are not meant to break. This helps to keep a strand of DNA or RNA intact. 4. What ...
... 3. What type of bond holds the sugar and phosphate together? Is this bond strong or weak? What is the significance of this? They are joined by covalent bonds called phosphodiester linkages. These are strong bonds that are not meant to break. This helps to keep a strand of DNA or RNA intact. 4. What ...
Evolution of genes and genomes
... Substitution of a mutation that increases fitness Accelerates the accumulation of non-synonymous mutations If the number of advantageous substitutions exceeds the number of neutral substitutions (ω >1), then positive selection has acted on the gene Adaptive convergent evolution ...
... Substitution of a mutation that increases fitness Accelerates the accumulation of non-synonymous mutations If the number of advantageous substitutions exceeds the number of neutral substitutions (ω >1), then positive selection has acted on the gene Adaptive convergent evolution ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.