
Chapter 14 Human Genetics - Hollidaysburg Area School
... No two individuals are exactly genetically alike. DNA fingerprinting analyzes sections of DNA that vary widely from person to person DNA separated into series of bands Useful in convictions (first used in England, 1986) Samples can be taken from blood, hair, and bodily fluids It’s easy to see in thi ...
... No two individuals are exactly genetically alike. DNA fingerprinting analyzes sections of DNA that vary widely from person to person DNA separated into series of bands Useful in convictions (first used in England, 1986) Samples can be taken from blood, hair, and bodily fluids It’s easy to see in thi ...
8.2 * 8.3 Notes
... double helix – two strands of DNA wind around each other like a twisted ladder ...
... double helix – two strands of DNA wind around each other like a twisted ladder ...
Chapter 21: Genomes & Their Evolution 1. Sequencing & Analyzing Genomes
... functions can arise by: 1) Duplication of existing gene followed by mutation producing distinct gene product • the 2 genes will share significant homology however may have very different functions (e.g., lysozyme and -lactalbumin) ...
... functions can arise by: 1) Duplication of existing gene followed by mutation producing distinct gene product • the 2 genes will share significant homology however may have very different functions (e.g., lysozyme and -lactalbumin) ...
Topic 2 & 3: Genetics Review
... b) DNA Polymerase which links up the nucleotides to form the new strand of DNA. This 2nd step, after the unwinding and separation of strands, involves having the single strands act as templates for the new strands. Free nucleotides are present in large numbers around the replication fork. The bases ...
... b) DNA Polymerase which links up the nucleotides to form the new strand of DNA. This 2nd step, after the unwinding and separation of strands, involves having the single strands act as templates for the new strands. Free nucleotides are present in large numbers around the replication fork. The bases ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... selectable marker flanked by homologous sequences. The chromosomal segment is replaced by this URA3 containing fragment after integration by homologous recombination. (B) The URA3 marker introduced in the YFG1 locus, can be excised if URA3 is also flanked by direct repeats of DNA, preferably not ori ...
... selectable marker flanked by homologous sequences. The chromosomal segment is replaced by this URA3 containing fragment after integration by homologous recombination. (B) The URA3 marker introduced in the YFG1 locus, can be excised if URA3 is also flanked by direct repeats of DNA, preferably not ori ...
That Come Close to the Bone - Max-Planck
... Moreover, in mice with certain Hox mutations, the long tubular bones are transformed into rounded ones. The Berlin team proved the existence of such homeotic transformations in the extremities of vertebrates for the first time. This shows that Hox genes influence the shape of bones. ...
... Moreover, in mice with certain Hox mutations, the long tubular bones are transformed into rounded ones. The Berlin team proved the existence of such homeotic transformations in the extremities of vertebrates for the first time. This shows that Hox genes influence the shape of bones. ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... -whether a gene is active or inactive -determines the level of activity and the amount of protein that is available. ...
... -whether a gene is active or inactive -determines the level of activity and the amount of protein that is available. ...
Gene Section chromosome 18-like 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Smailus DE, Schnerch A, Schein JE, Jones SJ, Marra MA. Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 24;99(26):16899-903 ...
... Smailus DE, Schnerch A, Schein JE, Jones SJ, Marra MA. Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 24;99(26):16899-903 ...
Variation - Elgin Academy
... o explain how sex is determined with reference to the X and Y chromosomes ...
... o explain how sex is determined with reference to the X and Y chromosomes ...
7th_Ch_4_SG
... 8) That adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine in a DNA strand 9) That proteins are made up of amino acids 10) The difference between RNA and DNA (RNA is single stranded and contains uracil rather than thymine) 11) That in cell division, the nucleus divides, then the cytoplasm d ...
... 8) That adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine in a DNA strand 9) That proteins are made up of amino acids 10) The difference between RNA and DNA (RNA is single stranded and contains uracil rather than thymine) 11) That in cell division, the nucleus divides, then the cytoplasm d ...
Biotechnology - The Bio Edge
... their size, by causing them to migrate within a gel in response to an electric field. ...
... their size, by causing them to migrate within a gel in response to an electric field. ...
Biomolecules
... Protein: the work horse of the biomolecules. These molecules carry out most of the functions of the cell, act as building blocks, and allow organisms to move and do many ...
... Protein: the work horse of the biomolecules. These molecules carry out most of the functions of the cell, act as building blocks, and allow organisms to move and do many ...
Planet Earth and Its Environment A 5000
... to a part of the DNA called the promoter and the DNA ‘unzips’— that is, the DNA unspirals, hydrogen bonds between the two strands break, and the strands separate over a short length, just in that part of the DNA that holds the gene to be used. Only one strand of DNA contains the genetic information ...
... to a part of the DNA called the promoter and the DNA ‘unzips’— that is, the DNA unspirals, hydrogen bonds between the two strands break, and the strands separate over a short length, just in that part of the DNA that holds the gene to be used. Only one strand of DNA contains the genetic information ...
Applied genetics - questions
... (a) Show how a plant breeder would cross these varieties to produce a high yielding, short stemmed variety. (b) Explain why this variety would not breed true. 2 Choose from the list of words below, to complete the following sentence. In genetic engineering, a …..A …..from one organism is introduced ...
... (a) Show how a plant breeder would cross these varieties to produce a high yielding, short stemmed variety. (b) Explain why this variety would not breed true. 2 Choose from the list of words below, to complete the following sentence. In genetic engineering, a …..A …..from one organism is introduced ...
14-3: Human Molecular Genetics
... Biologists search the volumes of the human genome using sequences of DNA ...
... Biologists search the volumes of the human genome using sequences of DNA ...
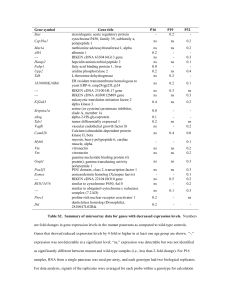
Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
Gene expression
... G1 –gap, decide whether to proliferate, wait or cross to non-dividing stage G0 S -- DNA Synthesis G2– gap, allow DNA repair ...
... G1 –gap, decide whether to proliferate, wait or cross to non-dividing stage G0 S -- DNA Synthesis G2– gap, allow DNA repair ...
1. Important Features
... (anticodon) with the triplet code (codon) of the mRNA. e.Enzyme "hooks" the amino acid to the last one in the chain forming a peptide bond. f. Protein chain continues to grow as each tRNA brings in its amino acid and adds it to the chain. - This is translation!! ...
... (anticodon) with the triplet code (codon) of the mRNA. e.Enzyme "hooks" the amino acid to the last one in the chain forming a peptide bond. f. Protein chain continues to grow as each tRNA brings in its amino acid and adds it to the chain. - This is translation!! ...
Document
... Representation of predicted R gene product structures and a model coupling the recognition of microbial Avr-dependent ligand and activation of plant defense. Pto can directly bind AvrPto (83, 92). The other R proteins probably bind the corresponding Avr gene products, either directly or in associati ...
... Representation of predicted R gene product structures and a model coupling the recognition of microbial Avr-dependent ligand and activation of plant defense. Pto can directly bind AvrPto (83, 92). The other R proteins probably bind the corresponding Avr gene products, either directly or in associati ...
1. Cellular control Booklet [A2]
... Sometimes, a mutation may be neutral and have no immediate effect. If there is no selective pressure against it, a mutation may be carried in the population and be of benefit (or harm) at some future time. Harmful mutations There are many well-documented examples of mutations that cause harmful effe ...
... Sometimes, a mutation may be neutral and have no immediate effect. If there is no selective pressure against it, a mutation may be carried in the population and be of benefit (or harm) at some future time. Harmful mutations There are many well-documented examples of mutations that cause harmful effe ...
Eukaryotic Genes
... molecules that each encode a different protein. • Alternative splicing often produces two forms of the same protein that are necessary at different stage of development or in different cell types. • Immunoglobulins of the IgM class exist as either a membrane bound protein displayed on the cell surfa ...
... molecules that each encode a different protein. • Alternative splicing often produces two forms of the same protein that are necessary at different stage of development or in different cell types. • Immunoglobulins of the IgM class exist as either a membrane bound protein displayed on the cell surfa ...
S3.Cell Signaling-Signaling and gene expression
... hearing loss. Waardenburg syndrome is a congenital disorder, caused by dominant loss-of-function mutations in a gene or genes in this pathway. Which gene or genes above could be mutated to give rise to Waardenburg syndrome 2A? Explain your answer. Loss-of-function mutations in MITF are also dominant ...
... hearing loss. Waardenburg syndrome is a congenital disorder, caused by dominant loss-of-function mutations in a gene or genes in this pathway. Which gene or genes above could be mutated to give rise to Waardenburg syndrome 2A? Explain your answer. Loss-of-function mutations in MITF are also dominant ...
Nervous System
... The change in DNA results in one or more different mRNA codons. The different codon(s) may result in a different amino acid(s). A change in the amino acid sequence of a protein will likely change the protein’s shape. (Remember-shape determines function!) ...
... The change in DNA results in one or more different mRNA codons. The different codon(s) may result in a different amino acid(s). A change in the amino acid sequence of a protein will likely change the protein’s shape. (Remember-shape determines function!) ...
some molecular basics
... actinin, vav and spectrin. In human ORF1 (IQGAP1), the Mp domain is homologous to the fly muscle protein mp20, and the GTPase activator is a rasGAP domain. The Y domain, shared by Yo61 and Ykb2, has no known function. Sizes of all proteins and domains are not to scale. ...
... actinin, vav and spectrin. In human ORF1 (IQGAP1), the Mp domain is homologous to the fly muscle protein mp20, and the GTPase activator is a rasGAP domain. The Y domain, shared by Yo61 and Ykb2, has no known function. Sizes of all proteins and domains are not to scale. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.


















![1. Cellular control Booklet [A2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003037943_1-e0be618182f13e07440d0dc63e34fbf9-300x300.png)



