some molecular basics
... actinin, vav and spectrin. In human ORF1 (IQGAP1), the Mp domain is homologous to the fly muscle protein mp20, and the GTPase activator is a rasGAP domain. The Y domain, shared by Yo61 and Ykb2, has no known function. Sizes of all proteins and domains are not to scale. ...
... actinin, vav and spectrin. In human ORF1 (IQGAP1), the Mp domain is homologous to the fly muscle protein mp20, and the GTPase activator is a rasGAP domain. The Y domain, shared by Yo61 and Ykb2, has no known function. Sizes of all proteins and domains are not to scale. ...
Section 1.1 Name:
... is getting the information from the DNA (genes), which cannot leave the nucleus, to the cytoplasm, where the protein building blocks await. The key to solving this problem lies in a nucleic acid called _______________, which carries the genetic information from DNA into the cytosol, and then assists ...
... is getting the information from the DNA (genes), which cannot leave the nucleus, to the cytoplasm, where the protein building blocks await. The key to solving this problem lies in a nucleic acid called _______________, which carries the genetic information from DNA into the cytosol, and then assists ...
regulatory-network
... Gene regulatory network: two genes are connected if the expression of one gene modulates expression of another one by either activation or inhibition Protein interaction network: proteins that are connected in physical interactions or metabolic and signaling pathways of the cell; Metabolic net ...
... Gene regulatory network: two genes are connected if the expression of one gene modulates expression of another one by either activation or inhibition Protein interaction network: proteins that are connected in physical interactions or metabolic and signaling pathways of the cell; Metabolic net ...
Huntington`s disease: Understanding a mutation - LENS
... The seminar will provide an opportunity for you to review concepts of gene expression, mutations and stem cells, explore the use of different biotechnologies, and consider the ethical questions that are faced by scientists as they work to understand a disease and find a potential cure. A very ...
... The seminar will provide an opportunity for you to review concepts of gene expression, mutations and stem cells, explore the use of different biotechnologies, and consider the ethical questions that are faced by scientists as they work to understand a disease and find a potential cure. A very ...
Slide 1
... amino-acylated tRNAs. • What was the significance of this work? • Nirenberg’s assay delivered a method to assign each specific amino acid to one or more trinucleotides. • Twenty amino acids were assigned at least one trinucleotide, 61 in total. • Three trinucleotides where determined to be “stop” co ...
... amino-acylated tRNAs. • What was the significance of this work? • Nirenberg’s assay delivered a method to assign each specific amino acid to one or more trinucleotides. • Twenty amino acids were assigned at least one trinucleotide, 61 in total. • Three trinucleotides where determined to be “stop” co ...
FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST DNA The coded information in a
... C. Phagocytes will be unable to function D. Macrophages will be unable to function 35. Which of the following statements is NOT true concerning bacteria A. Some bacteria break down the bodies of dead plants and animals B. All bacteria are parasites of living cells C. The digestive tract of humans ha ...
... C. Phagocytes will be unable to function D. Macrophages will be unable to function 35. Which of the following statements is NOT true concerning bacteria A. Some bacteria break down the bodies of dead plants and animals B. All bacteria are parasites of living cells C. The digestive tract of humans ha ...
About Genetic Diseases
... Genetic diseases are defined as diseases caused by aberrations of genetic material. Therefore, these diseases can potentially be passed from generation to generation. However, not every patient has a family history of a similar problem. This is because new mutations can occur when an individual inhe ...
... Genetic diseases are defined as diseases caused by aberrations of genetic material. Therefore, these diseases can potentially be passed from generation to generation. However, not every patient has a family history of a similar problem. This is because new mutations can occur when an individual inhe ...
Heredity and Environment
... have a marked percentage of abnormal “sickleshaped” red blood cells that interfere with oxygen transport throughout the body. • They also have normal (dominant) red blood cells as well. ...
... have a marked percentage of abnormal “sickleshaped” red blood cells that interfere with oxygen transport throughout the body. • They also have normal (dominant) red blood cells as well. ...
II. Transposable Elements in Bacteria Transposable Elements are
... Insertion sequences (IS's) are transposable elements whose only genes are directly related to promotion and regulation of their transposition, typically the gene for the so-called transposase enzyme. IS elements are between 700 - 2,000 bp in length and are characterized by short, terminal, inverted ...
... Insertion sequences (IS's) are transposable elements whose only genes are directly related to promotion and regulation of their transposition, typically the gene for the so-called transposase enzyme. IS elements are between 700 - 2,000 bp in length and are characterized by short, terminal, inverted ...
Fall 2009
... 90) The process in which DNA is copied and what does it assure? 91) What are the roles of proteins verses enzymes in the process of replication? 92) What are the names of the enzymes used in replication (_____ __________) and in transcription (______ ______________). 93) What feature is built in to ...
... 90) The process in which DNA is copied and what does it assure? 91) What are the roles of proteins verses enzymes in the process of replication? 92) What are the names of the enzymes used in replication (_____ __________) and in transcription (______ ______________). 93) What feature is built in to ...
Gene Section AF10 (ALL1 fused gene from chromosome 10)
... Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 May 14;93(10):4804-4809. Rubnitz JE, Behm FG, Downing JR. 11q23 rearrangements in acute leukemia. Leukemia 1996 Jan;10(1):74-82. (Review). Young BD and Saha V. Chromosome abnormalities in leukemia: the 11q23 paradigm. Cancer Surv 1996;28:225-245. Kobayashi H, Hosoda F, Maseki ...
... Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 May 14;93(10):4804-4809. Rubnitz JE, Behm FG, Downing JR. 11q23 rearrangements in acute leukemia. Leukemia 1996 Jan;10(1):74-82. (Review). Young BD and Saha V. Chromosome abnormalities in leukemia: the 11q23 paradigm. Cancer Surv 1996;28:225-245. Kobayashi H, Hosoda F, Maseki ...
Chapter 12-13 Notes
... The ends of DNA molecules, located at the telomeres, are particularly difficult to copy. Over time, DNA may be lost from telomeres each time a chromosome is replicated. Telomerase: 1. adds short, repeated DNA sequences to telomeres 2. lengthens the chromosomes 3. Reduces likelihood that gene sequenc ...
... The ends of DNA molecules, located at the telomeres, are particularly difficult to copy. Over time, DNA may be lost from telomeres each time a chromosome is replicated. Telomerase: 1. adds short, repeated DNA sequences to telomeres 2. lengthens the chromosomes 3. Reduces likelihood that gene sequenc ...
File
... 12. A gene G, containing two small introns, was inserted into a yeast transposon at a position where it did not interfere with transposition. The transposon moved to new locations, and the structure of the transposon in its new locations was studied. It was found that at each new location the transp ...
... 12. A gene G, containing two small introns, was inserted into a yeast transposon at a position where it did not interfere with transposition. The transposon moved to new locations, and the structure of the transposon in its new locations was studied. It was found that at each new location the transp ...
Review - Qc.edu
... In a Hardy-Weinberg population (infinitely large, randomly mating, no mutation, no migration): if fr(A) = p and fr(a) = q, then fr(AA) = p2, fr(Aa) = 2pq, fr(aa) = q2 and allele and genotype frequencies do not change from generation to generation If a population is at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the ...
... In a Hardy-Weinberg population (infinitely large, randomly mating, no mutation, no migration): if fr(A) = p and fr(a) = q, then fr(AA) = p2, fr(Aa) = 2pq, fr(aa) = q2 and allele and genotype frequencies do not change from generation to generation If a population is at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the ...
AIPVT Biology Botany and Zoology Sample Paper 2
... 170. Telomere repetitive DNA sequences control the function of eukaryotic chromosomes because they (a) are RNA transcription initiator (b) help chromosome pairing (c) prevent chromosome loss (d) act as replicons. 171. Spore diseminiation in some liverworts is aided by (a) indusium (b) calyptra (c) p ...
... 170. Telomere repetitive DNA sequences control the function of eukaryotic chromosomes because they (a) are RNA transcription initiator (b) help chromosome pairing (c) prevent chromosome loss (d) act as replicons. 171. Spore diseminiation in some liverworts is aided by (a) indusium (b) calyptra (c) p ...
1 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... b. contains 13-bp inverted repeat at the termini (TIR) c. forms a two-element system d. first cloned from the waxy locus e. moves via cut-and-paste (gain-and-loss) mechanism 6. Many transposons in plants are inactive, but can be activated. Which mechanism has not been shown to make a major contribut ...
... b. contains 13-bp inverted repeat at the termini (TIR) c. forms a two-element system d. first cloned from the waxy locus e. moves via cut-and-paste (gain-and-loss) mechanism 6. Many transposons in plants are inactive, but can be activated. Which mechanism has not been shown to make a major contribut ...
(Part 2) Mutation and genetic variation
... (synonymous) or replacement (nonsynonymous) changes. • in coding regions, insertions/deletions can also cause frameshift mutations. ...
... (synonymous) or replacement (nonsynonymous) changes. • in coding regions, insertions/deletions can also cause frameshift mutations. ...
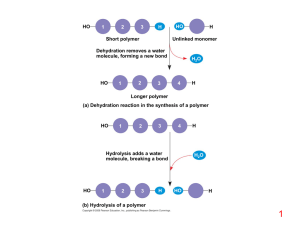
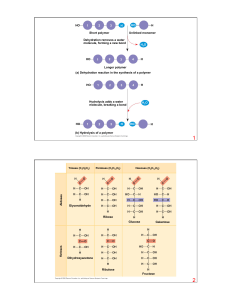
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Normal red blood cells are full of individual hemoglobin moledules, each carrying oxygen. ...
... Normal red blood cells are full of individual hemoglobin moledules, each carrying oxygen. ...
Karyn Sykes January 24, 2009 LLOG 1: Immortal Genes: Running in
... discoveries in the field of Biology. The first discovery that was made was a whole new domain of species. The name of the kingdom is called Archaea. This discovery was so profound because for many years scientists believed that there were only two domains of species in the world. This discovery comp ...
... discoveries in the field of Biology. The first discovery that was made was a whole new domain of species. The name of the kingdom is called Archaea. This discovery was so profound because for many years scientists believed that there were only two domains of species in the world. This discovery comp ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... (b) Cellulose: 1–4 linkage of β glucose monomers ...
... (b) Cellulose: 1–4 linkage of β glucose monomers ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.