Bio_11_Rev
... responds by making defensive proteins called antibodies. The immune system creates a defense system against this form of the disease. •In the future, if the same pathogen enters the body, the antibodies are now there to combat the pathogen and stop it’s growth before it can cause a disease. The immu ...
... responds by making defensive proteins called antibodies. The immune system creates a defense system against this form of the disease. •In the future, if the same pathogen enters the body, the antibodies are now there to combat the pathogen and stop it’s growth before it can cause a disease. The immu ...
Topic 4: Genetics - Peoria Public Schools
... 63. The Human Genome Project sequenced the entire human genome and found there to be 25000 to 30000 genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 64. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability ...
... 63. The Human Genome Project sequenced the entire human genome and found there to be 25000 to 30000 genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 64. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability ...
laboratory examination of cancer
... neuroblastomas. Clinical trials have shown that lung cancers with ALK mutations respond to ALK inhibitors, whereas other lung cancers do not, leading to recent FDA approval of ALK inhibitors for use in patients with “ALK-mutated” lung cancer. • Another recent dramatic example of molecularly “tailore ...
... neuroblastomas. Clinical trials have shown that lung cancers with ALK mutations respond to ALK inhibitors, whereas other lung cancers do not, leading to recent FDA approval of ALK inhibitors for use in patients with “ALK-mutated” lung cancer. • Another recent dramatic example of molecularly “tailore ...
Biology 1 Exam III Summer2005(ch8-9-10-11).doc
... 14) The sequence of nitrogen-containing bases on one strand of DNA could determine the A) sequence of nitrogen-containing bases in mRNA. B) sequence of amino acids in protein. C) sequence of nitrogen-containing bases in the other DNA strand. ...
... 14) The sequence of nitrogen-containing bases on one strand of DNA could determine the A) sequence of nitrogen-containing bases in mRNA. B) sequence of amino acids in protein. C) sequence of nitrogen-containing bases in the other DNA strand. ...
1. Molecular basis of human genetics a) Structure and function of the
... Pathological and neutral genetic variation at the DNA level: polymorphisms, mutations b) Transcription and translation i. DNA and RNA: flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA ii. RNA-processing: splicing, alternative splicing, RNA-editing iii. Protein synthesis: transport of mRNA from nucleus to ...
... Pathological and neutral genetic variation at the DNA level: polymorphisms, mutations b) Transcription and translation i. DNA and RNA: flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA ii. RNA-processing: splicing, alternative splicing, RNA-editing iii. Protein synthesis: transport of mRNA from nucleus to ...
Solutions to Molecular Biology Unit Exam
... i) Label which strand is human DNA and which is viral RNA in the picture. ii) Why can some regions form complementary base pairs, while other regions cannot? The DNA contains introns that are not present in the viral RNA. iii) If you were to isolate mature mRNA from the human cell and allow it to ba ...
... i) Label which strand is human DNA and which is viral RNA in the picture. ii) Why can some regions form complementary base pairs, while other regions cannot? The DNA contains introns that are not present in the viral RNA. iii) If you were to isolate mature mRNA from the human cell and allow it to ba ...
Lecture 8
... region and added to the growing 3’-end •! Nucleotides are added according to the rules of base pairing T!A, C!G, G!C, and A!U Only a short segment RNA is bound to the template at any one time ...
... region and added to the growing 3’-end •! Nucleotides are added according to the rules of base pairing T!A, C!G, G!C, and A!U Only a short segment RNA is bound to the template at any one time ...
AP Biology – Chapter 5: Macromolecules Carbohydrates 1. Define
... 11. What is the characteristic common to lipids? 12. Lipids are synthesized by the chemical reaction ____________________ and broken down by the reaction _______________________. 13. What makes fats hydrophobic? 14. State at least two differences between saturated and unsaturated fats. a. b. 15. How ...
... 11. What is the characteristic common to lipids? 12. Lipids are synthesized by the chemical reaction ____________________ and broken down by the reaction _______________________. 13. What makes fats hydrophobic? 14. State at least two differences between saturated and unsaturated fats. a. b. 15. How ...
File
... isolated and cut out of a human cell A plasmid is removed from a bacterial cell A piece of the plasmid is removed and the human gene is inserted The recombinant plasmid is inserted back into the bacterial cell The bacterial cell will now produce insulin as a product of its transcription and translat ...
... isolated and cut out of a human cell A plasmid is removed from a bacterial cell A piece of the plasmid is removed and the human gene is inserted The recombinant plasmid is inserted back into the bacterial cell The bacterial cell will now produce insulin as a product of its transcription and translat ...
Genes - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology The University of Arizona ...
... Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology The University of Arizona ...
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... • Amino acid sequence of polypeptide programmed by a gene. • 2 types of nucleic acids: ribonucleic ...
... • Amino acid sequence of polypeptide programmed by a gene. • 2 types of nucleic acids: ribonucleic ...
Nucleic Acids - Informational Polymers
... • During preparations for cell division each of the strands serves as a template to order nucleotides into a new complementary strand. • This results in two identical copies of the original double-stranded DNA molecule. – The copies are then distributed to the daughter cells. ...
... • During preparations for cell division each of the strands serves as a template to order nucleotides into a new complementary strand. • This results in two identical copies of the original double-stranded DNA molecule. – The copies are then distributed to the daughter cells. ...
Core – Practice test 4
... the Irish potato crop which was the main source of food for one third of the population. This led to a 7 year famine. Why did one little fungus cause so much trouble? • Potatoes grow by asexual reproduction therefore the potatoes lack variations that could have withstood the infection. ...
... the Irish potato crop which was the main source of food for one third of the population. This led to a 7 year famine. Why did one little fungus cause so much trouble? • Potatoes grow by asexual reproduction therefore the potatoes lack variations that could have withstood the infection. ...
No Slide Title
... The expression of different genes can be coordinated by a single protein in eucaryotic cells. This can result in rapid switching on or off of whole groups of genes. ...
... The expression of different genes can be coordinated by a single protein in eucaryotic cells. This can result in rapid switching on or off of whole groups of genes. ...
T T PowerPoint
... How an Organism’s Genotype Produces Its Phenotype – An organism’s genotype, its genetic makeup, is the sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA. • The phenotype is the organism’s specific traits (or what it looks like and how it functions), which arise from the actions of a wide variety of proteins. ...
... How an Organism’s Genotype Produces Its Phenotype – An organism’s genotype, its genetic makeup, is the sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA. • The phenotype is the organism’s specific traits (or what it looks like and how it functions), which arise from the actions of a wide variety of proteins. ...
PowerPoint
... BS.01.01. Investigate and explain the relationship between past, current and emerging applications of biotechnology in agriculture (e.g., major innovators, historical developments, potential applications of biotechnology, etc.). Sample Measurement: The following sample measurement strands are provid ...
... BS.01.01. Investigate and explain the relationship between past, current and emerging applications of biotechnology in agriculture (e.g., major innovators, historical developments, potential applications of biotechnology, etc.). Sample Measurement: The following sample measurement strands are provid ...
16792_bty100-4-2
... A Gene is a segment of DNA and is located on the chromosome. Gene specifies the structure of particular protein that make up each cell. ...
... A Gene is a segment of DNA and is located on the chromosome. Gene specifies the structure of particular protein that make up each cell. ...
6.7 Human Genetic Diseases
... • fats collect in cells destroying their function • symptoms begin few months after birth • seizures, blindness, muscular & mental degeneration • child usually dies before 5 ...
... • fats collect in cells destroying their function • symptoms begin few months after birth • seizures, blindness, muscular & mental degeneration • child usually dies before 5 ...
Gene Finding
... The snRNA recognizes the splice sites through RNA-RNA base-pairing Recognition must be precise: a 1nt error can shift the reading frame making nonsense of its message. Many genes have alternative splicing which changes the protein created. ...
... The snRNA recognizes the splice sites through RNA-RNA base-pairing Recognition must be precise: a 1nt error can shift the reading frame making nonsense of its message. Many genes have alternative splicing which changes the protein created. ...
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
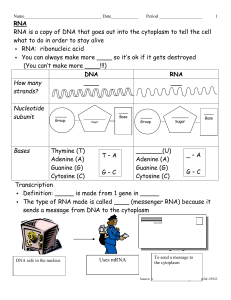
... o Unzip one gene in _____ o Match up bases to ____side of gene in DNA o mRNA detaches from the _____ o mRNA moves out of the nucleus and into the __________ ...
... o Unzip one gene in _____ o Match up bases to ____side of gene in DNA o mRNA detaches from the _____ o mRNA moves out of the nucleus and into the __________ ...
Informed Consent for TPMT Genetic Tests
... a toxic buildup of the active forms of these drugs. Variants in the TPMT gene that lead to low enzyme activity can lead to an increased risk of thiopurine toxicity. Because of the potentially severe bone marrow toxicity that can occur even with standard thiopurine dosages in patients with TPMT enzym ...
... a toxic buildup of the active forms of these drugs. Variants in the TPMT gene that lead to low enzyme activity can lead to an increased risk of thiopurine toxicity. Because of the potentially severe bone marrow toxicity that can occur even with standard thiopurine dosages in patients with TPMT enzym ...
Hershey-Chase Experiment
... Early genetics had several basic problems to solve, and chief among them was to determine what exactly was the genetic material inside cells. This was solved by two scientists, Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase. This discovery pointed the way for several subsequent studies that opened a new generation ...
... Early genetics had several basic problems to solve, and chief among them was to determine what exactly was the genetic material inside cells. This was solved by two scientists, Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase. This discovery pointed the way for several subsequent studies that opened a new generation ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.