Lab 7_Esterification
... Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, you need to use only a small amount of sulfuric acid in order for it to be effective. Heating is another way ...
... Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, you need to use only a small amount of sulfuric acid in order for it to be effective. Heating is another way ...
aldehyde ketone
... CH3-CH2-OH CH3-CHO + 2H+ + 2e CH3-CHO + H2O CH3COOH + 2H+ + 2e reduction; Cr2O72-(aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6e- 2Cr3+ (aq) +7H2O orange ...
... CH3-CH2-OH CH3-CHO + 2H+ + 2e CH3-CHO + H2O CH3COOH + 2H+ + 2e reduction; Cr2O72-(aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6e- 2Cr3+ (aq) +7H2O orange ...
PowerPoint **
... Why alkenyl halides such as CH3CBr=ChCH3 don’t undergo substitution upon treatment with a strong base(-NH2)? Ans: ring strain. ...
... Why alkenyl halides such as CH3CBr=ChCH3 don’t undergo substitution upon treatment with a strong base(-NH2)? Ans: ring strain. ...
Section 07 - Section Practice Exam II Solutions
... versus X=H. In the case of X=OMe, the inductive effect (oxygen is electronegative and electron withdrawing) appears to predominate over the resonance effect. This is easily explained by the substituent being meta to the carbocation—if it were oriented ortho or para, then we would expect considerable ...
... versus X=H. In the case of X=OMe, the inductive effect (oxygen is electronegative and electron withdrawing) appears to predominate over the resonance effect. This is easily explained by the substituent being meta to the carbocation—if it were oriented ortho or para, then we would expect considerable ...
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I
... The second step of the E1 mechanism in which the carbocation forms is rate determining The transition state for this reaction has carbocation character Tertiary alcohols react the fastest because they have the most stable tertiary carbocation-like transition state in the second step Chapter 7 ...
... The second step of the E1 mechanism in which the carbocation forms is rate determining The transition state for this reaction has carbocation character Tertiary alcohols react the fastest because they have the most stable tertiary carbocation-like transition state in the second step Chapter 7 ...
NaBH4 Reduction of Vanillin
... After the reaction mixture has stirred at room temperature for 15‐20 minutes, check the reaction progress by TLC. Prepare your TLC plate with 3 tick marks at the baseline and spot as follows: spot the left lane with just your vanillin starting material solution; spot the middle ...
... After the reaction mixture has stirred at room temperature for 15‐20 minutes, check the reaction progress by TLC. Prepare your TLC plate with 3 tick marks at the baseline and spot as follows: spot the left lane with just your vanillin starting material solution; spot the middle ...
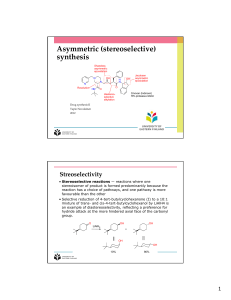
Asymmetric (stereoselective) synthesis
... then separated by chromatography. The resolving agent was removed from one of the diastereoisomers to give a single enantiomer of the alcohol, which could be cyclized to the natural (R)‐pheromone using base and then acid. ...
... then separated by chromatography. The resolving agent was removed from one of the diastereoisomers to give a single enantiomer of the alcohol, which could be cyclized to the natural (R)‐pheromone using base and then acid. ...
File
... larger molecule to leave a double bond in the larger molecule • Alcohol =water + alkene • Dehydration reaction since water is removed • Ethanol=ethene + water • 2 methanol +sulphuric acid =methoxymethane ether +water ...
... larger molecule to leave a double bond in the larger molecule • Alcohol =water + alkene • Dehydration reaction since water is removed • Ethanol=ethene + water • 2 methanol +sulphuric acid =methoxymethane ether +water ...
Organic-IB-Short-Exam Questions-Answers
... The compound 2-bromobutane, CH3CHBrCH2CH3, can react with sodium hydroxide to form compounds M, N and O. Compound M, C4H10O, exists as a pair of optically active isomers. Compounds N and O, C4H8, are structural isomers, and compound O exists as a pair of geometrical isomers. (a) ...
... The compound 2-bromobutane, CH3CHBrCH2CH3, can react with sodium hydroxide to form compounds M, N and O. Compound M, C4H10O, exists as a pair of optically active isomers. Compounds N and O, C4H8, are structural isomers, and compound O exists as a pair of geometrical isomers. (a) ...
CET MODEL QUESTION PAPER 1. Set of quantum numbers (n, /, m
... 12. For an endothermic reaction, where .:\11 represents the enthalpy of the reaction in KJ / mole, the minimum value for the energy of activation will be 1] less than ∆H 2] zero 3] more than ∆H 4] equal to ∆H 13. Zone refining is a method to obtain I] very high temperature 2] ultra pure Al 14. An or ...
... 12. For an endothermic reaction, where .:\11 represents the enthalpy of the reaction in KJ / mole, the minimum value for the energy of activation will be 1] less than ∆H 2] zero 3] more than ∆H 4] equal to ∆H 13. Zone refining is a method to obtain I] very high temperature 2] ultra pure Al 14. An or ...
3.8 Aldehydes and ketones
... Like the alkenes, the carbonyl group consists of a s bond and a p bond between the carbon and oxygen: ...
... Like the alkenes, the carbonyl group consists of a s bond and a p bond between the carbon and oxygen: ...
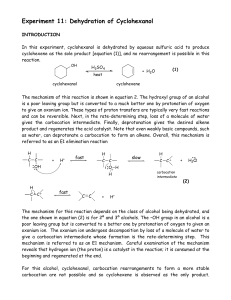
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
12SN-23-10 OBJECTIVE: Identify how alcohols are classified and
... Identify how alcohols are classified and named. Predict how the solubility of an alcohol varies with the length of its carbon chain. Name the reactions of alkenes that may be used to introduce functional groups. Construct the general structure of an ether and describe how ethers are named. Identify ...
... Identify how alcohols are classified and named. Predict how the solubility of an alcohol varies with the length of its carbon chain. Name the reactions of alkenes that may be used to introduce functional groups. Construct the general structure of an ether and describe how ethers are named. Identify ...
Set 1 - ExamResults.net
... 11. a) Give one example for paramagnetic substance. b) Which type of binding force existing in ice? 12. Write anodic and cathodic half-cell reactions taking place in Daniel cell. 13. Show that for first order reaction t87.5% = 3 t50%. 14. What is lanthanide contraction? What is the cause for it? 15. ...
... 11. a) Give one example for paramagnetic substance. b) Which type of binding force existing in ice? 12. Write anodic and cathodic half-cell reactions taking place in Daniel cell. 13. Show that for first order reaction t87.5% = 3 t50%. 14. What is lanthanide contraction? What is the cause for it? 15. ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 2 QUESTIONS SECTION A
... With reference to the above reaction state how the following factors will affect product yield and the value of the equilibrium constant. Write down the respective letter and next to the letter, one of the following: increase, decrease, no effect. ...
... With reference to the above reaction state how the following factors will affect product yield and the value of the equilibrium constant. Write down the respective letter and next to the letter, one of the following: increase, decrease, no effect. ...
Organic Chemistry (HL) Revision Questions
... 2-chloro-3-methylbutane reacts with sodium hydroxide via an SN2 mechanism. Explain the mechanism by using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs. ...
... 2-chloro-3-methylbutane reacts with sodium hydroxide via an SN2 mechanism. Explain the mechanism by using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs. ...
Alkenes undergo Addition Reactions Predict the product of each
... What functional group is used to make a π bond? How does a π bond react? What functional group is produced? What is the difference between cis/trans/E/Z? ...
... What functional group is used to make a π bond? How does a π bond react? What functional group is produced? What is the difference between cis/trans/E/Z? ...
Exam 1 from 2008
... 5. (10 pts) Allene has the structure H2C=C=CH2. a) Draw an accurate 3D structure of allene. (Hint: It is not planar.) On this structure show the p-orbitals and how they overlap to form the pi bonds in allene. Clearly indicate the 3D orientation of the p-orbitals relative to the atoms in the molecule ...
... 5. (10 pts) Allene has the structure H2C=C=CH2. a) Draw an accurate 3D structure of allene. (Hint: It is not planar.) On this structure show the p-orbitals and how they overlap to form the pi bonds in allene. Clearly indicate the 3D orientation of the p-orbitals relative to the atoms in the molecule ...
Organic Compounds Containing C, H and O
... Ans. i. a. Nitro (-NO2) group is an electron withdrawing whereas methoxy (-OCH3) group is electron releasing in nature. o-nitrophenol produces H+ ions easily but methoxyphenol does not. This is because o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilised due to resonance. This is not true with o-methoxyphenoxide ion. ...
... Ans. i. a. Nitro (-NO2) group is an electron withdrawing whereas methoxy (-OCH3) group is electron releasing in nature. o-nitrophenol produces H+ ions easily but methoxyphenol does not. This is because o-nitrophenoxide ion is stabilised due to resonance. This is not true with o-methoxyphenoxide ion. ...
Reaction of Alkenes
... reaction is regioselective (alcohol on the least‐substituted carbon) (alcohol on the least substituted carbon) and stereoselective (syn‐addition) ...
... reaction is regioselective (alcohol on the least‐substituted carbon) (alcohol on the least substituted carbon) and stereoselective (syn‐addition) ...
TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... regiochemically pure enolates Other carbanions in synthesis - dithianes and corresponding sulfoxides, nitrocompound, cyanoalkanes Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed ...
... regiochemically pure enolates Other carbanions in synthesis - dithianes and corresponding sulfoxides, nitrocompound, cyanoalkanes Acidites of phosphonium and sulfonium compounds and ylides (for chemistry see later) Enols, enamines and metalloenamines in synthesis Mechanism of acid and base catalyzed ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.