Diels-Alder Reaction
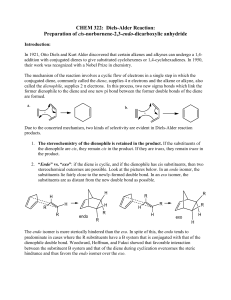
... The Diels-Alder reaction is probably the most familiar example of a reaction type known as a cycloaddition reaction, in which the conjugated p-systems of two reactants join to generate a new ring. The reactants in the Diels-Alder reaction are a 1,3-diene and an alkene called the dienophile. The carb ...
... The Diels-Alder reaction is probably the most familiar example of a reaction type known as a cycloaddition reaction, in which the conjugated p-systems of two reactants join to generate a new ring. The reactants in the Diels-Alder reaction are a 1,3-diene and an alkene called the dienophile. The carb ...
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes – Properties and Synthesis
... The formation of the more stable alkene is the general rule (Zaitsev's rule) in the acid-catalyzed dehydration reactions of alcohols. ...
... The formation of the more stable alkene is the general rule (Zaitsev's rule) in the acid-catalyzed dehydration reactions of alcohols. ...
Chapter 7
... Rearrangements • Only the carbocation rearranges, so dehydration of primary alcohols can not have rearrangements since they are E2 and not carbocation is formed! • However, as we will see in Ch 8, the alkene product can react with the acid by using its pi electrons to abstract a proton from an acid ...
... Rearrangements • Only the carbocation rearranges, so dehydration of primary alcohols can not have rearrangements since they are E2 and not carbocation is formed! • However, as we will see in Ch 8, the alkene product can react with the acid by using its pi electrons to abstract a proton from an acid ...
Seminar_1 1. Classification and nomenclature of organic
... Whilst many of the alkanes present in crude oil are aliphatic, having straight–or branched–chain molecules, some of them form rings – they are alicyclic. These compounds are denoted as cycloalkanes. These cycloalkanes have the general formula CnH2n instead of CnH2n+2 for the chain molecules. Cycloal ...
... Whilst many of the alkanes present in crude oil are aliphatic, having straight–or branched–chain molecules, some of them form rings – they are alicyclic. These compounds are denoted as cycloalkanes. These cycloalkanes have the general formula CnH2n instead of CnH2n+2 for the chain molecules. Cycloal ...
Synthesis of 1
... Alcohols are easily converted into the corresponding alkyl halides by reacting them with concentrated aqueous hydrogen halides. Tertiary alcohols react almost instantly at cool temperatures via an SN1 mechanism since 3o carbocations are relatively easy to form. Primary alcohols, on the other hand, r ...
... Alcohols are easily converted into the corresponding alkyl halides by reacting them with concentrated aqueous hydrogen halides. Tertiary alcohols react almost instantly at cool temperatures via an SN1 mechanism since 3o carbocations are relatively easy to form. Primary alcohols, on the other hand, r ...
reduction of ketones and imines with CaH2/ZnX2 in the presence of
... excellent yields. Thus, imines derived from aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes were cleanly converted to the corresponding amines. Imines having a benzyl, alkyl, or aromatic group as an N-substituent were good substrates. Functional groups such as bromo and alkenyl moieties present in the substrate we ...
... excellent yields. Thus, imines derived from aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes were cleanly converted to the corresponding amines. Imines having a benzyl, alkyl, or aromatic group as an N-substituent were good substrates. Functional groups such as bromo and alkenyl moieties present in the substrate we ...
Carbonyl Compounds
... nucleophilic addition reaction:in terms of electronic effect and steric effect of alkyl group: . HCHO > RCHO >RCR’O >CHO >CRO > CO ( REFERS TO BENZENE) ...
... nucleophilic addition reaction:in terms of electronic effect and steric effect of alkyl group: . HCHO > RCHO >RCR’O >CHO >CRO > CO ( REFERS TO BENZENE) ...
File - chemistryworkshopjr
... Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher reaction rate at the same temperature and for the same reactant concentrations. However, the mechanistic explanation of catalysis is complex ...
... Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher reaction rate at the same temperature and for the same reactant concentrations. However, the mechanistic explanation of catalysis is complex ...
Lecture Resource ()
... Amines do not undergo substitution reactions because NH2– is a very strong base (a very poor leaving group) RCH2F > RCH2OH > RCH2NH2 ...
... Amines do not undergo substitution reactions because NH2– is a very strong base (a very poor leaving group) RCH2F > RCH2OH > RCH2NH2 ...
Selective synthesis of cyclododec-2-en-1
... Relevant information about the mechanism of alkoxylation of cyclododec-2-en-1-yl acetates can be obtained from the dependence of the quantitative distribution of the products on reaction conditions. The products formed as a result of the alkoxylation of cyclododec-2-en-1-yl acetates (I) are, general ...
... Relevant information about the mechanism of alkoxylation of cyclododec-2-en-1-yl acetates can be obtained from the dependence of the quantitative distribution of the products on reaction conditions. The products formed as a result of the alkoxylation of cyclododec-2-en-1-yl acetates (I) are, general ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) ISSN: 2278-5736.
... Protection could be regarded as a special instance of a combine chemo and region selectivity since it embrace aspects of both. It is implicated when a reaction selectivity at one functional group is needed in the presence of other functional group. When the principles of chemo selectivity are not ap ...
... Protection could be regarded as a special instance of a combine chemo and region selectivity since it embrace aspects of both. It is implicated when a reaction selectivity at one functional group is needed in the presence of other functional group. When the principles of chemo selectivity are not ap ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and the carbon that was formerly the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule ...
... carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and the carbon that was formerly the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and the carbon that was formerly the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule ...
... carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and the carbon that was formerly the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule ...
File - Loreto Science
... • It is important to note that in the preaparation of aldehydes the acidified sodium dichromate is added slowly and the aldehyde is distilled off immediately to prevent further oxidation to carboxylic ...
... • It is important to note that in the preaparation of aldehydes the acidified sodium dichromate is added slowly and the aldehyde is distilled off immediately to prevent further oxidation to carboxylic ...
name Page 1 of 6 Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer for the
... Which of the following statements concerning a carbocation is not true? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) ...
... Which of the following statements concerning a carbocation is not true? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) ...
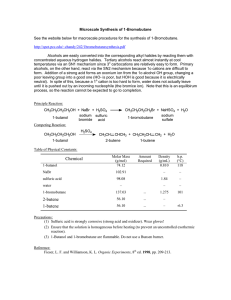
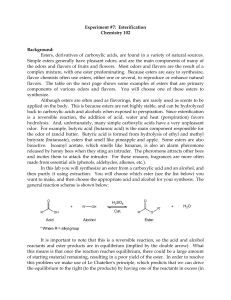
102 Lab 7 Esters Fall05
... Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, you need to use only a small amount of sulfuric acid in order for it to be effective. Heating is another way ...
... Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, you need to use only a small amount of sulfuric acid in order for it to be effective. Heating is another way ...
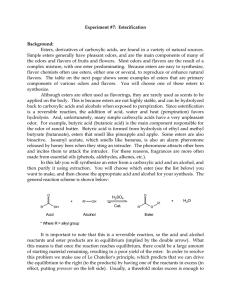
Diels-Alder Reaction:
... conformation is needed to carry out the Diels-Alder reaction. The s-cis conformation of the diene would yield a six membered ring with a cis double bond whereas a diene in s-trans conformation would demand a trans double bond in a six membered ring – an impossible feat. Cyclic dienes, which are lock ...
... conformation is needed to carry out the Diels-Alder reaction. The s-cis conformation of the diene would yield a six membered ring with a cis double bond whereas a diene in s-trans conformation would demand a trans double bond in a six membered ring – an impossible feat. Cyclic dienes, which are lock ...
CN>Chapter 22CT>Carbonyl Alpha
... transfer to water is slow In the reverse direction there is also a barrier to the addition of the proton from water to enolate carbon ...
... transfer to water is slow In the reverse direction there is also a barrier to the addition of the proton from water to enolate carbon ...
Mechanism
... base to drive the reaction. Limitations One of the main drawbacks of the Henry Reaction is the potential for side reactions throughout the course of the reaction. Aside from the reversibility of the reaction (Retro-Henry) which could prevent the reaction from proceeding, the β-nitro alcohol has the ...
... base to drive the reaction. Limitations One of the main drawbacks of the Henry Reaction is the potential for side reactions throughout the course of the reaction. Aside from the reversibility of the reaction (Retro-Henry) which could prevent the reaction from proceeding, the β-nitro alcohol has the ...
436
... Give an equation for a crossed cannizzaro reaction, give a mechanism, and explain why does it follow such a path ? ...
... Give an equation for a crossed cannizzaro reaction, give a mechanism, and explain why does it follow such a path ? ...
ESTERIFICATION
... Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, you need to use only a small amount of sulfuric acid in order for it to be effective. Heating is another way ...
... Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, you need to use only a small amount of sulfuric acid in order for it to be effective. Heating is another way ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.