EXPERIMENT 4 Objectives Principles
... From the reaction above, cyclohexene is the only alkene that can be formed under these conditions. Cyclohexene and water are removed via azeotropic distillation to drive the equilibrium to product. Traces of acid in crude product are removed by treatment with sodium carbonate solution. A final wash ...
... From the reaction above, cyclohexene is the only alkene that can be formed under these conditions. Cyclohexene and water are removed via azeotropic distillation to drive the equilibrium to product. Traces of acid in crude product are removed by treatment with sodium carbonate solution. A final wash ...
organic outline - No Brain Too Small
... Hint: for propene draw as and draw as “polyethene” with one CH3- on every other C atom in place of an H. H ...
... Hint: for propene draw as and draw as “polyethene” with one CH3- on every other C atom in place of an H. H ...
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... Activating groups cause the aromatic ring to be more reactive than benzene Deactivating groups cause the aromatic ring to be less reactive than benzene Ortho-para directors direct future substitution to the ortho and para positions Meta directors direct future substitution to the meta position ...
... Activating groups cause the aromatic ring to be more reactive than benzene Deactivating groups cause the aromatic ring to be less reactive than benzene Ortho-para directors direct future substitution to the ortho and para positions Meta directors direct future substitution to the meta position ...
CH102 Practice exam 2
... ____ 13.The carboxyl group found in carboxylic acids must be on a terminal carbon, like the carbonyl of an aldehyde ____ 14.Carboxylic acids have the functional groups found in both aldehyde / ketones and alcohols. ____ 15.Pure liquid carboxylic acids are strongly hydrogen bonded. ____ 16.Butyric ac ...
... ____ 13.The carboxyl group found in carboxylic acids must be on a terminal carbon, like the carbonyl of an aldehyde ____ 14.Carboxylic acids have the functional groups found in both aldehyde / ketones and alcohols. ____ 15.Pure liquid carboxylic acids are strongly hydrogen bonded. ____ 16.Butyric ac ...
NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION & ELIMINATION ON Csp 3
... Energy profile for an SN2 reaction contains one barrier only – that of the transition state, TS: ...
... Energy profile for an SN2 reaction contains one barrier only – that of the transition state, TS: ...
Organic Chemistry Introduction
... by a nucleophile Therefore, nucleophilic substitution appears to invert the configuration at a chiral center The presence of carboxyl groups in malic acid led to some dispute as to the nature of the reactions in Walden’s cycle ...
... by a nucleophile Therefore, nucleophilic substitution appears to invert the configuration at a chiral center The presence of carboxyl groups in malic acid led to some dispute as to the nature of the reactions in Walden’s cycle ...
Microsoft Word
... Debenzylation and CBZ deprotection in 47 was achieved with 10% Pd/C in methanol at room temperature under atmospheric hydrogen pressure. After 8 h stirring, the target molecule 35 was obtained in 86% yield (Scheme 12). CHAPTER–III Development of new synthetic methodologies is an important subject in ...
... Debenzylation and CBZ deprotection in 47 was achieved with 10% Pd/C in methanol at room temperature under atmospheric hydrogen pressure. After 8 h stirring, the target molecule 35 was obtained in 86% yield (Scheme 12). CHAPTER–III Development of new synthetic methodologies is an important subject in ...
Document
... The feature of a halogenoalkane molecule that allows it to undergo substitution reaction is the presence of a polar bond between the halogen atom and the carbon atom to which it is bonded. The halogen atom is slightly negatively charged and the carbon atom is slightly positively charged. This carbon ...
... The feature of a halogenoalkane molecule that allows it to undergo substitution reaction is the presence of a polar bond between the halogen atom and the carbon atom to which it is bonded. The halogen atom is slightly negatively charged and the carbon atom is slightly positively charged. This carbon ...
2.10 Reactions of alcohols
... iii. substitution reactions to form halogenoalkanes, including reaction with PCl5 and its use as a qualitative test for the presence of the –OH group iv. oxidation using potassium dichromate (VI) in dilute sulfuric acid on primary alcohols to produce aldehydes and carboxylic acids and on secondary a ...
... iii. substitution reactions to form halogenoalkanes, including reaction with PCl5 and its use as a qualitative test for the presence of the –OH group iv. oxidation using potassium dichromate (VI) in dilute sulfuric acid on primary alcohols to produce aldehydes and carboxylic acids and on secondary a ...
Reactions of Alcohols - John Carroll University
... • Ethers can be synthesized by the reaction of alkoxide ions with primary alkyl halides in what is known as the Williamson ether synthesis. • This is an SN2 displacement reaction and as such, works better with primary alkyl halides to facilitate back-side attack. • If a secondary or tertiary alkyl h ...
... • Ethers can be synthesized by the reaction of alkoxide ions with primary alkyl halides in what is known as the Williamson ether synthesis. • This is an SN2 displacement reaction and as such, works better with primary alkyl halides to facilitate back-side attack. • If a secondary or tertiary alkyl h ...
ALDEHYDES & KETONES - Rogue Community College
... NOT as part of ... Aliphatic rings or Aromatic rings ...
... NOT as part of ... Aliphatic rings or Aromatic rings ...
1072. A General Synthesis of Ethers.
... of the reaction mixtures was carried out with a,n Aerograph dual-column temperature-programming gas chromatograph, model A-350-B, from Wilkens Instrument & Research, Inc., Berkely, Calif. The columns (3 m.) were filled with Chromosorb W coated with 15% of Silicone oil 550 or Apiezon L. Analysis was ...
... of the reaction mixtures was carried out with a,n Aerograph dual-column temperature-programming gas chromatograph, model A-350-B, from Wilkens Instrument & Research, Inc., Berkely, Calif. The columns (3 m.) were filled with Chromosorb W coated with 15% of Silicone oil 550 or Apiezon L. Analysis was ...
13_lecture_ppt
... • Both aldehydes and ketones are readily reduced to alcohols – Reduction occurs with hydrogen as the reducing agent ...
... • Both aldehydes and ketones are readily reduced to alcohols – Reduction occurs with hydrogen as the reducing agent ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... NAMING ALDEHYDES • ALDEHYDES ARE NAMED BY REPLACING THE FINAL “E” OF THE NAME OF THE ALKANE WITH THE SAME NUMBER OF CARBONS TO “AL”. • BECAUSE IN ALDEHYDES THE CARBONYL GROUP IS ALWAYS ATTACHED TO THE FIRST CARBON, THERE IS NO NEED TO PLACE A 1 IN FRONT OF THE NAME. • IF THERE ARE SUBSTITUENTS PRES ...
... NAMING ALDEHYDES • ALDEHYDES ARE NAMED BY REPLACING THE FINAL “E” OF THE NAME OF THE ALKANE WITH THE SAME NUMBER OF CARBONS TO “AL”. • BECAUSE IN ALDEHYDES THE CARBONYL GROUP IS ALWAYS ATTACHED TO THE FIRST CARBON, THERE IS NO NEED TO PLACE A 1 IN FRONT OF THE NAME. • IF THERE ARE SUBSTITUENTS PRES ...
Reaction of orthoesters with alcohols in the presence of acidic
... find out whether such a transformation could be useful as a synthetic methodology and the results are summarized in Table I. Thus the reaction of alcohols and orthoester with various acid catalysts give following products at ambient temperature; unsymmetrical ether 1, Oacetylated compound 3, dimeric ...
... find out whether such a transformation could be useful as a synthetic methodology and the results are summarized in Table I. Thus the reaction of alcohols and orthoester with various acid catalysts give following products at ambient temperature; unsymmetrical ether 1, Oacetylated compound 3, dimeric ...
Chapter 1
... • Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of: – A hydrogen atom – A double bond – The keto form has a C=O while the enol form has a C=C. ...
... • Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of: – A hydrogen atom – A double bond – The keto form has a C=O while the enol form has a C=C. ...
final1-final_report
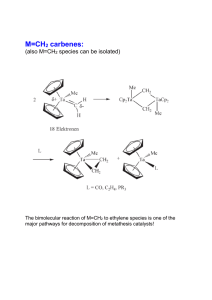
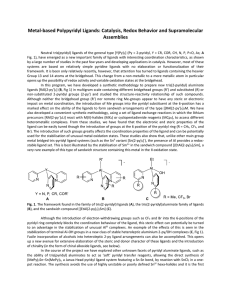
... Fig. 1), have emerged as a new important family of ligands with interesting coordination characteristics, as shown by a large number of studies in the past few years and developing applications in catalysis. However, most of these systems are based on relatively simple pyridine ligands with no elabo ...
... Fig. 1), have emerged as a new important family of ligands with interesting coordination characteristics, as shown by a large number of studies in the past few years and developing applications in catalysis. However, most of these systems are based on relatively simple pyridine ligands with no elabo ...
Chapter 1 - dan
... • Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of: – A hydrogen atom – A double bond – The keto form has a C=O while the enol form has a C=C. ...
... • Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of: – A hydrogen atom – A double bond – The keto form has a C=O while the enol form has a C=C. ...
Expt RO 1 Determination of Reaction Order (RO) Background Bonds
... watch to make sure everything is working correctly. If Q is too low or instrument not taking readings then you will need to start again. While the polarimeter is taking readings, prepare another acid/sucrose mixture using the same amounts as before. Heat this mixture in a flask in a water bath at 50 ...
... watch to make sure everything is working correctly. If Q is too low or instrument not taking readings then you will need to start again. While the polarimeter is taking readings, prepare another acid/sucrose mixture using the same amounts as before. Heat this mixture in a flask in a water bath at 50 ...
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
... Cyclobutadiene and cyclooctatetraene are NOT AROMATIC, because they have an even number of p electron pairs ...
... Cyclobutadiene and cyclooctatetraene are NOT AROMATIC, because they have an even number of p electron pairs ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.