Organic #2
... Name the structure you have drawn. Describe how you could simply in the lab distinguish between this compound and C4H10. Include any observations you would make. ...
... Name the structure you have drawn. Describe how you could simply in the lab distinguish between this compound and C4H10. Include any observations you would make. ...
Lecture 1: Key Concepts in Stereoselective Synthesis
... are, however, so reactive that their fast background reaction via uncatalyzed pathway would greatly diminish the enantioselectivity. Grignard reagent has been considered unsuitable for asymmetric alkylation. 2.2.1 Chiral ligands used in enantioselective Grignard additions There are a wide variety of ...
... are, however, so reactive that their fast background reaction via uncatalyzed pathway would greatly diminish the enantioselectivity. Grignard reagent has been considered unsuitable for asymmetric alkylation. 2.2.1 Chiral ligands used in enantioselective Grignard additions There are a wide variety of ...
Novel Brønsted-acidic ionic liquids based on benzothiazolium
... and Wang et al.16,17 investigated Brønsted acidic ILs in some esterification reactions and removed the ILs by simple filtration after the reaction. The employed ILs were not conventional ILs due to their high melting points (some above 100 °C) and their solubility in the reaction mixture could be va ...
... and Wang et al.16,17 investigated Brønsted acidic ILs in some esterification reactions and removed the ILs by simple filtration after the reaction. The employed ILs were not conventional ILs due to their high melting points (some above 100 °C) and their solubility in the reaction mixture could be va ...
Chapter 10_Organohalides
... later, but for now we will only discuss how they can be used to convert alkyl halides to alkanes • Not a very useful reaction but can eliminate halogens if necessary ...
... later, but for now we will only discuss how they can be used to convert alkyl halides to alkanes • Not a very useful reaction but can eliminate halogens if necessary ...
Sodium Borohydride Reduction of Vanillin
... When lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) was introduced as a reducing agent in the late 1940s, it brought about a revolution in the preparation of alcohols by reduction. At that time, the most popular reducing agents for carbonyl compounds were sodium metal and gaseous hydrogen under pressure. The gre ...
... When lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) was introduced as a reducing agent in the late 1940s, it brought about a revolution in the preparation of alcohols by reduction. At that time, the most popular reducing agents for carbonyl compounds were sodium metal and gaseous hydrogen under pressure. The gre ...
Results
... Conformation D is sufficiently destabilized so only A, B and C are expected to show decarbonylation reaction The following 3 families of mechanisms may be anticipated A: Unimolecular Internal SN2 type reactionmechanism (SNi) with alactone formation B: Unimolecular Internal Addition/elimination mecha ...
... Conformation D is sufficiently destabilized so only A, B and C are expected to show decarbonylation reaction The following 3 families of mechanisms may be anticipated A: Unimolecular Internal SN2 type reactionmechanism (SNi) with alactone formation B: Unimolecular Internal Addition/elimination mecha ...
Asymmetric catalytic routes to chiral building blocks of
... Enantiomerically pure P-hydroxy esters have served extensively as valuable chiral building blocks in synthetic organic and natural product chemistry.17 One of the most direct routes to enantiomerically-enriched P-hydroxy esters is through asymmetric hydrogenation of the corresponding P-keto esters, ...
... Enantiomerically pure P-hydroxy esters have served extensively as valuable chiral building blocks in synthetic organic and natural product chemistry.17 One of the most direct routes to enantiomerically-enriched P-hydroxy esters is through asymmetric hydrogenation of the corresponding P-keto esters, ...
Applications of trivalent and pentavalent tantalum in organic synthesis
... (S02C12. PClr) in conversion of 2" alcohol a, the respective chloride^.'^-'^ Thus TaClS proved :o he :i ...
... (S02C12. PClr) in conversion of 2" alcohol a, the respective chloride^.'^-'^ Thus TaClS proved :o he :i ...
Orbitals
... Two products can arise from the tetrahedral alkoxide ion intermediate • Protonation by water or acid gives an alcohol • The carbonyl oxygen atom can be protonated and then eliminated as HO- or H2O to give a product with a C=Nu double bond ...
... Two products can arise from the tetrahedral alkoxide ion intermediate • Protonation by water or acid gives an alcohol • The carbonyl oxygen atom can be protonated and then eliminated as HO- or H2O to give a product with a C=Nu double bond ...
File
... The nitro-group is an electron-withdrawing group. The presence of this group in the ortho position decreases the electron density in the O−H bond. As a result, it is easier to lose a proton. Also, the o-nitrophenoxide ion formed after the loss of protons is stabilized by resonance. Hence, ortho nitr ...
... The nitro-group is an electron-withdrawing group. The presence of this group in the ortho position decreases the electron density in the O−H bond. As a result, it is easier to lose a proton. Also, the o-nitrophenoxide ion formed after the loss of protons is stabilized by resonance. Hence, ortho nitr ...
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview
... • A non-bulky base favors the more substituted double bond while a bulky base favors in making the less substituted double bond ...
... • A non-bulky base favors the more substituted double bond while a bulky base favors in making the less substituted double bond ...
lecture 3 - aldehydes and ketones
... Because aldehydes and ketones lack a hydrogen on the oxygen, they cannot form hydrogen bonds between other aldehyde or ketone molecules. O ...
... Because aldehydes and ketones lack a hydrogen on the oxygen, they cannot form hydrogen bonds between other aldehyde or ketone molecules. O ...
oxidation and reduction
... same mechanism on the hydrates or hemiacetals; thus aldehydes form acids whereas ketones give esters. There are other mechanisms for further oxidation, for example by the enol, but it is clear that the absence of water would remove the above as a potential pathway for over-oxidation. To this end a n ...
... same mechanism on the hydrates or hemiacetals; thus aldehydes form acids whereas ketones give esters. There are other mechanisms for further oxidation, for example by the enol, but it is clear that the absence of water would remove the above as a potential pathway for over-oxidation. To this end a n ...
6.5. alcohols
... The optimum temperature for fermentation is around 38oC At lower temperatures the rate of reaction is too slow. At higher temperatures the yeast dies and the enzymes denature. Fermentation is done in an absence of air because the presence of air can cause extra reactions to occur. Air oxidises the e ...
... The optimum temperature for fermentation is around 38oC At lower temperatures the rate of reaction is too slow. At higher temperatures the yeast dies and the enzymes denature. Fermentation is done in an absence of air because the presence of air can cause extra reactions to occur. Air oxidises the e ...
Anhydrous copper (II) sulfate: an efficient catalyst for the liquid
... The olefin product was collected at atmospheric pressure or under reduced pressure for olefins with boiling points greater than -120 OC. The pressure was chosen so that the reaction temperature was at or near the boiling point of the starting alcohol, allowing smooth distillation of the olefin from ...
... The olefin product was collected at atmospheric pressure or under reduced pressure for olefins with boiling points greater than -120 OC. The pressure was chosen so that the reaction temperature was at or near the boiling point of the starting alcohol, allowing smooth distillation of the olefin from ...
1.4 The rate-determining step
... In pairs: remember the two mechanisms for the hydrolysis of haloalkanes. Discuss how can you make the reaction faster in each ...
... In pairs: remember the two mechanisms for the hydrolysis of haloalkanes. Discuss how can you make the reaction faster in each ...
INTRODUCING ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
... carbonyl group undergoes addition reactions, often followed by the loss of a water molecule. This gives a reaction known as addition-elimination or condensation Where aldehydes and ketones differ An aldehyde differs from a ketone by having a hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl group. This makes t ...
... carbonyl group undergoes addition reactions, often followed by the loss of a water molecule. This gives a reaction known as addition-elimination or condensation Where aldehydes and ketones differ An aldehyde differs from a ketone by having a hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl group. This makes t ...
A study of the mechanism of certain chemical reactions—I: The
... It has been shown, that the rate of reaction betw reen dibenzal-ethylenediamine formic acid is very slow at room temperature, and this could be an argument against the ionic mechanism for the reaction. The reaction of benzylidene-bismpiperidine and formic acid has been investigated under anhydrous c ...
... It has been shown, that the rate of reaction betw reen dibenzal-ethylenediamine formic acid is very slow at room temperature, and this could be an argument against the ionic mechanism for the reaction. The reaction of benzylidene-bismpiperidine and formic acid has been investigated under anhydrous c ...
1. Absorption of what type electromagnetic radiation results in
... 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one 4-methyl-4-penten-2-one 4-methyl-5-hexen-2-one 4-methyl-4-hexen-2-one 3-methyl-4-penten-2-one ...
... 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one 4-methyl-4-penten-2-one 4-methyl-5-hexen-2-one 4-methyl-4-hexen-2-one 3-methyl-4-penten-2-one ...
16.2: Structure and Bonding in Ethers and Epoxides
... Reaction of an alkoxide with an alkyl halide or tosylate to give an ether. Alkoxides are prepared by the reaction of an alcohol with a strong base such as sodium hydride (NaH) ...
... Reaction of an alkoxide with an alkyl halide or tosylate to give an ether. Alkoxides are prepared by the reaction of an alcohol with a strong base such as sodium hydride (NaH) ...
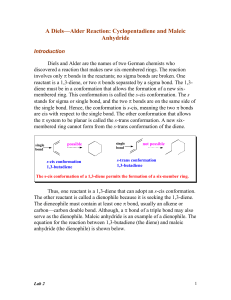
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
... Typical Dienophiles for Diels-Alder Reactions How does one recognize a Diels-Alder reaction? These reactions are easy to spot, because they involve two organic reactants and only heat as a reactant. One of the reactants (the diene) must have a conjugated diene system, and the other reactant (the die ...
... Typical Dienophiles for Diels-Alder Reactions How does one recognize a Diels-Alder reaction? These reactions are easy to spot, because they involve two organic reactants and only heat as a reactant. One of the reactants (the diene) must have a conjugated diene system, and the other reactant (the die ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.