2.10 Alcohols notes - A
... Like halogenoalkanes, alcohols can undergo elimination to give alkenes. Since alcohols lose water when they undergo elimination, the reaction is also called dehydration. The ethanol should be heated and passed over a catalyst (pumice can be used).It can also be refluxed at 180oC with concentrated su ...
... Like halogenoalkanes, alcohols can undergo elimination to give alkenes. Since alcohols lose water when they undergo elimination, the reaction is also called dehydration. The ethanol should be heated and passed over a catalyst (pumice can be used).It can also be refluxed at 180oC with concentrated su ...
Mill Hill County High School
... Like halogenoalkanes, alcohols can undergo elimination to give alkenes. Since alcohols lose water when they undergo elimination, the reaction is also called dehydration. The ethanol should be heated and passed over a catalyst (pumice can be used).It can also be refluxed at 180oC with concentrated su ...
... Like halogenoalkanes, alcohols can undergo elimination to give alkenes. Since alcohols lose water when they undergo elimination, the reaction is also called dehydration. The ethanol should be heated and passed over a catalyst (pumice can be used).It can also be refluxed at 180oC with concentrated su ...
CHM-373 American Women in Science and Society
... Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones • Hydration of Alkynes • Involves a keto-enol tautomerization • Mixture of ketones seen with internal alkynes ...
... Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones • Hydration of Alkynes • Involves a keto-enol tautomerization • Mixture of ketones seen with internal alkynes ...
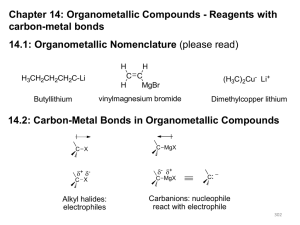
RULE
... Products from different (2° vs 3°) carbocations are constitutional isomers molecules with the same molecular formula, but differing in how atoms are connected Regioselective reaction - a reaction in which two or more constitutional isomers could be obtained as products, but one predominates. ...
... Products from different (2° vs 3°) carbocations are constitutional isomers molecules with the same molecular formula, but differing in how atoms are connected Regioselective reaction - a reaction in which two or more constitutional isomers could be obtained as products, but one predominates. ...
[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School
... pair of electrons. Since N is less electronegative than oxygen, therefore lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more easily available for bond formation. In other hand, nucleophillic attack occurs through N and hence silver nitrite predominantly gives nitro compounds. Q9. Explain, why the t ...
... pair of electrons. Since N is less electronegative than oxygen, therefore lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more easily available for bond formation. In other hand, nucleophillic attack occurs through N and hence silver nitrite predominantly gives nitro compounds. Q9. Explain, why the t ...
Microsoft Word - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... of organic chemists since it is a valuble precursor for the synthesis of nonpeptide neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists 43 and 44 as showed in figure III. These nonpeptidic ligands 43 and 44 are known to exhibit a variety of biological activities including neurogenic inflammation, pain transmission ...
... of organic chemists since it is a valuble precursor for the synthesis of nonpeptide neurokinin NK1 receptor antagonists 43 and 44 as showed in figure III. These nonpeptidic ligands 43 and 44 are known to exhibit a variety of biological activities including neurogenic inflammation, pain transmission ...
Barton Deoxygenation
... Hydrogenation: anti addition – Synthesis of trans-alkenes A dissolving metal reaction which uses lithium or sodium metal in low temperature ammonia or amine solvent produces trans-alkenes. This dissolving metal reduction process is different than other catalytic hydrogenation process. In this reacti ...
... Hydrogenation: anti addition – Synthesis of trans-alkenes A dissolving metal reaction which uses lithium or sodium metal in low temperature ammonia or amine solvent produces trans-alkenes. This dissolving metal reduction process is different than other catalytic hydrogenation process. In this reacti ...
$doc.title
... Prepared by José Laboy, MS http: www.chem.wisc.edu/areas /clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #5: Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Aldehydes ...
... Prepared by José Laboy, MS http: www.chem.wisc.edu/areas /clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #5: Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Aldehydes ...
Chapter 4. Functional Group Transformations: Oxidation and
... 4.3 Chemoselective agents for oxidizing alcohols MnO2 is a highly chemoselective oxidant-allylic, benzylic, and propargyl alcohols are oxidized faster than saturated alcohols. Solvent: H2O, acetone, or CHCl3. Low reactivity: use large amount of oxidant ...
... 4.3 Chemoselective agents for oxidizing alcohols MnO2 is a highly chemoselective oxidant-allylic, benzylic, and propargyl alcohols are oxidized faster than saturated alcohols. Solvent: H2O, acetone, or CHCl3. Low reactivity: use large amount of oxidant ...
View/Open
... a) When 3-iodo-2, 2-dimethyl butane is treated with silver nitrate in ethanol, three elimination products are formed. Give their structures, and predict which ones are formed in larger amounts (5 marks) b) Each of the carbocations in question (a) above can also react with ethanol to give substitutio ...
... a) When 3-iodo-2, 2-dimethyl butane is treated with silver nitrate in ethanol, three elimination products are formed. Give their structures, and predict which ones are formed in larger amounts (5 marks) b) Each of the carbocations in question (a) above can also react with ethanol to give substitutio ...
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
... hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced one functional group (the carbonyl) and left others alone (e.g. alkenes). If we want to reduce an alkene or alkyne, we need to u ...
... hydrogen to a carbonyl (using NaBH4 or LiAlH4 as the source of nucleophilic hydrogen). This was a chemoselective reaction – in other words, the reducing agent only reduced one functional group (the carbonyl) and left others alone (e.g. alkenes). If we want to reduce an alkene or alkyne, we need to u ...
Exam 3 Answer Key
... 3. (8) For a chiral compound (A), with 5 chiral centers, typically there will be 32 (a #) stereoisomers possible, unless one of these is a meso compound, where there are 2n -1 stereoisomers. A stereoisomer differing at only 4 chiral centers from compound (A) would be a(n) diastereoisomer of (A). If ...
... 3. (8) For a chiral compound (A), with 5 chiral centers, typically there will be 32 (a #) stereoisomers possible, unless one of these is a meso compound, where there are 2n -1 stereoisomers. A stereoisomer differing at only 4 chiral centers from compound (A) would be a(n) diastereoisomer of (A). If ...
Acylation of aromatic alcohols and phenols over InCl3
... from 7 to 96% on increasing the InCl3 loading from zero to 20%. The results clearly show that InCl3 (20%)/Mont. K-10 is a much superior catalyst than the Mont. K-10 without InCl3. It may be noted that use of InCl3 as a catalyst has also been reported earlier in a number of other other organic reacti ...
... from 7 to 96% on increasing the InCl3 loading from zero to 20%. The results clearly show that InCl3 (20%)/Mont. K-10 is a much superior catalyst than the Mont. K-10 without InCl3. It may be noted that use of InCl3 as a catalyst has also been reported earlier in a number of other other organic reacti ...
Limitations in Determining Enantiomeric Excess of Alcohols by 31P
... spectrum depicted in 2c for integrating purposes). The dialkylphosphonate derivative signals were further confirmed by proton coupled spectrum (Fig. 2a). The enantiomeric excess obtained by Feringa’s method was 97.0%, assuming that meso 1/meso 2 ratio follows the same value observed for the racemic ...
... spectrum depicted in 2c for integrating purposes). The dialkylphosphonate derivative signals were further confirmed by proton coupled spectrum (Fig. 2a). The enantiomeric excess obtained by Feringa’s method was 97.0%, assuming that meso 1/meso 2 ratio follows the same value observed for the racemic ...
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II
... t The hydration of alkenes and the dehydration of alcohols are simply reverse reactions of one other l The reaction is governed by the position of all the equilibria l Hydration is favored by addition of a low concentration of acid and a ...
... t The hydration of alkenes and the dehydration of alcohols are simply reverse reactions of one other l The reaction is governed by the position of all the equilibria l Hydration is favored by addition of a low concentration of acid and a ...
Silica Sulfuric Acid Promotes Aza-Michael Addition Reactions under
... procedures have been developed for the conjugate addition of amines to α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. In particular, various Lewis acid catalyzed reactions have been reported. This reaction has been investigated using catalysts such as lanthanum trichloride (LaCl3) [11], bromodimethylsulfonium ...
... procedures have been developed for the conjugate addition of amines to α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. In particular, various Lewis acid catalyzed reactions have been reported. This reaction has been investigated using catalysts such as lanthanum trichloride (LaCl3) [11], bromodimethylsulfonium ...
Formose reaction controlled by boronic acid - Beilstein
... Figure 3 compares 1H and 13C NMR spectra for the products obtained in the presence of SPB and pVPB/NaSS. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra for SPB exhibit broad signals, similar to those for a formose reaction without boronic acid compounds. Since it was difficult to remove SPB from the reaction mixture, t ...
... Figure 3 compares 1H and 13C NMR spectra for the products obtained in the presence of SPB and pVPB/NaSS. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra for SPB exhibit broad signals, similar to those for a formose reaction without boronic acid compounds. Since it was difficult to remove SPB from the reaction mixture, t ...
Epoxidation and oxidation reactions using 1,4
... substrate. The products were identified in comparison with the physical constants of authentic samples and from IR spectral values. The epoxidation reactions were found to be accelerated to a great extent by the presence of catalysts such as benzyl triethyl ammonium hydroxide (BTEAH), molybdenum tri ...
... substrate. The products were identified in comparison with the physical constants of authentic samples and from IR spectral values. The epoxidation reactions were found to be accelerated to a great extent by the presence of catalysts such as benzyl triethyl ammonium hydroxide (BTEAH), molybdenum tri ...
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... Secondary alcohols can easily be converted to alkenes by acid-catalyzed dehydration, an E1 reaction. In this experiment, a mixture of concentrated phosphoric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is used to prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol via an E1 reaction. The mechanism of this E1 reaction inv ...
... Secondary alcohols can easily be converted to alkenes by acid-catalyzed dehydration, an E1 reaction. In this experiment, a mixture of concentrated phosphoric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is used to prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol via an E1 reaction. The mechanism of this E1 reaction inv ...
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Alkenes are
... Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions ...
... Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions ...
CI 12.4 - Sackville School
... this page Add the reaction types to the arrows Click here to go to the Key words and definitions for help Click here to check ...
... this page Add the reaction types to the arrows Click here to go to the Key words and definitions for help Click here to check ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.



![[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015878975_1-55791b331e05591620375059b6f74bac-300x300.png)