Organolithium reagent
... completion if the acidic compound is 2 pKA units stronger than the lithium species, although in practice a larger pKA difference is required for useful rates of deprotonation of weakly acidic C-H acids. As alkyl groups are weakly electron donating, the basicity of the organolithium compound increase ...
... completion if the acidic compound is 2 pKA units stronger than the lithium species, although in practice a larger pKA difference is required for useful rates of deprotonation of weakly acidic C-H acids. As alkyl groups are weakly electron donating, the basicity of the organolithium compound increase ...
Oxidation - Sciencemadness
... •This reaction can also be done using CrO3 (chromic oxide) in sulfuric acid. •The aldehyde is distilled away from the reaction vessel as quickly as it is formed. If the aldehyde is not removed, it will suffer a second oxidation, and the product will be the carboxylic acid. ...
... •This reaction can also be done using CrO3 (chromic oxide) in sulfuric acid. •The aldehyde is distilled away from the reaction vessel as quickly as it is formed. If the aldehyde is not removed, it will suffer a second oxidation, and the product will be the carboxylic acid. ...
Alcohols - City University of New York
... Acid Catalyzed Dehydration of an Alcohol, discussed earlier as reverse of hydration Secondary and tertiary alcohols, carbocations Protonation, establishing of good leaving group. Elimination of water to yield carbocation in rate determining step. ...
... Acid Catalyzed Dehydration of an Alcohol, discussed earlier as reverse of hydration Secondary and tertiary alcohols, carbocations Protonation, establishing of good leaving group. Elimination of water to yield carbocation in rate determining step. ...
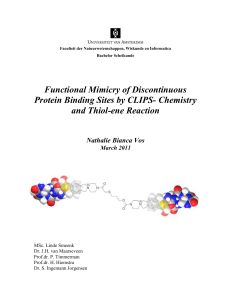
In the bachelor thesis of Esther Schippers, research is
... therefore also be soluble in aqueous solvents. To achieve this, for instance an ionic charge can be brought in the molecule. Ions are often good soluble in aqueous solutions. 3. The scaffold should have a part of the molecule that can easily be synthesized with another functional group. When differe ...
... therefore also be soluble in aqueous solvents. To achieve this, for instance an ionic charge can be brought in the molecule. Ions are often good soluble in aqueous solutions. 3. The scaffold should have a part of the molecule that can easily be synthesized with another functional group. When differe ...
Year 1 Foundation course, section B2
... The balance between substitution and elimination is often a close one and depend upon many factors, including the structure of the substrate and the other reagents, the solvent, temperature etc. You should also be aware that substitution reactions are not observed at sp 2 C atoms (i.e. on alkenes an ...
... The balance between substitution and elimination is often a close one and depend upon many factors, including the structure of the substrate and the other reagents, the solvent, temperature etc. You should also be aware that substitution reactions are not observed at sp 2 C atoms (i.e. on alkenes an ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 14 – Ethers
... which has a double bond to oxygen. o Thioethers are also called sulfides. o Thioethers tend to have unpleasant odors, similar to thiols. This odor has been described as the smell of oysters stored in the fridge for too long. o We used a thioether in the reaction of ozones with alkenes – dimethyl sul ...
... which has a double bond to oxygen. o Thioethers are also called sulfides. o Thioethers tend to have unpleasant odors, similar to thiols. This odor has been described as the smell of oysters stored in the fridge for too long. o We used a thioether in the reaction of ozones with alkenes – dimethyl sul ...
Ruthenium(II) Complexes Bearing a Pyridyl-Supported Pyrazolyl
... transfer hydrogenation of cyclohexanone and acetophenone in refluxing 2-propanol revealed only poor to moderate catalytic activity for them.4a,b,5b Mixed-donor ligands have been widely used due to the versatility arising from the different stereoelectronic properties of the multiple coordination sit ...
... transfer hydrogenation of cyclohexanone and acetophenone in refluxing 2-propanol revealed only poor to moderate catalytic activity for them.4a,b,5b Mixed-donor ligands have been widely used due to the versatility arising from the different stereoelectronic properties of the multiple coordination sit ...
lecture 2 - alcohols-ethers
... organic chemistry. "SN" stands for nucleophilic substitution and the "1" represents the fact that the rate-determining step is unimolecular. ...
... organic chemistry. "SN" stands for nucleophilic substitution and the "1" represents the fact that the rate-determining step is unimolecular. ...
Expt #7: Synthesis of Esters using Acetic
... The balanced equation for acetate ester synthesis [equation 2] shows that the reaction requires the same number of moles of acetic anhydride as of the alcohol used. Thus, complete conversion of the starting materials to product requires equimolar amounts of anhydride and alcohol. What would happen i ...
... The balanced equation for acetate ester synthesis [equation 2] shows that the reaction requires the same number of moles of acetic anhydride as of the alcohol used. Thus, complete conversion of the starting materials to product requires equimolar amounts of anhydride and alcohol. What would happen i ...
Oxidation Reactions
... Directed epoxidation reactions, as their name implies are reactions in which the reagent containing the oxygen that is to be transferred to the substrate is tethered to the reacting substrate through a non-covalent interaction (e.g. H-bond or metal-ligand interaction). Typical substrates are allylic ...
... Directed epoxidation reactions, as their name implies are reactions in which the reagent containing the oxygen that is to be transferred to the substrate is tethered to the reacting substrate through a non-covalent interaction (e.g. H-bond or metal-ligand interaction). Typical substrates are allylic ...
SULFONATION OF BY SO3
... 1.1 Disadvantage in conventional sulfonation A serious disadvantage inherent in conventional sulfation and sulfonation techniques using gaseous diluents is that substantial portions, e.g. as high as three to five percent, of the liquid products which are formed become entrained in the diluent gas st ...
... 1.1 Disadvantage in conventional sulfonation A serious disadvantage inherent in conventional sulfation and sulfonation techniques using gaseous diluents is that substantial portions, e.g. as high as three to five percent, of the liquid products which are formed become entrained in the diluent gas st ...
Alkene - Synthesis
... NaI/acetone or Zn/acetic acid Acetone can dissolve both the iodide and the alkyl halide (if small). If Zn is used, reaction is heterogeneous and takes place on the surface of the Zn. Reduction because “Br2” is removed. ...
... NaI/acetone or Zn/acetic acid Acetone can dissolve both the iodide and the alkyl halide (if small). If Zn is used, reaction is heterogeneous and takes place on the surface of the Zn. Reduction because “Br2” is removed. ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... • Aldehydes and Ketones have ↓ b.p. than alcohols of similar molecular weight. – Due to the inability of aldehydes and ketones to ...
... • Aldehydes and Ketones have ↓ b.p. than alcohols of similar molecular weight. – Due to the inability of aldehydes and ketones to ...
Document
... Addition, Substitution, and Elimination Reactions Addition reactions, substitution reactions, and elimination reactions are the three main types of organic reactions. Most organic reactions can be classified as one of these three types. Addition Reactions In an addition reaction, atoms are added to ...
... Addition, Substitution, and Elimination Reactions Addition reactions, substitution reactions, and elimination reactions are the three main types of organic reactions. Most organic reactions can be classified as one of these three types. Addition Reactions In an addition reaction, atoms are added to ...
Aldehydes can react with alcohols to form hemiacetals
... Cyclic acetals like this are more resistant to hydrolysis than acyclic ones and easier to make—they form quite readily even from ketones. Again, we have entropic factors to thank for their stability. For the formation of a cyclic acetal, two molecules go in (ketone plus diol) and two molecules come ...
... Cyclic acetals like this are more resistant to hydrolysis than acyclic ones and easier to make—they form quite readily even from ketones. Again, we have entropic factors to thank for their stability. For the formation of a cyclic acetal, two molecules go in (ketone plus diol) and two molecules come ...
$doc.title
... • Proton is lost from N and adds to O to yield an amino alcohol (carbinolamine) • Protona3on of OH converts it into water as the leaving group • Result is iminium ion, which loses proton • ...
... • Proton is lost from N and adds to O to yield an amino alcohol (carbinolamine) • Protona3on of OH converts it into water as the leaving group • Result is iminium ion, which loses proton • ...
thiols and sulfides.
... Ethers are prepared by SN2 reactions. Ethers can be prepared by the reaction of an alkoxide with a primary haloalkane or sulfonate ester under SN2 conditions. The parent alcohol of the alkoxide can be used as the solvent, however other polar solvents are often better, such as DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxid ...
... Ethers are prepared by SN2 reactions. Ethers can be prepared by the reaction of an alkoxide with a primary haloalkane or sulfonate ester under SN2 conditions. The parent alcohol of the alkoxide can be used as the solvent, however other polar solvents are often better, such as DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxid ...
Organic Chemistry Introduction
... • At high temperatures, sufficient E for both reactions to occur •A B (fast) and A C (slower) • or B A C • We see more stable product dominate. Fall, 2009 ...
... • At high temperatures, sufficient E for both reactions to occur •A B (fast) and A C (slower) • or B A C • We see more stable product dominate. Fall, 2009 ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 13 – Alcohols (II)
... OH is not a good leaving group, so nucleophiles cannot attack them. o Reduction: Although in theory the alcohol could lose a bond to oxygen, there are no reagents available to accomplish this reaction (the only way to do this is using more than one step). ...
... OH is not a good leaving group, so nucleophiles cannot attack them. o Reduction: Although in theory the alcohol could lose a bond to oxygen, there are no reagents available to accomplish this reaction (the only way to do this is using more than one step). ...
print
... Oxidizing Agents with Metal Oxygen Bonds • The most common oxidizing agents with metal-oxygen bonds contain either chromium +6 or manganese +7. • Common Cr6+ reagents include CrO3 and sodium or potassium dichromate (Na2Cr2O7 and K2Cr2O7). • Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a more selective Cr6+ ...
... Oxidizing Agents with Metal Oxygen Bonds • The most common oxidizing agents with metal-oxygen bonds contain either chromium +6 or manganese +7. • Common Cr6+ reagents include CrO3 and sodium or potassium dichromate (Na2Cr2O7 and K2Cr2O7). • Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a more selective Cr6+ ...
Baylis–Hillman reaction

The Baylis–Hillman reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction between the α-position of an activated alkene and an aldehyde, or generally a carbon electrophile. Employing a nucleophilic catalyst, such as tertiary amine and phosphine, this reaction provides a densely functionalized product (e.g. functionalized allyl alcohol in the case of aldehyde as the electrophile). This reaction is also known as the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction or MBH reaction. It is named for the Japanese chemist Ken-ichi Morita, the British chemist Anthony B. Baylis and the German chemist Melville E. D. Hillman.DABCO is one of the most frequently used tertiary amine catalysts for this reaction. In addition, nucleophilic amines such as DMAP and DBU as well as phosphines have been found to successfully catalyze this reaction.MBH reaction has several advantages as a useful synthetic method: 1) It is an atom-economic coupling of easily prepared starting materials. 2) Reaction of a pro-chiral electrophile generates a chiral center, therefore an asymmetric synthesis is possible. 3) Reaction products usually contain multiple functionalities in a proximity so that a variety of further transformations are possible. 4) It can employ a nucleophilic organo-catalytic system without the use of heavy metal under mild conditions.Several reviews have been written.