out of this world crossword
... 9. In 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ to set foot on the moon. ...
... 9. In 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ to set foot on the moon. ...
Brobo_solarsystem_faceoff
... Discovered the mysterious “Planet X” who’s exsistance had been proven but not observed F. His insite to the motion of the stars was rejected by the Catholic church for several decades. Basic Understanding of the Planets, Dwarf Planets, and Other Bodies 57. Why is Venus’ temperature paterns the way t ...
... Discovered the mysterious “Planet X” who’s exsistance had been proven but not observed F. His insite to the motion of the stars was rejected by the Catholic church for several decades. Basic Understanding of the Planets, Dwarf Planets, and Other Bodies 57. Why is Venus’ temperature paterns the way t ...
Solar System Notes
... Our sun provides light and heat for earth Our sun is a star When the sun rises and sets it looks like it is moving but it is not actually moving E.Q. Why is the sun the most important object in our solar system? Seasons: Are caused by the Earth revolving around the sun and the tilt of the earth on i ...
... Our sun provides light and heat for earth Our sun is a star When the sun rises and sets it looks like it is moving but it is not actually moving E.Q. Why is the sun the most important object in our solar system? Seasons: Are caused by the Earth revolving around the sun and the tilt of the earth on i ...
UNIT 4 STUDY GUIDE Objectives
... The force of gravity depends on what two factors? What two factors keep moons and planets in orbit? What causes the phases of the moon? What are the eight phases of the moon? Sketch each one. What is an eclipse? What are the two types of eclipses? What causes each one? What is the difference between ...
... The force of gravity depends on what two factors? What two factors keep moons and planets in orbit? What causes the phases of the moon? What are the eight phases of the moon? Sketch each one. What is an eclipse? What are the two types of eclipses? What causes each one? What is the difference between ...
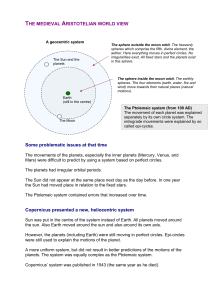
THE MEDIEVAL ARISTOTELIAN WORLD VIEW Some
... spheres. The four elements (earth, water, fire and wind) move towards their natural places (natural motions). Earth (still in the centre) ...
... spheres. The four elements (earth, water, fire and wind) move towards their natural places (natural motions). Earth (still in the centre) ...
NOTES April 21, 2008 Earth Science – 6th Grade Mrs. Elliott
... Union (IAU), is a celestial body orbiting the Sun that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity but which has not cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals and is not a satellite.[1][2] More explicitly, it has to have sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body force ...
... Union (IAU), is a celestial body orbiting the Sun that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity but which has not cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals and is not a satellite.[1][2] More explicitly, it has to have sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body force ...
The Solar System
... • Gas Giants: (Jupiter & Saturn) – Thick H/He atmosphere, liquid hydrogen mantle, ice core ...
... • Gas Giants: (Jupiter & Saturn) – Thick H/He atmosphere, liquid hydrogen mantle, ice core ...
Jim_lecture_Chapter
... • 1.2 b.y.: The rapid rise in surface temperature causes the stratosphere to become wet Earth’s oceans should be lost over the next few hundred million years, and all life will go extinct Is there any way to counteract these effects? Yes, one could do this by building a solar shield! ...
... • 1.2 b.y.: The rapid rise in surface temperature causes the stratosphere to become wet Earth’s oceans should be lost over the next few hundred million years, and all life will go extinct Is there any way to counteract these effects? Yes, one could do this by building a solar shield! ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 9
... 35. Use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to explain the differences between white dwarfs, mainsequence stars and giant stars. 36. Agree or disagree: Scientists cannot directly observe the entire life cycle of a star. 37. What is a nova? 38. During the main-sequence stage, how do stars make energy? 39 ...
... 35. Use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to explain the differences between white dwarfs, mainsequence stars and giant stars. 36. Agree or disagree: Scientists cannot directly observe the entire life cycle of a star. 37. What is a nova? 38. During the main-sequence stage, how do stars make energy? 39 ...
Space 8.1 notes
... A star is a large celestial body made up of hot gases. It releases large amounts of energy and is held together by its own gravity, keeping it intact Stars are considered luminous because they produce and give off their own light. SUN The sun is an average sized star, as most stars are signifi ...
... A star is a large celestial body made up of hot gases. It releases large amounts of energy and is held together by its own gravity, keeping it intact Stars are considered luminous because they produce and give off their own light. SUN The sun is an average sized star, as most stars are signifi ...
Astronomy Study Guide axis - A real or imaginary line through the
... meteoroids, n. Small pieces of metal or rock that travel through the solar system and that are much smaller than an asteroid ...
... meteoroids, n. Small pieces of metal or rock that travel through the solar system and that are much smaller than an asteroid ...
Objective 10 Study Guide
... sun to keep its water from freezing and cool enough to keep its water from boiling away. 43. What evidence suggests that there was once liquid water on Mars? a. the Martian icecaps c. features like ...
... sun to keep its water from freezing and cool enough to keep its water from boiling away. 43. What evidence suggests that there was once liquid water on Mars? a. the Martian icecaps c. features like ...
8th Grade Midterm Test Review
... cool) temperature while blue and white stars have a relatively (hot or cool) temperature. • Red & Yellow Stars= Cool • Blue & White Stars= Hot ...
... cool) temperature while blue and white stars have a relatively (hot or cool) temperature. • Red & Yellow Stars= Cool • Blue & White Stars= Hot ...
Review Handout - Sturgeon Moodle
... 5. Match each of the planets with the description that best fits. Put the letters beside the right planet. a) cold, small, rocky, used to be a planet. ...
... 5. Match each of the planets with the description that best fits. Put the letters beside the right planet. a) cold, small, rocky, used to be a planet. ...
Astronomy Test Review
... a long, narrow ellipse. Meteor – streak of light in the sky produced by the burning of a meteoroid in the Earth’s atmosphere. Asteroid – objects revolving around the sun that are too small and too numerous to be considered planets. ...
... a long, narrow ellipse. Meteor – streak of light in the sky produced by the burning of a meteoroid in the Earth’s atmosphere. Asteroid – objects revolving around the sun that are too small and too numerous to be considered planets. ...
Astronomy Powerpoint
... Mercury closest planet to the sun, it takes 59 days to make one rotation but only 88 days to orbit the Sun. That means that there are fewer than 2 days in a year! Venus is the brightest planet in our sky. It is called Earth’s sister planet because it is a similar size. Venus is hotter than Mercury ...
... Mercury closest planet to the sun, it takes 59 days to make one rotation but only 88 days to orbit the Sun. That means that there are fewer than 2 days in a year! Venus is the brightest planet in our sky. It is called Earth’s sister planet because it is a similar size. Venus is hotter than Mercury ...
File
... Large natural objects which revolve around a planet many planets have more than one moon Earth’s moon has no atmosphere and has hills/valleys/craters after the invention of the telescope Galileo saw 4 moons of Jupiter Moons can come in a variety of size and with a variety of surfaces ...
... Large natural objects which revolve around a planet many planets have more than one moon Earth’s moon has no atmosphere and has hills/valleys/craters after the invention of the telescope Galileo saw 4 moons of Jupiter Moons can come in a variety of size and with a variety of surfaces ...
Chapter 7 Solar System study guide
... Sun – made of hydrogen and helium Sun is a star – it is the largest object in the S.S. 1,000,000 Earths Photosphere Chromosphere Corona (inside outside) Sunspots are cooler spots on the sun – they tend to look black. Sunspots come and go in cycles of about 11 years. Solar flares – explosion/ribb ...
... Sun – made of hydrogen and helium Sun is a star – it is the largest object in the S.S. 1,000,000 Earths Photosphere Chromosphere Corona (inside outside) Sunspots are cooler spots on the sun – they tend to look black. Sunspots come and go in cycles of about 11 years. Solar flares – explosion/ribb ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.