Maybe We Are Alone in the Universe, After All
... increasingly seen as critical for making Earth so favorable to complex life. Among them are these: *An orbit that keeps a planet at exactly the right distance from its star to ensure that water remains liquid, not vapor or ice. *A large moon at just the right distance to minimize changes in a planet ...
... increasingly seen as critical for making Earth so favorable to complex life. Among them are these: *An orbit that keeps a planet at exactly the right distance from its star to ensure that water remains liquid, not vapor or ice. *A large moon at just the right distance to minimize changes in a planet ...
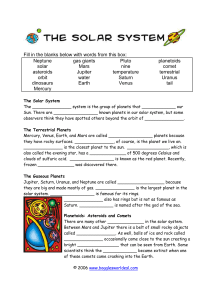
Fill in the blanks below with words from this box: Neptune solar
... Fill in the blanks below with words from this box: Neptune gas giants Pluto solar Mars nine asteroids Jupiter temperature water Saturn orbit dinosaurs Earth Venus Mercury ...
... Fill in the blanks below with words from this box: Neptune gas giants Pluto solar Mars nine asteroids Jupiter temperature water Saturn orbit dinosaurs Earth Venus Mercury ...
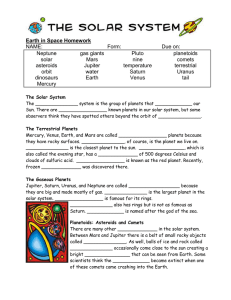
Solar System Cloze
... Form: Neptune gas giants Pluto solar Mars nine asteroids Jupiter temperature orbit water Saturn dinosaurs Earth Venus Mercury ...
... Form: Neptune gas giants Pluto solar Mars nine asteroids Jupiter temperature orbit water Saturn dinosaurs Earth Venus Mercury ...
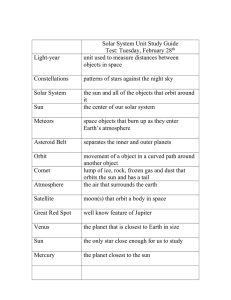
Solar System Unit Study Guide
... massive star that has collapsed and pulls everything in, even light the largest planet the smallest planet, now known as a dwarf planet Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto ...
... massive star that has collapsed and pulls everything in, even light the largest planet the smallest planet, now known as a dwarf planet Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto ...
Document
... Newly found planets orbiting Red Dwarf stars, in their Habitable Zones, will receive low quantum energy photon radiation which cannot drive earth-like photosynthesis! (So, no life?!). However, there may be non Earth-like photosynthesis, operating with low energy photons at wavelengths > 800nm (< 720 ...
... Newly found planets orbiting Red Dwarf stars, in their Habitable Zones, will receive low quantum energy photon radiation which cannot drive earth-like photosynthesis! (So, no life?!). However, there may be non Earth-like photosynthesis, operating with low energy photons at wavelengths > 800nm (< 720 ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.