* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Galilean moons wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
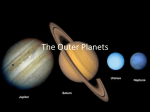
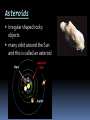
Lesson 4a CELESTIAL OBJECTS IN SPACE Comets chunks of frozen gases, rock & dust that orbit the sun tail is formed when the comet comes close to the Sun Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 hit Jupiter in 1994. Asteroids Irregular shaped rocky objects many orbit around the Sun and this is called an asteroid belt Meteors & Meteorites A meteoroid is a clump of rock or metal which is pulled towards Earth by gravity In Earth’s atmosphere it heats up, begins to glow and becomes a meteor If the object is not vaporized before it contacts the Earth’s surface it is called a meteorite meteoroid meteor meteor shower What’s the difference? Asteroid: -Small; inactive - made of rock, carbon or metal - Orbits the sun Comet: - small; sometimes active object - made of dirt, gas and ice Meteoroid: - small particle from an asteroid or comet - orbits the sun - A meteoroid that burns up in the Earth's atmosphere - a shooting star. - A meteoroid that survives its passage through the Earth's atmosphere and impacts the Earth's surface. Meteor: Meteorite: Moons/Satellites Large natural objects which revolve around a planet many planets have more than one moon Earth’s moon has no atmosphere and has hills/valleys/craters after the invention of the telescope Galileo saw 4 moons of Jupiter Moons can come in a variety of size and with a variety of surfaces Stars A STAR is a luminous ball of plasma that is held together by gravity. What is the nearest star to Earth? What is the nearest star to the Sun? Binary Solar System Stars Polaris pole star for the Northern Hemisphere 390 light years from Earth part of a binary star system Sirius the brightest star in the sky (70 times more luminous than the sun) 8.6 light years from the Earth Betelgeuse one of the brightest stars in the sky supergiant 1,000 times bigger than the Sun but cooler than the Sun Outside our Solar System Voyager I, Pioneer 10 & 11 and Voyager 2 built to explore outside our solar system Took 20 years to leave solar system will reach the nearest star in 50 000 years video Bill Nye- Comets and Meteors















![Global Warming_Notes_for_Test_Review[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009490554_1-1d4a9735243ab8423aa4808909f160ae-150x150.png)