Organize Your Space PowerPoint.
... mass of the earth and if all the asteroids were combined together their diameter would be only half the diameter of our moon. ...
... mass of the earth and if all the asteroids were combined together their diameter would be only half the diameter of our moon. ...
04 Aug 2007
... monitor 60,000 stars and discover hundreds of planets including tens of Earth-like planets. NASA's Kepler mission in 2008 will monitor 100,000 sun-like stars and probably find dozens of Earth-like planets in the habitable zone. Europe's Darwin mission in 2014 will comprise several space vehicles "fl ...
... monitor 60,000 stars and discover hundreds of planets including tens of Earth-like planets. NASA's Kepler mission in 2008 will monitor 100,000 sun-like stars and probably find dozens of Earth-like planets in the habitable zone. Europe's Darwin mission in 2014 will comprise several space vehicles "fl ...
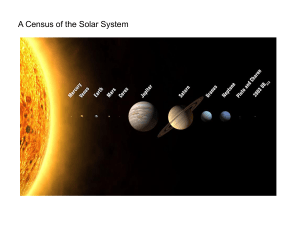
A Census of the Solar System
... Uses the transit method and survey thousands of stars repeatedly at least 3 – 4 times to determine period and orbit of transiting planet. ...
... Uses the transit method and survey thousands of stars repeatedly at least 3 – 4 times to determine period and orbit of transiting planet. ...
Topic 9/10
... Asteroid- rocky objects up to 600 miles across, there is a belt b/t Mars and Jupiter Meteor- falling star Comet- icy objects caught in highly elliptical orbits Star- large self-luminous body in space that creates its own energy Nuclear fusion- where the sun gets its energy, 2 hydrogens fuse (combine ...
... Asteroid- rocky objects up to 600 miles across, there is a belt b/t Mars and Jupiter Meteor- falling star Comet- icy objects caught in highly elliptical orbits Star- large self-luminous body in space that creates its own energy Nuclear fusion- where the sun gets its energy, 2 hydrogens fuse (combine ...
Astronomy Unit Notes - sciencepowerpoint.com
... Craters can be found on earth, but most craters are eroded away by wind and water. Most meteorites also burn up in our atmosphere. Phases of the Moon ...
... Craters can be found on earth, but most craters are eroded away by wind and water. Most meteorites also burn up in our atmosphere. Phases of the Moon ...
The Solar System
... everything going around it. We now know that this is not correct. The idea that fits scientific observations and allows us to predict the movement of the planets is called the heliocentric model. This just means that the Sun is at the centre of the solar system, and the Earth and other planets go ar ...
... everything going around it. We now know that this is not correct. The idea that fits scientific observations and allows us to predict the movement of the planets is called the heliocentric model. This just means that the Sun is at the centre of the solar system, and the Earth and other planets go ar ...
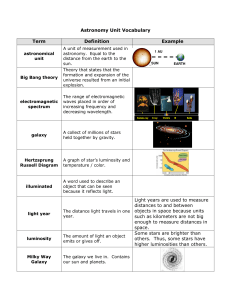
Astronomy Unit Vocabulary Term Definition Example Light years are
... A unit of measurement used in astronomy. Equal to the distance from the earth to the sun. Theory that states that the formation and expansion of the universe resulted from an initial ...
... A unit of measurement used in astronomy. Equal to the distance from the earth to the sun. Theory that states that the formation and expansion of the universe resulted from an initial ...
hw1
... describe and predict some observable phenomenon. Extensive tests are carried out to measure the validity of any hypothesis. When the evidence in favor of the hypothesis is overwhelming, it becomes a scientific theory. p. 8 RQ #3 What is the difference between our solar system, our galaxy and the uni ...
... describe and predict some observable phenomenon. Extensive tests are carried out to measure the validity of any hypothesis. When the evidence in favor of the hypothesis is overwhelming, it becomes a scientific theory. p. 8 RQ #3 What is the difference between our solar system, our galaxy and the uni ...
SNC1PL Celestial Objects and Constellations
... Tails: The dust tail reflects the Sun’s light and may be influenced by the movement of the comet. The Ion tail is created by solar wind reacting with material on the comet to produce a tail that is directed away from the comet ...
... Tails: The dust tail reflects the Sun’s light and may be influenced by the movement of the comet. The Ion tail is created by solar wind reacting with material on the comet to produce a tail that is directed away from the comet ...
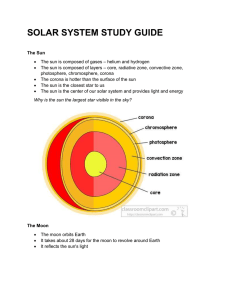
solar system study guide
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
Solar System
... Earth • Earth has one moon. • Earth is the only planet with liquid water. • Earth is the only planet with living organisms. ...
... Earth • Earth has one moon. • Earth is the only planet with liquid water. • Earth is the only planet with living organisms. ...
File
... sunlight and eternal darkness. Another problem with the habitable zones around these long-lived stars is that they are extremely narrow; a planet in a random orbit is unlikely to find itself at a distance that is “just right.” Conversely, large, hot, luminous stars have enormous habitable zones in w ...
... sunlight and eternal darkness. Another problem with the habitable zones around these long-lived stars is that they are extremely narrow; a planet in a random orbit is unlikely to find itself at a distance that is “just right.” Conversely, large, hot, luminous stars have enormous habitable zones in w ...
Earth Science 2nd 9 wk review
... leucite (KAISi206) may be grouped together because they all contain silicon. ...
... leucite (KAISi206) may be grouped together because they all contain silicon. ...
34_alone
... • How close have we ever come to the total extinction of all life on earth? • A very large impact could kill all life. – It would have to be so large that the heat boiled away all the oceans and filled the atmosphere with molten rock! – Perhaps this happened very early on and life had to start more ...
... • How close have we ever come to the total extinction of all life on earth? • A very large impact could kill all life. – It would have to be so large that the heat boiled away all the oceans and filled the atmosphere with molten rock! – Perhaps this happened very early on and life had to start more ...
And let there be light!
... The Universe – Everything there is; all energy, space, and matter Astronomy – The study of the universe beyond the earth’s atmosphere. Solar System – the Sun and all the objects that travel around it due to gravitational force. Objects = planets, over 60 satellites (moons) orbiting the planets, thou ...
... The Universe – Everything there is; all energy, space, and matter Astronomy – The study of the universe beyond the earth’s atmosphere. Solar System – the Sun and all the objects that travel around it due to gravitational force. Objects = planets, over 60 satellites (moons) orbiting the planets, thou ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.