Ass3_ans - The University of Sydney
... The following information relates to questions 9 -18 (1 mark each). The oxidation of glucose is often summarised as the balanced equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 32 ADP + 32 P 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 32 ATP Of course, this misses out all the juicy steps of glucose transport, glycolysis, PDH, Krebs cycle, electro ...
... The following information relates to questions 9 -18 (1 mark each). The oxidation of glucose is often summarised as the balanced equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 32 ADP + 32 P 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 32 ATP Of course, this misses out all the juicy steps of glucose transport, glycolysis, PDH, Krebs cycle, electro ...
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... Denaturation of Proteins The tertiary structure of a globular protein is the result of many ...
... Denaturation of Proteins The tertiary structure of a globular protein is the result of many ...
Ass3 - The University of Sydney
... The following information relates to questions 9 -18 (1 mark each). The oxidation of glucose is often summarised as the balanced equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 32 ADP + 32 P 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 32 ATP Of course, this misses out all the juicy steps of glucose transport, glycolysis, PDH, Krebs cycle, electro ...
... The following information relates to questions 9 -18 (1 mark each). The oxidation of glucose is often summarised as the balanced equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 32 ADP + 32 P 6CO2 + 6 H2O + 32 ATP Of course, this misses out all the juicy steps of glucose transport, glycolysis, PDH, Krebs cycle, electro ...
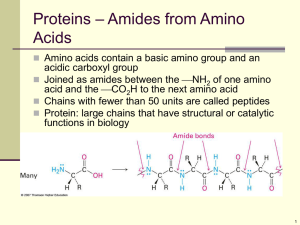
amino acids
... • Lipids are rich in carbon and hydrogen, but contain little oxygen • Lipids are not soluble in water • Fatty acids are the simplest lipids: long chain hydrocarbons, a carboxylate group at one end • Fatty acids are often components of glycerophospholipids ...
... • Lipids are rich in carbon and hydrogen, but contain little oxygen • Lipids are not soluble in water • Fatty acids are the simplest lipids: long chain hydrocarbons, a carboxylate group at one end • Fatty acids are often components of glycerophospholipids ...
Organic Molecules - University of Dayton
... Q: Are cow amino acids identical to human amino acids? ...
... Q: Are cow amino acids identical to human amino acids? ...
digestion - KingSNC2D
... solid as it is moved along due to peristalsis If peristalsis occurs too quickly, water cannot be reabsorbed into the body and remains in the feces causing diarrhea. If peristalsis occurs too slowly, too much water may be ...
... solid as it is moved along due to peristalsis If peristalsis occurs too quickly, water cannot be reabsorbed into the body and remains in the feces causing diarrhea. If peristalsis occurs too slowly, too much water may be ...
chem_1 ILO 2013-9-19 - Faculty Members Websites
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
chem_1 ILO 2013-9-19 - Faculty Members Websites
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
Aerobic Metabolism: The Citric Acid Cycle
... the energy charge of the cell is high. Such enzymes include the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex that synthesizes the acetyl-CoA needed for the first reaction of the TCA cycle. Also the enzymes citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, that regulate the firs ...
... the energy charge of the cell is high. Such enzymes include the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex that synthesizes the acetyl-CoA needed for the first reaction of the TCA cycle. Also the enzymes citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, that regulate the firs ...
Key Terms:
... pyruvate CO2 and reduced coenzymes 3. Electron Transport red. coenzymes are re-ox.; e- passed to O2; H+ gradient 4. Chemiosmosis H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of py ...
... pyruvate CO2 and reduced coenzymes 3. Electron Transport red. coenzymes are re-ox.; e- passed to O2; H+ gradient 4. Chemiosmosis H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of py ...
Chapter 41
... 2-Digestion: process of food break down – enzymatic hydrolysis – intracellular: breakdown within cells (sponges) – extracellular: breakdown outside cells (most animals) – alimentary canals (digestive tract) 3- Absorption: cells take up small molecules 4- Elimination: removal of undigested material ...
... 2-Digestion: process of food break down – enzymatic hydrolysis – intracellular: breakdown within cells (sponges) – extracellular: breakdown outside cells (most animals) – alimentary canals (digestive tract) 3- Absorption: cells take up small molecules 4- Elimination: removal of undigested material ...
Organic Compounds
... (fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). • These molecules are usually in the form of polymers, long chains of similar subunits. Because they are large, these molecules are called macromolecules. The subunits are called monomers. • The cell also contains water, inorganic salts and ions, an ...
... (fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). • These molecules are usually in the form of polymers, long chains of similar subunits. Because they are large, these molecules are called macromolecules. The subunits are called monomers. • The cell also contains water, inorganic salts and ions, an ...
mid-term-exam-versio..
... made, it crosses the ER membrane and that portion of the ER pinches off and forms a sac called a vesicle that protects the protein from other proteins in the cytoplasm. ...
... made, it crosses the ER membrane and that portion of the ER pinches off and forms a sac called a vesicle that protects the protein from other proteins in the cytoplasm. ...
Acyl-CoA
... - Triglycerides (or triacylglycerols) are fatty acid esters (usually with different fatty acid R groups) of glycerol—see §1.4! - Triglycerides are largely stored in the adipose tissue where they function as “high-energy” reservoirs—due to being more reduced (carry more electrons, or more hydrogens!) ...
... - Triglycerides (or triacylglycerols) are fatty acid esters (usually with different fatty acid R groups) of glycerol—see §1.4! - Triglycerides are largely stored in the adipose tissue where they function as “high-energy” reservoirs—due to being more reduced (carry more electrons, or more hydrogens!) ...
5 Metabolism - bloodhounds Incorporated
... • Pairs of high-energy electrons pass from complex to complex along the etc. • Energy released by these reactions is used to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane ...
... • Pairs of high-energy electrons pass from complex to complex along the etc. • Energy released by these reactions is used to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane ...
Ch. 2 Macromolecules
... You are in the fourth quarter of a basketball or football game and you are completely exhausted (and I mean gassed). You slam a bottle of Gatorade and you immediately begin to get your “second wind.” What macromolecule in Gatorade is responsible for this? Carbohydrates because they are the body’s p ...
... You are in the fourth quarter of a basketball or football game and you are completely exhausted (and I mean gassed). You slam a bottle of Gatorade and you immediately begin to get your “second wind.” What macromolecule in Gatorade is responsible for this? Carbohydrates because they are the body’s p ...
powerpoint 24 Aug
... Tertiary structure is extremely important to the functioning of amylase. The tertiary structure is formed by the whole peptide chain (protein) folding and coiling around itself. This forms the active site (binding site) of the enzyme. The enzyme is held in a specific configuration (tertiary struct ...
... Tertiary structure is extremely important to the functioning of amylase. The tertiary structure is formed by the whole peptide chain (protein) folding and coiling around itself. This forms the active site (binding site) of the enzyme. The enzyme is held in a specific configuration (tertiary struct ...
Chapter 27-28 - Bakersfield College
... - Acetyl CoA combine together to produce ketone bodies. - They are produced in liver. ...
... - Acetyl CoA combine together to produce ketone bodies. - They are produced in liver. ...
406 PRELIMINARY NOTES Formation of lysophosphatidyl
... concentrations and times giving optimal activity were determined and used throughout these experiments. It was found that sonication of the mitochondria stimulated the activity, particularly that giving rise to the fo~ation of tritiated lyso-PE (Table II). The microsomal fraction, on the other hand, ...
... concentrations and times giving optimal activity were determined and used throughout these experiments. It was found that sonication of the mitochondria stimulated the activity, particularly that giving rise to the fo~ation of tritiated lyso-PE (Table II). The microsomal fraction, on the other hand, ...
CHE-09 Biochemistry
... example of substrate level phosphorylation. Explain how? How is the proton motive force determined during oxidative phosphorylation? What would happen if the mitochondrial membrane became permeable to protons freely? In an actively working muscle there is a lot of glycolytic activity. Explain why? W ...
... example of substrate level phosphorylation. Explain how? How is the proton motive force determined during oxidative phosphorylation? What would happen if the mitochondrial membrane became permeable to protons freely? In an actively working muscle there is a lot of glycolytic activity. Explain why? W ...
Determination of Fatty Acids and Carbohydrate Monomers in Micro
... tuberculostearic acids. When analysing a methanolysate of M . scrofulaceum which had not been subjected to trifluoroacetylation, it was observed that the compounds representing peaks (7) and (10) eluted approximately 2 min later, than when such derivatization was made, indicating that they contained ...
... tuberculostearic acids. When analysing a methanolysate of M . scrofulaceum which had not been subjected to trifluoroacetylation, it was observed that the compounds representing peaks (7) and (10) eluted approximately 2 min later, than when such derivatization was made, indicating that they contained ...