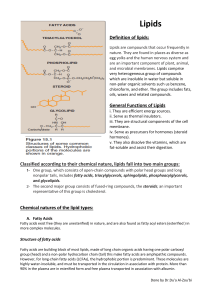
Lipids
... increases surface area of the hydrophobic lipid droplets so that the digestive enzymes, which work at the interface of the droplet and the surrounding aqueous solution, can act effectively. Emulsification is accomplished by two complementary mechanisms: 1. Use of the detergent properties of the bile ...
... increases surface area of the hydrophobic lipid droplets so that the digestive enzymes, which work at the interface of the droplet and the surrounding aqueous solution, can act effectively. Emulsification is accomplished by two complementary mechanisms: 1. Use of the detergent properties of the bile ...
Macromolecule notes
... Carbon can bond with numerous other elements 1. Carbon has 4 free e- in it’s outer energy level 2. It has the ability to form up to 4 covalent bonds ...
... Carbon can bond with numerous other elements 1. Carbon has 4 free e- in it’s outer energy level 2. It has the ability to form up to 4 covalent bonds ...
Biomolecules Test Review -KEY
... 9. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acid? Which is better for you? Why? Saturated fatty acid- single bonds, straight and tightly packed. Solid at room temperature. (Bad for us!) Unsaturated fatty acid- double bonds bend the tails and it’s crooked (not straight). Liquid ...
... 9. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acid? Which is better for you? Why? Saturated fatty acid- single bonds, straight and tightly packed. Solid at room temperature. (Bad for us!) Unsaturated fatty acid- double bonds bend the tails and it’s crooked (not straight). Liquid ...
For lecture notes click here
... STEP 2: In peripheral capillaries, lipoprotein lipase removes many of the triglycerides from VLDLs, leaving IDLs; the triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids and monoglycerides. STEP 3: When IDLs reach the liver, additional triglycerides are removed and the protein content is altered. This pr ...
... STEP 2: In peripheral capillaries, lipoprotein lipase removes many of the triglycerides from VLDLs, leaving IDLs; the triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids and monoglycerides. STEP 3: When IDLs reach the liver, additional triglycerides are removed and the protein content is altered. This pr ...
group “head” dehydration synthesis H 2 O enzyme AP
... (Helps keep membranes flexible) But…high levels in blood may contribute to cardiovascular disease ...
... (Helps keep membranes flexible) But…high levels in blood may contribute to cardiovascular disease ...
Carbon Compounds
... • Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. • Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. ...
... • Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. • Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. ...
Biosynthesis of Plant Primary metabolites
... • The processes and products of primary metabolism are similar in most organisms, while those of secondary metabolism are more specific. • In plants, primary metabolism is made up of photosynthesis, respiration, etc., using CO2, H2O, and NH3 as starting materials, and forming products such as glucos ...
... • The processes and products of primary metabolism are similar in most organisms, while those of secondary metabolism are more specific. • In plants, primary metabolism is made up of photosynthesis, respiration, etc., using CO2, H2O, and NH3 as starting materials, and forming products such as glucos ...
polar charged phosphate head and nonpolar uncharged fatty acid
... Polymer: a macromolecules made of repeating units called monomers Macromolecules are made by dehydration reactions: linking of monomers together with the removal of water ...
... Polymer: a macromolecules made of repeating units called monomers Macromolecules are made by dehydration reactions: linking of monomers together with the removal of water ...
Pinar Tulay cell molecules_17
... Phospholipid structure and orientation of phospholipids in membranes ...
... Phospholipid structure and orientation of phospholipids in membranes ...
Page 1 Introduction to Biochemistry
... polysaccharides with the alternating isomers allowing cross linking between chains (by hydrogen bonds), forming microfibrils (being laid down in different directions). In chitin second carbon –OH groups are replaced by amino groups. 16. The elements which make up lipid molecules are carbon, hydrogen ...
... polysaccharides with the alternating isomers allowing cross linking between chains (by hydrogen bonds), forming microfibrils (being laid down in different directions). In chitin second carbon –OH groups are replaced by amino groups. 16. The elements which make up lipid molecules are carbon, hydrogen ...
Chapter 5 - Scranton Prep Biology
... Fats, phospholipids, and steroids are a diverse assemblage of macromoleculesthat are classedtogether as lipids basedon their hydrophobic behavior. Lipids do not form polymers. Eats Fats are composed of fatty acids attached to the three-carbon alcohol, glycerol. A fatty acid consists of a long hydroc ...
... Fats, phospholipids, and steroids are a diverse assemblage of macromoleculesthat are classedtogether as lipids basedon their hydrophobic behavior. Lipids do not form polymers. Eats Fats are composed of fatty acids attached to the three-carbon alcohol, glycerol. A fatty acid consists of a long hydroc ...
Carbon-Based Molecules
... energy by plant and animal cells. Glycogen is known as “animal starch”. It is formed in muscles and the liver and can be broken down to make energy. ...
... energy by plant and animal cells. Glycogen is known as “animal starch”. It is formed in muscles and the liver and can be broken down to make energy. ...
Lipid Metabolism
... To obtain energy from fat, triglycerides must rst be broken down by hydrolysis into their two principal components, fatty acids and glycerol. This process, called lipolysis, takes place in the cytoplasm. The resulting fatty acids are oxidized by β -oxidation into acetyl CoA, which is used by the Kr ...
... To obtain energy from fat, triglycerides must rst be broken down by hydrolysis into their two principal components, fatty acids and glycerol. This process, called lipolysis, takes place in the cytoplasm. The resulting fatty acids are oxidized by β -oxidation into acetyl CoA, which is used by the Kr ...
Chem*4570 Applied Biochemistry Lecture 7 Overproduction of lysine
... In these cases, the pathway arose as a process of natural adaptation for survival under anaerobic conditions. Before the development of our O2 -rich atmosphere, pathways such as butanol production or other reactions involving hydrogenases for oxidation reactions may well have been more common, but w ...
... In these cases, the pathway arose as a process of natural adaptation for survival under anaerobic conditions. Before the development of our O2 -rich atmosphere, pathways such as butanol production or other reactions involving hydrogenases for oxidation reactions may well have been more common, but w ...
III: Cells Utilizing Oxygen to Form Lipid Regulators and
... 7) PROSTACYCLIN* synthesis and release (resting state) (PGI2) prevents platelet aggregation arachidonic phospholipid PGG2 PGI2 acid phospholipase A2 ...
... 7) PROSTACYCLIN* synthesis and release (resting state) (PGI2) prevents platelet aggregation arachidonic phospholipid PGG2 PGI2 acid phospholipase A2 ...
WHAT IS EXPANDED B-12 AND WHAT DOES EACH COMPOUND
... of the liver in its' processing and excretion of chemical waste products. VITAMIN B 12: Boosts energy, helping to increase activity levels and its essential for helping to form new cells in the body. VITAMIN B-6: Controls water weight by maintaining sodium and potassium balance. It is necessary for ...
... of the liver in its' processing and excretion of chemical waste products. VITAMIN B 12: Boosts energy, helping to increase activity levels and its essential for helping to form new cells in the body. VITAMIN B-6: Controls water weight by maintaining sodium and potassium balance. It is necessary for ...
Homeostatic Control of Metabolism
... Insulin Increases Glucose Transport • Required for resting skeletal muscle and adipose tissue • Moves GLUT-4 transporters to cell membrane • Exercising skeletal muscle does not require insulin for glucose uptake • In liver cells, indirect influence on glucose ...
... Insulin Increases Glucose Transport • Required for resting skeletal muscle and adipose tissue • Moves GLUT-4 transporters to cell membrane • Exercising skeletal muscle does not require insulin for glucose uptake • In liver cells, indirect influence on glucose ...
Biochemistry 3020 1. All of the following enzymes involved in the
... glucose 6-phosphate without the investment of energy from ATP. Hydrolysis of glycogen yields free glucose, which must be converted into glucose 6-phosphate (at the expense of ATP) before it can enter glycolysis. ...
... glucose 6-phosphate without the investment of energy from ATP. Hydrolysis of glycogen yields free glucose, which must be converted into glucose 6-phosphate (at the expense of ATP) before it can enter glycolysis. ...
Standard Assays Offered by the Lipomics Laboratory. • Lipid
... preparation methodology, with the goal of ensuring maximum metabolite recovery with minimum disruption to the metabolome. A typical extraction protocol for recovery of polar metabolites from tissue begins with cryo-pulverization to yield a fine powder. Ice-cold extraction solvent, typically 75% 9:1 ...
... preparation methodology, with the goal of ensuring maximum metabolite recovery with minimum disruption to the metabolome. A typical extraction protocol for recovery of polar metabolites from tissue begins with cryo-pulverization to yield a fine powder. Ice-cold extraction solvent, typically 75% 9:1 ...























