LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 4. Which one of the following cell type is least effective against extra cellular bacterial pathogen? a) B cells b) cytotoxic Tcells c) TNFγ d) macrophages 5. Immuno suppression is not induced by a) anti histamines b) removal of lymphoid tissue c)use of anti lymphocyte antibodies d) cytotoxic drugs ...
... 4. Which one of the following cell type is least effective against extra cellular bacterial pathogen? a) B cells b) cytotoxic Tcells c) TNFγ d) macrophages 5. Immuno suppression is not induced by a) anti histamines b) removal of lymphoid tissue c)use of anti lymphocyte antibodies d) cytotoxic drugs ...
Aarhus University Application Form – Analysis
... FACS Core Facility - Aarhus University Application Form – Analysis Details for each separate analysis appointment ...
... FACS Core Facility - Aarhus University Application Form – Analysis Details for each separate analysis appointment ...
Immune System - Mayfield City Schools
... Putting Pathogens in their place Pasteurization Vaccines & Immunity Antibiotics ...
... Putting Pathogens in their place Pasteurization Vaccines & Immunity Antibiotics ...
Stem cells from fat outperform those from bone marrow Singapore
... and Blood Transfusion, Leiden University Medical Center, The Netherlands, have discovered that stem cells harvested from fat (adipose) are more potent than those collected from bone marrow in helping to modulate the body's immune system. The research, which was led by led by Dr Helene Roelofs, has b ...
... and Blood Transfusion, Leiden University Medical Center, The Netherlands, have discovered that stem cells harvested from fat (adipose) are more potent than those collected from bone marrow in helping to modulate the body's immune system. The research, which was led by led by Dr Helene Roelofs, has b ...
The Immune System : (page 382) Recognizes and destroys
... Specialized cells that attack only certain identified pathogens. Unique to an individual. Includes “lymphocytes” ( B cells and T cells) from your bone marrow. Form the 2nd and 3rd lines of defence. To attack a pathogen, you must recognize cells that don’t belong to you ( shape of their antigens) fir ...
... Specialized cells that attack only certain identified pathogens. Unique to an individual. Includes “lymphocytes” ( B cells and T cells) from your bone marrow. Form the 2nd and 3rd lines of defence. To attack a pathogen, you must recognize cells that don’t belong to you ( shape of their antigens) fir ...
Section Assignment 1.3 Part C: Defence Systems
... White blood cells that kill virus-infected cells and tumor cells by cell-to-cell combat Digested invaders and fragments of white blood cells Promotes production of antibodies without causing disease Disease-causing agent, such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi Unicellular organisms that are neither pl ...
... White blood cells that kill virus-infected cells and tumor cells by cell-to-cell combat Digested invaders and fragments of white blood cells Promotes production of antibodies without causing disease Disease-causing agent, such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi Unicellular organisms that are neither pl ...
The Immune System Learning Module | Vaccine Education Center
... Monocytes: Become macrophages; digest dead or damaged cells and pathogens ...
... Monocytes: Become macrophages; digest dead or damaged cells and pathogens ...
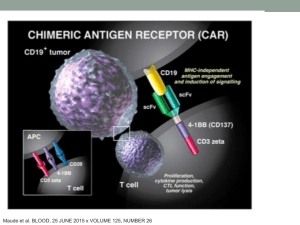
Spleen-thymus-09
... Absent in some immune deficiency states Enlargement: childhood, myasthenia gravis, autoimmune diseases • Tumours: • thymic carcinoid • germ cell tumours • lymphomas (Hodgkin, lymphoblastic lymphoma, large cell lymphoma) • thymoma ...
... Absent in some immune deficiency states Enlargement: childhood, myasthenia gravis, autoimmune diseases • Tumours: • thymic carcinoid • germ cell tumours • lymphomas (Hodgkin, lymphoblastic lymphoma, large cell lymphoma) • thymoma ...
The Immune System Learning Module | Vaccine Education Center
... Monocytes: Become macrophages; digest dead or damaged cells and pathogens ...
... Monocytes: Become macrophages; digest dead or damaged cells and pathogens ...
The Immune System - Children`s Hospital of Philadelphia
... Monocytes: Become macrophages; digest dead or damaged cells and pathogens Lymphocytes: Two major classes of these white blood cells ...
... Monocytes: Become macrophages; digest dead or damaged cells and pathogens Lymphocytes: Two major classes of these white blood cells ...
Organism: Homo sapiens sapiens http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neanderthal ...
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neanderthal ...
Slide 1
... • Follicular involution & lymphocyte depletion-burnt out lymph nodes • Opportunistic infections • lymphomas ...
... • Follicular involution & lymphocyte depletion-burnt out lymph nodes • Opportunistic infections • lymphomas ...
What causes an immune response and increase of
... • Viruses are nonliving particles of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. They can only survive & reproduce in a host, change over time and attach to only 1 specific type of cell/receptor ...
... • Viruses are nonliving particles of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. They can only survive & reproduce in a host, change over time and attach to only 1 specific type of cell/receptor ...
The Immune System
... T cell receptors bind to antigens on antigen presenting cells (AHCs) on their major histocompatibilty complex molecules (MHCs). MHCs: proteins that are the product of gene groups. Class I MHCs are on all body cells except for red blood cells. Class II MHCs are made by B cells, macrophages, and dendr ...
... T cell receptors bind to antigens on antigen presenting cells (AHCs) on their major histocompatibilty complex molecules (MHCs). MHCs: proteins that are the product of gene groups. Class I MHCs are on all body cells except for red blood cells. Class II MHCs are made by B cells, macrophages, and dendr ...
Nrsg 407 Disorders of Blood Cells
... • The number of WBCs, RBCs, & platelets in blood is a function of their life span and the rate of their production versus the rate of their loss ...
... • The number of WBCs, RBCs, & platelets in blood is a function of their life span and the rate of their production versus the rate of their loss ...
AP Chapters 42 Study Guide: Circulation and Gas Exchange
... 1. The defenses that prevent germs from entering the body are the __________________ and mucus membrane. 2. The openings of the skin are also protected. Mucus and wax trap germs that attempt to enter the nose and ears. Gastric acid destroys pathogens that enter them mouth. Body secretions such as te ...
... 1. The defenses that prevent germs from entering the body are the __________________ and mucus membrane. 2. The openings of the skin are also protected. Mucus and wax trap germs that attempt to enter the nose and ears. Gastric acid destroys pathogens that enter them mouth. Body secretions such as te ...
To the Admissions Committee
... region genes that give the Ig its classification, IgM. The N-terminus provides the antibody combining site (V region) that was generated by V(D)J rearrangement (see Figure 1). By definition a cell expressing IgM on its surface (sIgM+) is a B lymphocyte. After stimulation by antigen in secondary lymp ...
... region genes that give the Ig its classification, IgM. The N-terminus provides the antibody combining site (V region) that was generated by V(D)J rearrangement (see Figure 1). By definition a cell expressing IgM on its surface (sIgM+) is a B lymphocyte. After stimulation by antigen in secondary lymp ...
Lymphopoiesis
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, one of the five types of white blood cell (WBC). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.Pathosis in lymphopoiesis leads to any of various lymphoproliferative disorders, such as the lymphomas and lymphoid leukemias.