The Immune System - Blue Valley School District
... • Becomes activated as physical barriers and inflammation fail. Phagocytic cells produce cytokines that initiate the acquired immune response. • Specialized lymphocytes called B and T-cells initiate the humoral and cellmediated responses, respectively. ...
... • Becomes activated as physical barriers and inflammation fail. Phagocytic cells produce cytokines that initiate the acquired immune response. • Specialized lymphocytes called B and T-cells initiate the humoral and cellmediated responses, respectively. ...
DOC - General Practice Associates, LLC
... A low white blood cell count, or leucopenia, is a decrease in disease-fighting cells (leukocytes) circulating in your blood. CAUSES ...
... A low white blood cell count, or leucopenia, is a decrease in disease-fighting cells (leukocytes) circulating in your blood. CAUSES ...
The objectives of this course
... byy a pprocess called "clonal deletion",, leadingg to duringg development "self-tolerance". A lymphocyte y p y needs to meet its antigen g before it can get g activated and start producing identical daughter cells, a process called "clonal expansion". This ensures the specificity of the immune respo ...
... byy a pprocess called "clonal deletion",, leadingg to duringg development "self-tolerance". A lymphocyte y p y needs to meet its antigen g before it can get g activated and start producing identical daughter cells, a process called "clonal expansion". This ensures the specificity of the immune respo ...
immune response
... IMMUNE RESPONSE It includes reactions against any antigen. The consequences are usually beneficial or some times may be injurious to the host. The adaptive response can be antibody-mediated (humoral), cell-mediated (cellular), or both. ...
... IMMUNE RESPONSE It includes reactions against any antigen. The consequences are usually beneficial or some times may be injurious to the host. The adaptive response can be antibody-mediated (humoral), cell-mediated (cellular), or both. ...
Objectives Resistance Nonspecific Defense Inflammatory Response
... Initially occur in bone marrow The blue spheres seen in this SEM image are T cells attacking a much larger cancer cell. The cells are a significant part of our defense against cancer and other types of foreign cells. ...
... Initially occur in bone marrow The blue spheres seen in this SEM image are T cells attacking a much larger cancer cell. The cells are a significant part of our defense against cancer and other types of foreign cells. ...
The Body Has Methods of Protecting Itself from Diseases
... 2nd Defense occurs when injured cells release chemicals that increase blood flow to an area (cut or scrape). The blood brings Macrophage: a white blood cell that engulfs and kills pathogens • 3rd Defense macrophages along with T cells and B cells attach and kill infected cells. ...
... 2nd Defense occurs when injured cells release chemicals that increase blood flow to an area (cut or scrape). The blood brings Macrophage: a white blood cell that engulfs and kills pathogens • 3rd Defense macrophages along with T cells and B cells attach and kill infected cells. ...
nonspecific defense
... 2. Combine & Interfere “neutralization” 3. With complement, lyse & destroy. ...
... 2. Combine & Interfere “neutralization” 3. With complement, lyse & destroy. ...
Immunity Questions
... 7. Describe the differences between the antigens that B cell receptors and antibodies recognize, and the antigens that T cell receptors on cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells recognize. 8. Describe the differences between the humoral immune response and the cell-mediate immune response. 9. Describe ...
... 7. Describe the differences between the antigens that B cell receptors and antibodies recognize, and the antigens that T cell receptors on cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells recognize. 8. Describe the differences between the humoral immune response and the cell-mediate immune response. 9. Describe ...
Aankondiging_Immuno_7nov
... and thus determines the outcome of antigen-specific responses. Specific immune responses are driven by antigen-specific T cells, which do not only expand after initial MHC-dependent antigen contact, but do also polarize into effector cells.These differentiated cells are characterized by their functi ...
... and thus determines the outcome of antigen-specific responses. Specific immune responses are driven by antigen-specific T cells, which do not only expand after initial MHC-dependent antigen contact, but do also polarize into effector cells.These differentiated cells are characterized by their functi ...
Fig 1.1
... cells responsible for innate immunity and lymphocytes responsible for specific immunity. The guardian cells of the innate immune system form the first line of defence against infection and can digest pathogens or vaccine particles and use these to activate lymphocytes. In addition they produce chemi ...
... cells responsible for innate immunity and lymphocytes responsible for specific immunity. The guardian cells of the innate immune system form the first line of defence against infection and can digest pathogens or vaccine particles and use these to activate lymphocytes. In addition they produce chemi ...
the immune response - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... the immune system to shut down. • Helper T cells and memory B cells, made by the B cells, remain in the blood, ready to trigger another immune response if the body is infected with the same pathogen. ...
... the immune system to shut down. • Helper T cells and memory B cells, made by the B cells, remain in the blood, ready to trigger another immune response if the body is infected with the same pathogen. ...
Figure 1.1 The human immune system All blood cells originally
... guardian cells responsible for innate immunity and lymphocytes responsible for specific immunity. The guardian cells of the innate immune system form the first line of defence against infection and can digest pathogens or vaccine particles and use these to activate lymphocytes. In addition they prod ...
... guardian cells responsible for innate immunity and lymphocytes responsible for specific immunity. The guardian cells of the innate immune system form the first line of defence against infection and can digest pathogens or vaccine particles and use these to activate lymphocytes. In addition they prod ...
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... • Some activated B cells MEMORY CELLS. • Memory cells divide rapidly as soon as the antigen is reintroduced. • When the pathogen/infection infects again it is destroyed before any symptoms show. ...
... • Some activated B cells MEMORY CELLS. • Memory cells divide rapidly as soon as the antigen is reintroduced. • When the pathogen/infection infects again it is destroyed before any symptoms show. ...
DRAK2 negatively regulates T Cell Receptor Signaling by
... Mentor: Craig Walsh T cells play a central role in controlling acquired immune response. Regulatory molecules expressed in T cells participate in setting the threshold for T cell activation and limit the response via negative feedback regulation; hence, these molecules maintain T cell homeostasis. D ...
... Mentor: Craig Walsh T cells play a central role in controlling acquired immune response. Regulatory molecules expressed in T cells participate in setting the threshold for T cell activation and limit the response via negative feedback regulation; hence, these molecules maintain T cell homeostasis. D ...
microarray_intro.pdf
... WBCs are blocked in their development so they stop maturing at some particular stage. The stage at which the WBCs stop developing varies from cancer to cancer. Lymphocytic leukemias are stopped at the lymphoid precursor stage, or as immature T or B cells (Fig 1). Myeloid leukemias affect white blood ...
... WBCs are blocked in their development so they stop maturing at some particular stage. The stage at which the WBCs stop developing varies from cancer to cancer. Lymphocytic leukemias are stopped at the lymphoid precursor stage, or as immature T or B cells (Fig 1). Myeloid leukemias affect white blood ...
File - The Building Blocks For Learning
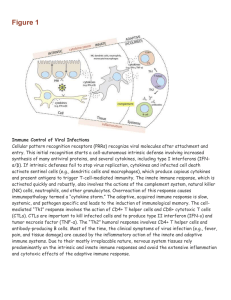
... Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I interferons (IFNα/β). If intrinsic ...
... Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I interferons (IFNα/β). If intrinsic ...
Regulatory T
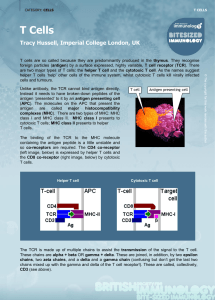
... Unlike antibody, the TCR cannot bind antigen directly. Instead it needs to have broken-down peptides of the antigen ‘presented’ to it by an antigen presenting cell (APC). The molecules on the APC that present the antigen are called major histocompatibility complexes (MHC). There are two types of MHC ...
... Unlike antibody, the TCR cannot bind antigen directly. Instead it needs to have broken-down peptides of the antigen ‘presented’ to it by an antigen presenting cell (APC). The molecules on the APC that present the antigen are called major histocompatibility complexes (MHC). There are two types of MHC ...
Leaving Cert Agricultural Science Notes - Potato Blight
... The cytoplasm now begins to divide into two separate two cells. This is called cytokinesis. The chromosomes uncoil to from chromatin. ...
... The cytoplasm now begins to divide into two separate two cells. This is called cytokinesis. The chromosomes uncoil to from chromatin. ...
Drugs for Modifying Biologic Response
... Adverse: hypotension, dizziness , confusion Avoid infection, teach admin. & use within 30 days,get blood tests, avoid pregnancy & breastfeeding Nsg.- maintain nutrition, stomatitis care, anxiety r/t disorder ...
... Adverse: hypotension, dizziness , confusion Avoid infection, teach admin. & use within 30 days,get blood tests, avoid pregnancy & breastfeeding Nsg.- maintain nutrition, stomatitis care, anxiety r/t disorder ...
Chapter 7 * Cell Structures and Function
... Transmission electron microscopes can be used to explore cell _________________ and large ____________________ molecules. Scanning electron microscopes produce [ 2D ] [ 3D ] [ 4D ] images of the cell. (circle) Specimens viewed under electron microscopes must first be [preserved ] [stained ]. (circle ...
... Transmission electron microscopes can be used to explore cell _________________ and large ____________________ molecules. Scanning electron microscopes produce [ 2D ] [ 3D ] [ 4D ] images of the cell. (circle) Specimens viewed under electron microscopes must first be [preserved ] [stained ]. (circle ...
Lymphopoiesis
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, one of the five types of white blood cell (WBC). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.Pathosis in lymphopoiesis leads to any of various lymphoproliferative disorders, such as the lymphomas and lymphoid leukemias.