Matching - use the key below to answer questions 1
... Suppressor T cells: suppress T cells when there’s no longer an infection Memory T cells: protects body from future invasion. 4. What is the difference between an open and a closed circulatory system? An open circulatory system is found in arthropods, and involves the blood flowing over the organs. A ...
... Suppressor T cells: suppress T cells when there’s no longer an infection Memory T cells: protects body from future invasion. 4. What is the difference between an open and a closed circulatory system? An open circulatory system is found in arthropods, and involves the blood flowing over the organs. A ...
specific defenses: the immune system
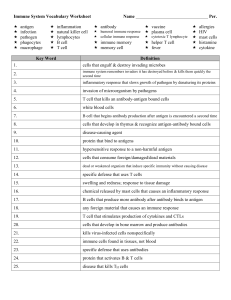
... VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. plasma cell ...
... VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. plasma cell ...
Cell Division
... Decrease in concentration of solutes in a solution (making it more dilute) will reduce osmolarity Cell Division ...
... Decrease in concentration of solutes in a solution (making it more dilute) will reduce osmolarity Cell Division ...
Unit A Chap. 1
... Lesson One Vocabulary cell—basic unit of structure and function of all living things cell membrane- thin cell covering that holds the parts of the cell together nucleus—organelle that determines a cell’s activities cytoplasm- jelly like substance that contains many chemicals to keep a cell functioni ...
... Lesson One Vocabulary cell—basic unit of structure and function of all living things cell membrane- thin cell covering that holds the parts of the cell together nucleus—organelle that determines a cell’s activities cytoplasm- jelly like substance that contains many chemicals to keep a cell functioni ...
Specific Immunity POGIL
... The Facts on HIV/AIDS AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) was first recognized in North America in the early 1980s. It is caused by a virus known as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV infection has become a worldwide epidemic. About 33 million people are currently infected with the virus ...
... The Facts on HIV/AIDS AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) was first recognized in North America in the early 1980s. It is caused by a virus known as HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). HIV infection has become a worldwide epidemic. About 33 million people are currently infected with the virus ...
Immune System Flow Chart
... T-Cell The killer T cells serve to then prevent the replication of the virus. The helper T cells activate an infected cell of the immune system so that it is able to cure itself. The basic function of a helper T cell is to stimulate the macrophages and focus other immune cells onto the infection. A ...
... T-Cell The killer T cells serve to then prevent the replication of the virus. The helper T cells activate an infected cell of the immune system so that it is able to cure itself. The basic function of a helper T cell is to stimulate the macrophages and focus other immune cells onto the infection. A ...
IMMUNOLOGY AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... - general introduction in immunology ( innate and adaptive immunity - Antigen characteristic - Antibody characteristic - B and T cells - Complement - Hypersensitivity types - Oncogenic immunity - Autoimmune disease - Immune deficiency diseases ...
... - general introduction in immunology ( innate and adaptive immunity - Antigen characteristic - Antibody characteristic - B and T cells - Complement - Hypersensitivity types - Oncogenic immunity - Autoimmune disease - Immune deficiency diseases ...
A1981LE35900001
... burst of haemolytic plaque-forming cells was generated when a single spleen cell suspension was placed in a dialysis bag with sheep erythrocytes, the bag being immersed in medium. It was from this experiment that the culture vessel was developed. It was obvious in 1966 that culture techniques were b ...
... burst of haemolytic plaque-forming cells was generated when a single spleen cell suspension was placed in a dialysis bag with sheep erythrocytes, the bag being immersed in medium. It was from this experiment that the culture vessel was developed. It was obvious in 1966 that culture techniques were b ...
lec #1 done by Leen AbdelFattah / Slides #1
... -slide 20: stem cells that are in the primary organs originally developed in the fetal liver . B cells in the bone marrow move to other lymphatic organs during its maturation , it express different receptors on its surface at different stages, to specify its location we depend on the surface recepto ...
... -slide 20: stem cells that are in the primary organs originally developed in the fetal liver . B cells in the bone marrow move to other lymphatic organs during its maturation , it express different receptors on its surface at different stages, to specify its location we depend on the surface recepto ...
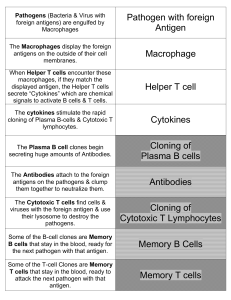
Pathogens (Bacteria with foreign antigens) are
... Pathogens (Bacteria & Virus with foreign antigens) are engulfed by Macrophages ...
... Pathogens (Bacteria & Virus with foreign antigens) are engulfed by Macrophages ...
Chapter 4.3: Tissues
... Support/Protection Transportation Storage of energy reserves (Adipose cells— AKA fat cells) Defense ...
... Support/Protection Transportation Storage of energy reserves (Adipose cells— AKA fat cells) Defense ...
09.13.10 Lecture Cells and Size
... The “extracellular matrix” in which cells are embedded can be simple, or very complex, involving a network of protein fibers ...
... The “extracellular matrix” in which cells are embedded can be simple, or very complex, involving a network of protein fibers ...
Tissues of the immune system
... The sites for cell proliferation and maturation Such as Bone marrow and thymus B- peripheral lymphoid organs or secondary organs Where lymphocytes responses to foreign Ags Such as :spleen ,lymph nodes,cutaneous and mucosal immune system . ...
... The sites for cell proliferation and maturation Such as Bone marrow and thymus B- peripheral lymphoid organs or secondary organs Where lymphocytes responses to foreign Ags Such as :spleen ,lymph nodes,cutaneous and mucosal immune system . ...
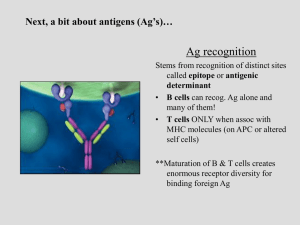
adaptive immunity
... Circulating B cells which have not been exposed to the antigen naive B cells When BCR binds to the antigen, the antigen is internalised by the B cell and presented to the T cells ...
... Circulating B cells which have not been exposed to the antigen naive B cells When BCR binds to the antigen, the antigen is internalised by the B cell and presented to the T cells ...
Langerhans` cells can take up antigen in the skin and migrate to
... The specialized regions of lymphoid tissue provide and environment where antigen-specific B cells can interact with armed helper T cells specific for the same antigen. ...
... The specialized regions of lymphoid tissue provide and environment where antigen-specific B cells can interact with armed helper T cells specific for the same antigen. ...
Lymphopoiesis
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, one of the five types of white blood cell (WBC). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis.Pathosis in lymphopoiesis leads to any of various lymphoproliferative disorders, such as the lymphomas and lymphoid leukemias.