Simon Rasmussen Assistant professor CBS
... proteins are the active units, eg. cell building blocks, enzymes, ... Ribosome ...
... proteins are the active units, eg. cell building blocks, enzymes, ... Ribosome ...
Protein Synthesis Facts
... of an amino acid to the polypeptide chain this hydolysis frees the polypeptide from the ribosome. The ribosome then separates into its small and large subunits ...
... of an amino acid to the polypeptide chain this hydolysis frees the polypeptide from the ribosome. The ribosome then separates into its small and large subunits ...
BY2208 SF Genetics Central Dogma McConnell_1.1
... Textbook: Introduction to Genetic Analysis, Griffiths et al., 9th Ed. ...
... Textbook: Introduction to Genetic Analysis, Griffiths et al., 9th Ed. ...
3rd Quarter Assessment Review - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Transcription—What? Making of mRNA from DNA • Where? Nucleus • Why? To make the template for a Protein • How? • 1. RNA Polymerase breaks HYDROGEN bonds between nitrogen bases of the DNA molecule • 2. An RNA nucleotides NOW fills in next to ONE of the exposed DNA nucleotides creating a strand of Mes ...
... Transcription—What? Making of mRNA from DNA • Where? Nucleus • Why? To make the template for a Protein • How? • 1. RNA Polymerase breaks HYDROGEN bonds between nitrogen bases of the DNA molecule • 2. An RNA nucleotides NOW fills in next to ONE of the exposed DNA nucleotides creating a strand of Mes ...
Chapter 1 Answers
... transcribed by mRNA. The cell will then be using those instructions to manufacture amino acid chains and proteins. When the DNA winds up into a short chromosome it is preparing for mitosis, which would be very difficult if the DNA were all stretched out. 2. Despite all we know about cancer today, so ...
... transcribed by mRNA. The cell will then be using those instructions to manufacture amino acid chains and proteins. When the DNA winds up into a short chromosome it is preparing for mitosis, which would be very difficult if the DNA were all stretched out. 2. Despite all we know about cancer today, so ...
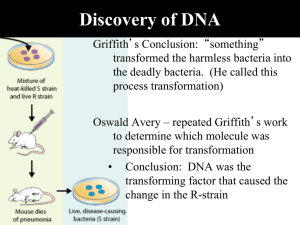
Discovery of DNA
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
ANNEX B: Selected Biotechnology Terms
... nitric oxide, norepinephrine, serotonin, substance P, tumor necrosis factor, vasoactive intestinal peptide. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – a method for the selective amplification of a DNA bas sequence using heatstable polymerase and two 20-base primers. Because the newly synthesized DNA strands ...
... nitric oxide, norepinephrine, serotonin, substance P, tumor necrosis factor, vasoactive intestinal peptide. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – a method for the selective amplification of a DNA bas sequence using heatstable polymerase and two 20-base primers. Because the newly synthesized DNA strands ...
Nucleosides, Nucleotides, and Nucleic Acids
... The most common form of DNA is B-DNA, which exists as a right-handed double helix. The carbohydrate– phosphate backbone lies on the outside, the purine and pyrimidine bases on the inside. The double helix is stabilized by complementary hydrogen bonding (base pairing) between adenine (A) and thymine ...
... The most common form of DNA is B-DNA, which exists as a right-handed double helix. The carbohydrate– phosphate backbone lies on the outside, the purine and pyrimidine bases on the inside. The double helix is stabilized by complementary hydrogen bonding (base pairing) between adenine (A) and thymine ...
PRE-AP Stage 3 – Learning Plan
... SCAFFOLD: Students will identify the components of DNA and describe how genetic information is carried in DNA. After identifying the components of the structure of DNA, students will explain how DNA is transcribed and translated into amino acids to make proteins. ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimid ...
... SCAFFOLD: Students will identify the components of DNA and describe how genetic information is carried in DNA. After identifying the components of the structure of DNA, students will explain how DNA is transcribed and translated into amino acids to make proteins. ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimid ...
Section 5.1
... DNA – (pg 74) = Code. The genetic material found in all living cells that contains the information needed for an organism to grow, maintain itself, and reproduce. Deoxyribonucleic acid A = T C = G ...
... DNA – (pg 74) = Code. The genetic material found in all living cells that contains the information needed for an organism to grow, maintain itself, and reproduce. Deoxyribonucleic acid A = T C = G ...
Vocabulary List
... 11. mRNA – messenger RNA (Messenger Ribonucleic Acid); single stranded molecule that carries the genetic message from DNA within the nucleus to ribosomesoutside the nucleus 12. tRNA – transfer RNA (transfer Ribonucleic Acid); molecule the carries amino acids to ribosomes 13. rRNA – ribosomal RNA (Ri ...
... 11. mRNA – messenger RNA (Messenger Ribonucleic Acid); single stranded molecule that carries the genetic message from DNA within the nucleus to ribosomesoutside the nucleus 12. tRNA – transfer RNA (transfer Ribonucleic Acid); molecule the carries amino acids to ribosomes 13. rRNA – ribosomal RNA (Ri ...
Ch. 15
... • 3. DNA polymerase copies the region between the primers. These copies then serve as templates to make more copies. • 4. In this way, just a few dozen cycles of replication can produce billions of copies of the DNA between the primers. ...
... • 3. DNA polymerase copies the region between the primers. These copies then serve as templates to make more copies. • 4. In this way, just a few dozen cycles of replication can produce billions of copies of the DNA between the primers. ...
Science 103: Outline 17
... DNARNAProtein = The Central Dogma 1. Gene Expression Expressing a gene = Synthesizing the corresponding protein. Involves 2 steps: (a) Transcription (b) Translation 2. Transcription (a) Overall Process Gene (DNA) (b) Functions (i) (ii) (c) Location (d) Process A single-stranded RNA copy of the D ...
... DNARNAProtein = The Central Dogma 1. Gene Expression Expressing a gene = Synthesizing the corresponding protein. Involves 2 steps: (a) Transcription (b) Translation 2. Transcription (a) Overall Process Gene (DNA) (b) Functions (i) (ii) (c) Location (d) Process A single-stranded RNA copy of the D ...
Nucleic Acids - cpprashanths Chemistry
... • Polymers of nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides joined by condensation reactions • They are held together by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of another - called phosphodiester bonds ...
... • Polymers of nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides joined by condensation reactions • They are held together by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of another - called phosphodiester bonds ...
Chapter 10 Study Guide Know the definitions for: Cross
... amino acids to construct polypeptide sequence (protein). rRNA – ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein that provides site for translation of DNA code to construct protein sequence. Study diagram on page 294 to better understand translation. Mutagens are X rays, ultraviolet light, and radioactive ...
... amino acids to construct polypeptide sequence (protein). rRNA – ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein that provides site for translation of DNA code to construct protein sequence. Study diagram on page 294 to better understand translation. Mutagens are X rays, ultraviolet light, and radioactive ...
Okazaki Fragments
... Replication requires the following steps 1-Unwinding Begins at Origins of Replication Two strands open forming Replication ...
... Replication requires the following steps 1-Unwinding Begins at Origins of Replication Two strands open forming Replication ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Hundreds of useful bacterial strains have been produced • Bacteria can even digest oil ...
... • Hundreds of useful bacterial strains have been produced • Bacteria can even digest oil ...
DNA REVIEW SHEET
... 14. What are the three kinds of RNA? 15. Where is an anticodon located? 16. A codon that has no anticodon match would be called a ___________________. 17. What does DNA polymerase do? 18. Anything ending in –ase would be classified as an ____________________> 19. What 3 things make up DNA? 20. DNA i ...
... 14. What are the three kinds of RNA? 15. Where is an anticodon located? 16. A codon that has no anticodon match would be called a ___________________. 17. What does DNA polymerase do? 18. Anything ending in –ase would be classified as an ____________________> 19. What 3 things make up DNA? 20. DNA i ...
Cell Cycle SG
... 4. ____________________: process of sorting and distributing chromosomes for cell division Phase prophase ...
... 4. ____________________: process of sorting and distributing chromosomes for cell division Phase prophase ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.