Walk the Dogma - Nutley Public Schools
... There are 3 types of RNA: Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Structure: Linear Single Strand • Function: Carries genetic info from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm ...
... There are 3 types of RNA: Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Structure: Linear Single Strand • Function: Carries genetic info from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... produce a new chain •Each new DNA helix contains one “old” and one “new” chain ...
... produce a new chain •Each new DNA helix contains one “old” and one “new” chain ...
1 - contentextra
... else within the DNA molecule. The covalent bonds are much stronger than the hydrogen bonds. Because of the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases of the two DNA chains, the DNA can be opened down the middle thus exposing the bases on both chains. ...
... else within the DNA molecule. The covalent bonds are much stronger than the hydrogen bonds. Because of the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases of the two DNA chains, the DNA can be opened down the middle thus exposing the bases on both chains. ...
DNA REPLICATION
... and the enzyme “falls off”the DNA template strand, thus stopping transcription! The sequence of RNA nitrogen bases determine the sequence of the ___________________ to be assembled into polypetptides which make up a _________________. 1. The code word for each amino acid is _______bases long. A thre ...
... and the enzyme “falls off”the DNA template strand, thus stopping transcription! The sequence of RNA nitrogen bases determine the sequence of the ___________________ to be assembled into polypetptides which make up a _________________. 1. The code word for each amino acid is _______bases long. A thre ...
You Light Up My Life
... Mixture cooled; basepairing between primers and ends of single DNA strands ...
... Mixture cooled; basepairing between primers and ends of single DNA strands ...
PCR-Presentation
... • Usually Taq Polymerase or anyone of the natural or Recombinant thermostable ...
... • Usually Taq Polymerase or anyone of the natural or Recombinant thermostable ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
... OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
DNA structure
... • 1 ‘parent’ DNA strand produces 2 new ‘daughter’ strands • Occurs rapidly, both strands simultaneously – Humans with 6 billion pairs a few hours, with only about 1 error every 10 billion nucleotides ...
... • 1 ‘parent’ DNA strand produces 2 new ‘daughter’ strands • Occurs rapidly, both strands simultaneously – Humans with 6 billion pairs a few hours, with only about 1 error every 10 billion nucleotides ...
DNAstructureandReplication
... • Order of bases on the nucleotides in one strand of DNA complements the order of bases on the opposite strand – base sequence ...
... • Order of bases on the nucleotides in one strand of DNA complements the order of bases on the opposite strand – base sequence ...
Additional Lab Exercise: Amino Acid Sequence in
... Enzymes are proteins. In order to carry on their very specific functions, the sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, messenger RNA, and trans ...
... Enzymes are proteins. In order to carry on their very specific functions, the sequence of the amino acids in their structure must be precise. The DNA in the chromosomes of cells, through its own order of bases, is the determining factor in the amino acid sequence. Ribosomes, messenger RNA, and trans ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... Types of macromolecules, their structures, and functions: lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins Water and its unique properties Types of bonds Enzyme structure and function; different types of enzymes, factors that affect enzyme function Metabolism: catabolic vs. anabolic Atomic ...
... Types of macromolecules, their structures, and functions: lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins Water and its unique properties Types of bonds Enzyme structure and function; different types of enzymes, factors that affect enzyme function Metabolism: catabolic vs. anabolic Atomic ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
... living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
Planet Detection - University of Washington
... 3. Some individuals are more successful at surviving and reproducing than others. ...
... 3. Some individuals are more successful at surviving and reproducing than others. ...
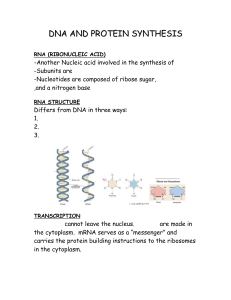
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... -Another Nucleic acid involved in the synthesis of -Subunits are -Nucleotides are composed of ribose sugar, ,and a nitrogen base RNA STRUCTURE ...
... -Another Nucleic acid involved in the synthesis of -Subunits are -Nucleotides are composed of ribose sugar, ,and a nitrogen base RNA STRUCTURE ...
This is to serve as a general overview of important topics. I highly
... Epigenetics looks at the impact on genome function not based on sequence variation but on differences of heterochromatin and euchromatin. In the “Lick Your Rats” video, rat pups who grew to be aggressive had __________ ...
... Epigenetics looks at the impact on genome function not based on sequence variation but on differences of heterochromatin and euchromatin. In the “Lick Your Rats” video, rat pups who grew to be aggressive had __________ ...
Genomics - West High School
... What makes Genomics a new way to study biology? Genomics: Using tools to study all the genes in an organism (the entire genome) simultaneously once its sequence is known. (~ 190 organisms as of March ...
... What makes Genomics a new way to study biology? Genomics: Using tools to study all the genes in an organism (the entire genome) simultaneously once its sequence is known. (~ 190 organisms as of March ...
rsc prize and award lecture
... RNA are decoded - in the process of translation - to synthesize polymers of the natural 20 amino acids. This process (DNA RNA protein) describes the central dogma of molecular biology and is conserved in terrestrial life. We are interested in re-writing the central dogma to create organisms that syn ...
... RNA are decoded - in the process of translation - to synthesize polymers of the natural 20 amino acids. This process (DNA RNA protein) describes the central dogma of molecular biology and is conserved in terrestrial life. We are interested in re-writing the central dogma to create organisms that syn ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.