DNA - Royal Society of Chemistry
... construct and operate an organism. This code is based on the order of nucleotide triplets (GAA, CTG etc.) in a gene which specify the order of particular amino acids in a protein. Other sections of DNA are responsible for switching genes on and off and regulating how much of each type of protein is ...
... construct and operate an organism. This code is based on the order of nucleotide triplets (GAA, CTG etc.) in a gene which specify the order of particular amino acids in a protein. Other sections of DNA are responsible for switching genes on and off and regulating how much of each type of protein is ...
Introduction to Genetics Klug 8th Edition
... Homologous chromosomes – one set from Mom and one set from Dad (23 each for humans) Haploid number (n)- 23 for humans ...
... Homologous chromosomes – one set from Mom and one set from Dad (23 each for humans) Haploid number (n)- 23 for humans ...
word play - Discovery Education
... 12. A winding shape, similar to a spiral; the DNA molecule has a double-helix shape, which is two helixes twisted around each other. 13. The process used to make genetically identical copies of an organism. 14. An organism's physical feature, determined by a gene. Down 1. Substance within the cell b ...
... 12. A winding shape, similar to a spiral; the DNA molecule has a double-helix shape, which is two helixes twisted around each other. 13. The process used to make genetically identical copies of an organism. 14. An organism's physical feature, determined by a gene. Down 1. Substance within the cell b ...
Assignment 1 solution
... 9. Shear stress in cells cultured in bioreactors arises due to (a) Presence of relative velocities (b) Active stirrers and agitators (c) Aeration of medium (d) All of the above 10. Choose the correct statement (a) High membrane fluidity allows for better shear resistance (b) Low membrane fluidity im ...
... 9. Shear stress in cells cultured in bioreactors arises due to (a) Presence of relative velocities (b) Active stirrers and agitators (c) Aeration of medium (d) All of the above 10. Choose the correct statement (a) High membrane fluidity allows for better shear resistance (b) Low membrane fluidity im ...
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
... • Enzymes unwind the double helix and separate the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
... • Enzymes unwind the double helix and separate the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template ...
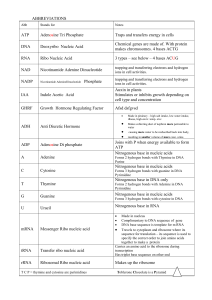
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
Part I, for Exam 1: 1. Based on Chargaff`s rules, which of the
... 3. The E. coli recombinant plasmid pBR322 has been widely utilized in genetic engineering experiments. pBR322 has all of the following features except: A) a number of conveniently located recognition sites for restriction enzymes. B) a number of palindromic sequences near the EcoRI site, which permi ...
... 3. The E. coli recombinant plasmid pBR322 has been widely utilized in genetic engineering experiments. pBR322 has all of the following features except: A) a number of conveniently located recognition sites for restriction enzymes. B) a number of palindromic sequences near the EcoRI site, which permi ...
human biochemistry - churchillcollegebiblio
... Humans and other organisms have short sequences of bases that are repeated many times called satellite DNA. This satellite DNA varies greatly between different individuals in the number of repeats. If it is coped using a methods which is called PCR and then cut up into small fragments using restrict ...
... Humans and other organisms have short sequences of bases that are repeated many times called satellite DNA. This satellite DNA varies greatly between different individuals in the number of repeats. If it is coped using a methods which is called PCR and then cut up into small fragments using restrict ...
DNA Polymerase
... sequence in which they are linked together determines the proteins function. Change the sequence, type, or number of amino acids in a protein you change the function. Amino Acids without water sensitive R-groups ...
... sequence in which they are linked together determines the proteins function. Change the sequence, type, or number of amino acids in a protein you change the function. Amino Acids without water sensitive R-groups ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA
... • To analyze chromosomes, cell biologists PHOTOGRAPH cells in MITOSIS. • Next, they cut out the chromosomes and group them in pairs. • This is called a KARYOTYPE ...
... • To analyze chromosomes, cell biologists PHOTOGRAPH cells in MITOSIS. • Next, they cut out the chromosomes and group them in pairs. • This is called a KARYOTYPE ...
Mutations and Their Significance
... RNA Splicing • Many RNA molecules from eukaryotic genes have sections, called __________, edited out of them before they become functional. The remaining pieces, called __________, are splice together. ...
... RNA Splicing • Many RNA molecules from eukaryotic genes have sections, called __________, edited out of them before they become functional. The remaining pieces, called __________, are splice together. ...
Review Sheet NYS Regents Lab Activity #1 Relationships and Biodiversity
... Use low power on the microscope to examine cross sections of the stems. Look for a scattered arrangement of bundles or a circular arrangement of bundles. d. Paper Chromatography to Separate Plant Pigments Using clean, separate pipettes for each sample, transfer two drops of each plant extract to ...
... Use low power on the microscope to examine cross sections of the stems. Look for a scattered arrangement of bundles or a circular arrangement of bundles. d. Paper Chromatography to Separate Plant Pigments Using clean, separate pipettes for each sample, transfer two drops of each plant extract to ...
Manipulating DNA
... Boon, a 26-year-old American Quarter Horse now past breeding age, has earned more than $380,000 as a competition and show horse. ...
... Boon, a 26-year-old American Quarter Horse now past breeding age, has earned more than $380,000 as a competition and show horse. ...
Bell work Objectives: DNA replication DNA Replication
... keychain, label the bases on the paper model with A, T, G, or C exactly as they are on your keychain from the bottom to the top. ...
... keychain, label the bases on the paper model with A, T, G, or C exactly as they are on your keychain from the bottom to the top. ...
DNA – the heredity material DNA - genetic material Discovering
... Weak hydrogen bonds between base pairs hold DNA strands together. Each chain in the helix is a complimentary mirror image of the other. – Double helix unzips and undergoes semi-conservative replication. Confirmed ...
... Weak hydrogen bonds between base pairs hold DNA strands together. Each chain in the helix is a complimentary mirror image of the other. – Double helix unzips and undergoes semi-conservative replication. Confirmed ...
bioknowledgy note pkt - Peoria Public Schools
... 2.6.U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. (includes 2.6.S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, p ...
... 2.6.U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. (includes 2.6.S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, p ...
Some No-Nonsense Facts on
... improve plants and animals. Geneticists specific location on a chromosome selectively control traits to benefit the and determines a particular community. An example is teosinte characteristic in an organism. Teosinte has been selectively bred since Genes undergo mutation when 8000BC. Teosinte has b ...
... improve plants and animals. Geneticists specific location on a chromosome selectively control traits to benefit the and determines a particular community. An example is teosinte characteristic in an organism. Teosinte has been selectively bred since Genes undergo mutation when 8000BC. Teosinte has b ...
2. Molecular Biology (Core) – 2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA Name
... 2.6.U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. (includes 2.6.S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, p ...
... 2.6.U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs. (includes 2.6.S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to represent phosphates, p ...
Pre-AP Biology 2009
... 4. Sketch a DNA molecule composed of 6 base pairs. Label. 5. When does a DNA molecule replicate? Be specific. 6. Make a sketch to illustrate DNA replication. 7. What are the three types of RNA and what are their functions? Review Figure 12-18 to note these differences. What is difference between an ...
... 4. Sketch a DNA molecule composed of 6 base pairs. Label. 5. When does a DNA molecule replicate? Be specific. 6. Make a sketch to illustrate DNA replication. 7. What are the three types of RNA and what are their functions? Review Figure 12-18 to note these differences. What is difference between an ...
DNA Structure
... However: Rosalind Franklin played a role in helping them discover DNA’s structure. She used x-ray crystallography to take pictures of DNA. ...
... However: Rosalind Franklin played a role in helping them discover DNA’s structure. She used x-ray crystallography to take pictures of DNA. ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.