Wheel of Amino Acids Wheel of Amino Acids
... In this activity you will use your knowledge of protein synthesis to decode the DNA strand and build a partial chain of amino acids (protein). ...
... In this activity you will use your knowledge of protein synthesis to decode the DNA strand and build a partial chain of amino acids (protein). ...
2015/5/13 9:24 AM
... 5. During translation, the type of amino acid that is added to the growing polypeptide depends on the codon on the mRNA and the anti-codon on the tRNA to which the amino acid is attached. 6. Genes contain instructions for assembling nucleosomes. 7. Phosphate groups, guanine, and thymine are found in ...
... 5. During translation, the type of amino acid that is added to the growing polypeptide depends on the codon on the mRNA and the anti-codon on the tRNA to which the amino acid is attached. 6. Genes contain instructions for assembling nucleosomes. 7. Phosphate groups, guanine, and thymine are found in ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... Mature RNA and histones • Which base is connected to its complementary base in a base pair by three hydrogen bonds? A. Uracil B. Thymine C. Guanine D. Adenine • What is the distinction between highly repetitive DNA sequences and single-copy genes? A. The highly repetitive sequences have greater amou ...
... Mature RNA and histones • Which base is connected to its complementary base in a base pair by three hydrogen bonds? A. Uracil B. Thymine C. Guanine D. Adenine • What is the distinction between highly repetitive DNA sequences and single-copy genes? A. The highly repetitive sequences have greater amou ...
Self-Assembly at nano-Scale Binary Nanoparticles Superlattices
... The probe strands are arrayed on a solid support and the detection strand is bound to an Au nanosphere. • The selectively assembled Au nanospheres then act as nucleation sites for Ag deposition upon the chemical reduction of Ag+ from solution. • The resulting Ag deposits can be quantified by a simpl ...
... The probe strands are arrayed on a solid support and the detection strand is bound to an Au nanosphere. • The selectively assembled Au nanospheres then act as nucleation sites for Ag deposition upon the chemical reduction of Ag+ from solution. • The resulting Ag deposits can be quantified by a simpl ...
CH 14 notes - Lincoln Park High School
... * genes (DNA) proteins traits Date: Mutations – mistakes that result in Δ ’s in the DNA nucleotide sequence (p.307) • May occur during DNA replication, meiosis, or by a mutagen o Mutagens: chemical or physical agents that cause mutations Ex: high-E radiation like X-rays & UV rays Carcinogens ...
... * genes (DNA) proteins traits Date: Mutations – mistakes that result in Δ ’s in the DNA nucleotide sequence (p.307) • May occur during DNA replication, meiosis, or by a mutagen o Mutagens: chemical or physical agents that cause mutations Ex: high-E radiation like X-rays & UV rays Carcinogens ...
Fifth Lecture
... strand breaks. • In many cases breaks in the double-strand DNA can be repaired by the enzymes, DNA polymerase, and DNA ligase. • The repair of double strand breaks involves recombinational events, depending upon the nature of the initial break. ...
... strand breaks. • In many cases breaks in the double-strand DNA can be repaired by the enzymes, DNA polymerase, and DNA ligase. • The repair of double strand breaks involves recombinational events, depending upon the nature of the initial break. ...
Small-Molecule Detection and Enantiopurity Measurement using
... properties for applications in biosensing and bioimaging. One area of our research involves using DNA aptamers as recognition elements for the development of new small-molecule detection and characterization assays. A central goal in these experiments is to pursue novel analysis techniques that are ...
... properties for applications in biosensing and bioimaging. One area of our research involves using DNA aptamers as recognition elements for the development of new small-molecule detection and characterization assays. A central goal in these experiments is to pursue novel analysis techniques that are ...
Slide 1
... Which enzyme brings in new nucleotides during DNA Replication? A) Primase B) DNA ligase C) DNA polymerase D) Topoisomerase E) Helicase C ...
... Which enzyme brings in new nucleotides during DNA Replication? A) Primase B) DNA ligase C) DNA polymerase D) Topoisomerase E) Helicase C ...
Bio Quiz #4 Review Sheet
... Structures with the same function found in animals that have a different common ancestor Caused by random events that remove genes from a population Theory that living things come from other living things Structures found in organisms with common evolutionary ancestry Adaptation in which one animal ...
... Structures with the same function found in animals that have a different common ancestor Caused by random events that remove genes from a population Theory that living things come from other living things Structures found in organisms with common evolutionary ancestry Adaptation in which one animal ...
Revisiting Genetics
... • Proteins are made of different combinations of 20 amino acids. We have over 100,000 proteins that carry out vital functions. • Two proteins can have the same 50 amino acids but in a different order = different function. ...
... • Proteins are made of different combinations of 20 amino acids. We have over 100,000 proteins that carry out vital functions. • Two proteins can have the same 50 amino acids but in a different order = different function. ...
Protein Synthesis
... Transcription is the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA Occurs in the nucleus DNA does not leave the nucleus! ...
... Transcription is the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA Occurs in the nucleus DNA does not leave the nucleus! ...
TIP Translation - dna
... ____ 6. Nitrogenous bases are held to the sides of the DNA ladder by a. helix bonds. c. hydrogen bonds. b. covalent bonds. d. ionic bonds. ____ 7. The first step in making a protein is a. amino acids linked together. b. transfer RNA matching mRNA. ...
... ____ 6. Nitrogenous bases are held to the sides of the DNA ladder by a. helix bonds. c. hydrogen bonds. b. covalent bonds. d. ionic bonds. ____ 7. The first step in making a protein is a. amino acids linked together. b. transfer RNA matching mRNA. ...
Document
... Amino acid – a chain of these make up a protein Replication – the copying of a DNA molecule mRNA – a chemical used to read the DNA in the nucleus which takes the message to the ribosomes where proteins are made Mutation – an abnormality or deformation of an organism due to pollutants in the ...
... Amino acid – a chain of these make up a protein Replication – the copying of a DNA molecule mRNA – a chemical used to read the DNA in the nucleus which takes the message to the ribosomes where proteins are made Mutation – an abnormality or deformation of an organism due to pollutants in the ...
Nuclease Digestion
... Tertiary structure: • Side chain interaction determines how the protein will fold within itself. – i.e positively charged side chains might ...
... Tertiary structure: • Side chain interaction determines how the protein will fold within itself. – i.e positively charged side chains might ...
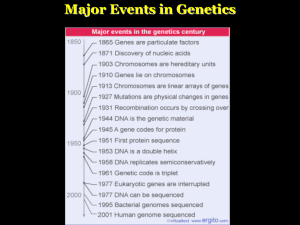
Major Events in Genetics
... – Produced a picture of the DNA molecule using this technique – Already determined that the sugar-phosphate ladder was on the outside of the molecule – Wilkins received Nobel Prize in 1962 – Franklin –and Chargaff- did not. ...
... – Produced a picture of the DNA molecule using this technique – Already determined that the sugar-phosphate ladder was on the outside of the molecule – Wilkins received Nobel Prize in 1962 – Franklin –and Chargaff- did not. ...
Lecture 14
... e. Bond energy: used for synthesis, now used for encoding II. Information a. Since its beginning life has persisted by this survival of information for capture of energy to make bonds i. Energy production via enzymes ii. Replication of information b. Joint quest of info persistence and energy captur ...
... e. Bond energy: used for synthesis, now used for encoding II. Information a. Since its beginning life has persisted by this survival of information for capture of energy to make bonds i. Energy production via enzymes ii. Replication of information b. Joint quest of info persistence and energy captur ...
Research Questions
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...
AZBio Ch 13
... This practice continued for thousands of years. The original plant is believed to be extinct, but the modern corn plant flourishes. ...
... This practice continued for thousands of years. The original plant is believed to be extinct, but the modern corn plant flourishes. ...
Study Guide Foldable .Answer Key
... The structures that carry the information for the inheritance of traits. A gene has the information for making a specific protein. ...
... The structures that carry the information for the inheritance of traits. A gene has the information for making a specific protein. ...
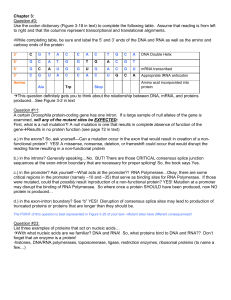
Document
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
Exploratorium Presentation
... DNA is housed in the nucleus (“brain”) of the cell. It contains all of the information the cell needs. ...
... DNA is housed in the nucleus (“brain”) of the cell. It contains all of the information the cell needs. ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.