DNA - hdueck
... What is important about base pairs? Can predict sequence of one strand based on the sequence of the other because it is complementary Replication and Transcription: a single strand of DNA acts as a TEMPLATE for a new strand, or for making RNA. Repair of damaged DNA—the template DNA allows for ...
... What is important about base pairs? Can predict sequence of one strand based on the sequence of the other because it is complementary Replication and Transcription: a single strand of DNA acts as a TEMPLATE for a new strand, or for making RNA. Repair of damaged DNA—the template DNA allows for ...
Composition and structure of DNA and RNA and differences
... a cytotoxic effect by intercalating into the narrow grove and interfering with DNA synthesis. ...
... a cytotoxic effect by intercalating into the narrow grove and interfering with DNA synthesis. ...
1, 2, 5, 6, 7 Time: 08:00
... enzymes involved in the replication of DNA. -Summarize the process of DNA replication. -Students will extract a sample of DNA. ...
... enzymes involved in the replication of DNA. -Summarize the process of DNA replication. -Students will extract a sample of DNA. ...
Gel electrophoresis - University of California, Santa Barbara
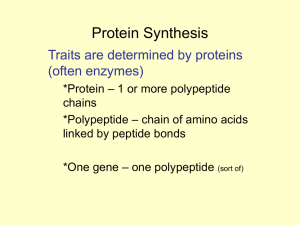
... translated into amino acid sequences • The “words” of the DNA “language” are triplets of bases called codons – 3 bases or nucleotides make one codon – Each codon specifies an amino acid – The codons in a gene specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide ...
... translated into amino acid sequences • The “words” of the DNA “language” are triplets of bases called codons – 3 bases or nucleotides make one codon – Each codon specifies an amino acid – The codons in a gene specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide ...
D5 Phylogeny and systematics – summary of mark
... phylogeny / evolutionary history of a species / relationship between species can be determined; proteins analysed for amino acid sequences; more similar the amino acid sequence, the more closely related the species are; eg cytochrome C / hemoglobin / chlorophyll / other valid example; DNA / mitochon ...
... phylogeny / evolutionary history of a species / relationship between species can be determined; proteins analysed for amino acid sequences; more similar the amino acid sequence, the more closely related the species are; eg cytochrome C / hemoglobin / chlorophyll / other valid example; DNA / mitochon ...
Protein Synthesis
... 1. Initiation – RNA polymerase attaches to DNA at promoter region (beginning of gene – 3’ end) - unzips DNA strands 2. Elongation – RNA polymerase links RNA nucleotides -mRNA strand made 5’3’ ...
... 1. Initiation – RNA polymerase attaches to DNA at promoter region (beginning of gene – 3’ end) - unzips DNA strands 2. Elongation – RNA polymerase links RNA nucleotides -mRNA strand made 5’3’ ...
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: THE GENETIC CODE
... 1. The table below (taken from the Chemguide page) shows the three-base combinations used to code for the various amino acids in messenger RNA chains. ...
... 1. The table below (taken from the Chemguide page) shows the three-base combinations used to code for the various amino acids in messenger RNA chains. ...
Microbiology (Notes)
... 8. Where do proteins function in a cell and why are they important? Proteins function in all parts of a cell and they act as enzymes (biological catalysts) of reactions within the cell. Proteins are also the major structural building blocks of cells. – Proteins in the cell membrane form channels and ...
... 8. Where do proteins function in a cell and why are they important? Proteins function in all parts of a cell and they act as enzymes (biological catalysts) of reactions within the cell. Proteins are also the major structural building blocks of cells. – Proteins in the cell membrane form channels and ...
DNA Replication Practice Worksheet
... depends upon whether the cells is a prokaryote or a eukaryote (see the RNA sidebar on the previous page for more about the types of cells). DNA replication occurs in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Regardless of where DNA replication occurs, the basic process is the sa ...
... depends upon whether the cells is a prokaryote or a eukaryote (see the RNA sidebar on the previous page for more about the types of cells). DNA replication occurs in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Regardless of where DNA replication occurs, the basic process is the sa ...
bio 1406 final exam review
... 1. Are living things made of cell? 2. Know how electrons are distributed on atoms. 3. What is homeostasis? 4. know hierarchy of biological organization 5. What is the nucleus of atoms made of? 6. What is atomic number? 7. What type of chemical bond holds oxygen and hydrogen together in H2O. 8. Water ...
... 1. Are living things made of cell? 2. Know how electrons are distributed on atoms. 3. What is homeostasis? 4. know hierarchy of biological organization 5. What is the nucleus of atoms made of? 6. What is atomic number? 7. What type of chemical bond holds oxygen and hydrogen together in H2O. 8. Water ...
Chapter 16 and 17 Review
... The monomer of DNA is called _____________. What are the three parts that make up the DNA monomer? Name the four DNA nucleotides. How do the nucleotides pair? How many strands are in a DNA molecule? What kind of bond holds DNA strands together? The two DNA strands are said to be antiparallel. What d ...
... The monomer of DNA is called _____________. What are the three parts that make up the DNA monomer? Name the four DNA nucleotides. How do the nucleotides pair? How many strands are in a DNA molecule? What kind of bond holds DNA strands together? The two DNA strands are said to be antiparallel. What d ...
Chap 12 VOCAB - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Nitrogen base with 1 ring such as cytosine and thymine pyrimidine ...
... Nitrogen base with 1 ring such as cytosine and thymine pyrimidine ...
understanding dna molecule of heredity - Cal State LA
... The nucleotide is held together by a backbone made of sugars and phosphate group The backbone carries four types of molecules called bases It is the sequence of these four bases that encodes information The main job of the DNA is to encode the sequence of amino acids residues ...
... The nucleotide is held together by a backbone made of sugars and phosphate group The backbone carries four types of molecules called bases It is the sequence of these four bases that encodes information The main job of the DNA is to encode the sequence of amino acids residues ...
DNA Jeopardy Review
... bacterial DNA into another bacteria either through a prophage & Lysogenic Cycle or through the lytic cycle. What is this process ...
... bacterial DNA into another bacteria either through a prophage & Lysogenic Cycle or through the lytic cycle. What is this process ...
DNA Structure Content Standards 3.A.1: DNA, and in some cases
... 5. DNA replication ensures continuity of hereditary information. i. replication is a semi-conservative process. ii. replication requires DNA polymerase plus many other essential cellular enzymes (including ligase, RNA polymerase, helicase, and topoisomerase), occurs bidirectionally, and differs in t ...
... 5. DNA replication ensures continuity of hereditary information. i. replication is a semi-conservative process. ii. replication requires DNA polymerase plus many other essential cellular enzymes (including ligase, RNA polymerase, helicase, and topoisomerase), occurs bidirectionally, and differs in t ...
Notes 14 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis Questions and
... symbolize the various types of nucleotide? 10. Give three synonymous terms that refer to one side of the functional DNA unit. 11. How is the shape of DNA similar to the shape of a ladder? 12. What part of the DNA monomer reaches across and binds to a similar monomer on the other strand? How do these ...
... symbolize the various types of nucleotide? 10. Give three synonymous terms that refer to one side of the functional DNA unit. 11. How is the shape of DNA similar to the shape of a ladder? 12. What part of the DNA monomer reaches across and binds to a similar monomer on the other strand? How do these ...
MCDB 1030
... 3. Describe the principle events that occur in the life cycle of a + strand RNA virus. ...
... 3. Describe the principle events that occur in the life cycle of a + strand RNA virus. ...
DNA Assessment - WordPress.com
... 6) Individual genes store bits of information that make cells function. Identify which of the following describes a gene. A) a segment of DNA B) a segment of RNA C) a segment of protein D) a segment of carbohydrate 7) Genetic information is stored in________________. A) DNA molecules B) RNA molecule ...
... 6) Individual genes store bits of information that make cells function. Identify which of the following describes a gene. A) a segment of DNA B) a segment of RNA C) a segment of protein D) a segment of carbohydrate 7) Genetic information is stored in________________. A) DNA molecules B) RNA molecule ...
DNA ppt
... – discovered that inherited traits are determined by discrete units, or 'genes,’ passed on from the parents. ...
... – discovered that inherited traits are determined by discrete units, or 'genes,’ passed on from the parents. ...
Chapter 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7 Study Guide Key terms: Ribonucleic acid
... 7. What are point mutations? 8. Name and provide examples of 3 types of point mutations. 9. List the differences between DNA and RNA. 10. What happens when a tRNA anticodon binds to an mRNA codon? 11. What are the roles of the activator, enhancer, and promoter in eukaryotic gene regulation? 12. Name ...
... 7. What are point mutations? 8. Name and provide examples of 3 types of point mutations. 9. List the differences between DNA and RNA. 10. What happens when a tRNA anticodon binds to an mRNA codon? 11. What are the roles of the activator, enhancer, and promoter in eukaryotic gene regulation? 12. Name ...
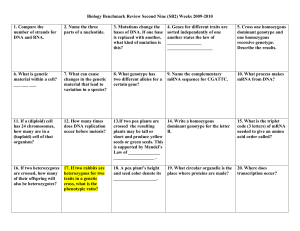
Biology Benchmark Review Second Nine (SB2) Weeks 2009-2010
... plants may be tall or B. short and produce yellow seeds or green seeds. This is supported by Mendel’s Law of ______________ __________________ . ...
... plants may be tall or B. short and produce yellow seeds or green seeds. This is supported by Mendel’s Law of ______________ __________________ . ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.