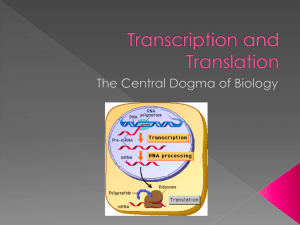
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... Details Of The Structure • DNA is formed from two nucleotide polymers each with covalent bonds between the sugar and phosphate groups (backbone structure) and variable nucleotide bases capable of Hydrogen bonding Conserved region ...
... Details Of The Structure • DNA is formed from two nucleotide polymers each with covalent bonds between the sugar and phosphate groups (backbone structure) and variable nucleotide bases capable of Hydrogen bonding Conserved region ...
Name:
... September. Please use this as a reference to make your study guide. All information on this review sheet can be found in your class notes, labs or handouts. Do not wait until the last minute to review and study for the exam. It is a lot of information!! Extra help for the should be scheduled in adva ...
... September. Please use this as a reference to make your study guide. All information on this review sheet can be found in your class notes, labs or handouts. Do not wait until the last minute to review and study for the exam. It is a lot of information!! Extra help for the should be scheduled in adva ...
nucleic acids - onlinebiosurgery
... One organic nitrogenous base. These subunits are joined by covalent bonds to form a nucleotide molecule. ...
... One organic nitrogenous base. These subunits are joined by covalent bonds to form a nucleotide molecule. ...
DNA functions worksheet
... DNA Structure and Replication: 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for A. the sequence of amino acids in a protein B. the sequence of base pairs C. producing mutations D. making a recipe 2. What is the main difference between the structure of chromatin and the st ...
... DNA Structure and Replication: 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for A. the sequence of amino acids in a protein B. the sequence of base pairs C. producing mutations D. making a recipe 2. What is the main difference between the structure of chromatin and the st ...
Worksheet 6 - Iowa State University
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
... 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu ...
AP BIO Unit 6 Review Ch. 14,15,16,18,19 Westbrook Gene
... A _______ occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. What kind of mutation results in a single base pair replacement? If a mutation occurs in these types of cells it will be passed on to the next generation. What is it called when ...
... A _______ occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. What kind of mutation results in a single base pair replacement? If a mutation occurs in these types of cells it will be passed on to the next generation. What is it called when ...
Chapter 10 Vocabulary Review
... A Y-shaped point that results when the two strands of a DNA double helix separate so that the DNA molecule can be replicated ...
... A Y-shaped point that results when the two strands of a DNA double helix separate so that the DNA molecule can be replicated ...
Molecular Techniques in Cell & Molecular Biology
... cell and molecular biology in the last 20 years. These techniques are used to recombine DNA from different sources and to replicate and express these genes in other cells. They make possible new ways to study the functions of genes and their protein products and also commercial production of specifi ...
... cell and molecular biology in the last 20 years. These techniques are used to recombine DNA from different sources and to replicate and express these genes in other cells. They make possible new ways to study the functions of genes and their protein products and also commercial production of specifi ...
RNA - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Human Genome Project • 15 year project with scientist all over the world. Mapped out the sequence and location of all traits (genes) on all chromosomes of a human. • Humans have 3,200,000,000 base pairs per sex cell. (It would take about 10yrs. to read each base.) ...
... Human Genome Project • 15 year project with scientist all over the world. Mapped out the sequence and location of all traits (genes) on all chromosomes of a human. • Humans have 3,200,000,000 base pairs per sex cell. (It would take about 10yrs. to read each base.) ...
Name
... A gene of interest is identified. The plasmid and gene of interest are both cut with the same restriction enzyme. The gene is then inserted into the bacteria and DNA ligase binds the two fragments together ...
... A gene of interest is identified. The plasmid and gene of interest are both cut with the same restriction enzyme. The gene is then inserted into the bacteria and DNA ligase binds the two fragments together ...
106 DNA- Proteins
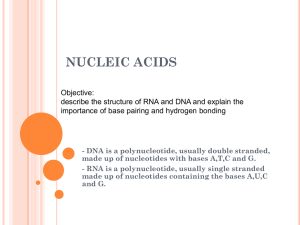
... Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA) • Nucleic acids carry genetic information. • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acids) have molecular weights around 6 - 16 106 amu and are found inside the nucleus of the cell. • RNA (ribonucleic acids) have molecular weights around 20,000 to 40,000 amu and are found in the cytoplas ...
... Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA) • Nucleic acids carry genetic information. • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acids) have molecular weights around 6 - 16 106 amu and are found inside the nucleus of the cell. • RNA (ribonucleic acids) have molecular weights around 20,000 to 40,000 amu and are found in the cytoplas ...
Proein Synthesis Note Fill-in
... 50. A ribosome is made of _____________% of rRNA and _____________% of proteins. 51. A ribosome contains 2 sites for tRNA to bind called _____ and ______. 52. Sketch and label a ribosome. Include the attachment sites and the mRNA in your drawing. 53. What is the purpose of translation? 54. What 4 th ...
... 50. A ribosome is made of _____________% of rRNA and _____________% of proteins. 51. A ribosome contains 2 sites for tRNA to bind called _____ and ______. 52. Sketch and label a ribosome. Include the attachment sites and the mRNA in your drawing. 53. What is the purpose of translation? 54. What 4 th ...
Biotechnology Key Terms and Concepts
... B. Much of biotechnology deals with analyzing and manipulating genomes of organisms at the molecular level (DNA technology) C. Genome-complete set of an organism’s genetic material D. Human genome project– a project aimed at sequencing the human genome and identifying its genes E. Recombinant DNA te ...
... B. Much of biotechnology deals with analyzing and manipulating genomes of organisms at the molecular level (DNA technology) C. Genome-complete set of an organism’s genetic material D. Human genome project– a project aimed at sequencing the human genome and identifying its genes E. Recombinant DNA te ...
Genes to Proteins Nucleic Acid Structure
... – H‐bonding in RNA structure – Reactions of catalytic RNA (rare) – Hydrolysis ...
... – H‐bonding in RNA structure – Reactions of catalytic RNA (rare) – Hydrolysis ...
2 - Blue Valley Schools
... 1. You should be familiar with the stages of the cell cycle and know the role of the nuclear membrane, centrioles, and spindle fibers in this cycle. 2. You be able to explain the enzymatic steps involved in DNA replication and know the general goal of the mitosis and the other stages of the cell cyc ...
... 1. You should be familiar with the stages of the cell cycle and know the role of the nuclear membrane, centrioles, and spindle fibers in this cycle. 2. You be able to explain the enzymatic steps involved in DNA replication and know the general goal of the mitosis and the other stages of the cell cyc ...
Genetics - California Science Teacher
... 16. Process in which naked DNA is taken up by bacterial or yeast cell 17. Process in which RNA is produced by using a DNA template. 18. Process that results in the production of cDNA from an RNA molecule. 19. Process in which DNA is produced by using a DNA template ...
... 16. Process in which naked DNA is taken up by bacterial or yeast cell 17. Process in which RNA is produced by using a DNA template. 18. Process that results in the production of cDNA from an RNA molecule. 19. Process in which DNA is produced by using a DNA template ...
Manipulating DNA - Lemon Bay High School
... • A Transgenic Tobacco Plant Genetic engineering has changed the way we interact with living things. This transgenic tobacco plant, which glows in the dark, was grown from a tobacco cell transformed with the firefly luciferase gene. The plant illustrates how DNA from one organism contains informat ...
... • A Transgenic Tobacco Plant Genetic engineering has changed the way we interact with living things. This transgenic tobacco plant, which glows in the dark, was grown from a tobacco cell transformed with the firefly luciferase gene. The plant illustrates how DNA from one organism contains informat ...
Nucleic Acids - Biology Innovation
... 1. DNA replicates by unwinding into separate strands with help from DNA polymerase which adds free nucleotides to the exposed bases. 2. Each chain acts as a template for free nucleotides so that they can be joined to their complementary bases. 3. The result is that there are two DNA molecules, each ...
... 1. DNA replicates by unwinding into separate strands with help from DNA polymerase which adds free nucleotides to the exposed bases. 2. Each chain acts as a template for free nucleotides so that they can be joined to their complementary bases. 3. The result is that there are two DNA molecules, each ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.