Powerpoint
... contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
... contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
B8. Nucleic Acids (HL)
... each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid – This is known as the genetic code and it is both universal and degenerate • These amino acids will be brought to the ribosome by tRNA and the formation of a polypeptide will commence • Once the specific protein is formed, the mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA wil ...
... each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid – This is known as the genetic code and it is both universal and degenerate • These amino acids will be brought to the ribosome by tRNA and the formation of a polypeptide will commence • Once the specific protein is formed, the mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA wil ...
END OF SEMESTER EXAM PREPARATION AND REVISION
... − A=T or A=U is a weak bond – hydrogen bonding − G≡C is a strong bond – hydrogen bonding − Two complementary strands in DNA – double helix − Direction is from 5’ –> 3’ ends ...
... − A=T or A=U is a weak bond – hydrogen bonding − G≡C is a strong bond – hydrogen bonding − Two complementary strands in DNA – double helix − Direction is from 5’ –> 3’ ends ...
Outline
... nucleotides are composed of a base (G, A, T, or C) and a deoxyribose sugar A and G are purines; C and T are pyrimidines polymer of nucleotides joined by sugar-phosphate linkages distince 5’ and 3’ ends, based on the deoxyribose sugar base-pairing (G to C and A to T) holds two strands together in an ...
... nucleotides are composed of a base (G, A, T, or C) and a deoxyribose sugar A and G are purines; C and T are pyrimidines polymer of nucleotides joined by sugar-phosphate linkages distince 5’ and 3’ ends, based on the deoxyribose sugar base-pairing (G to C and A to T) holds two strands together in an ...
MCDB 1030 – Spring 2003
... Furthermore, many bacteria cannot be grown in pure culture, probably because we don’t understand their growth requirements. Thus, it may be impossible to isolate a bacterium that is in fact that cause of a disease. 4. (6 points) a) What is the difference between a nucleotide and a polynucleotide? A ...
... Furthermore, many bacteria cannot be grown in pure culture, probably because we don’t understand their growth requirements. Thus, it may be impossible to isolate a bacterium that is in fact that cause of a disease. 4. (6 points) a) What is the difference between a nucleotide and a polynucleotide? A ...
I. DNA A. WHAT IS IT?
... • Process to make a copy of the DNA. Both strands of DNA act as a pattern for the new DNA strands. ...
... • Process to make a copy of the DNA. Both strands of DNA act as a pattern for the new DNA strands. ...
from innovative technologies ...to superior key products
... F R O M I N N O VAT I V E T E C H N O L O G I E S . . . Nucleic Acid Testing Nucleic acids store and transfer genetic information in cells. The main types of nucleic acids are DNA and R NA, which are made up of chains of chemicals called nucleotides. Most DNA exists in cells as a double-stranded str ...
... F R O M I N N O VAT I V E T E C H N O L O G I E S . . . Nucleic Acid Testing Nucleic acids store and transfer genetic information in cells. The main types of nucleic acids are DNA and R NA, which are made up of chains of chemicals called nucleotides. Most DNA exists in cells as a double-stranded str ...
Chapter 17 Powerpoint
... More Modification • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
... More Modification • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
C8. Nucleic Acids
... hang upside down from light fixtures or dark corners of the ceiling. Superman begins to suspect that Lois may have had a fling with her old boyfriend, Batman. Superman gets a court order for a blood sample from himself, Lois, Batman and Johnny. The DNA in each blood sample is amplified (increased is ...
... hang upside down from light fixtures or dark corners of the ceiling. Superman begins to suspect that Lois may have had a fling with her old boyfriend, Batman. Superman gets a court order for a blood sample from himself, Lois, Batman and Johnny. The DNA in each blood sample is amplified (increased is ...
Ch 16-17 High
... Your job is to make a poster of your selected topic. -The poster should be kid-friendly as to say an intelligent 8-10 year old would be able to understand it yet make sure that all information communicated is true to the text. - Finally, you may not use English, do the best you can, ask friends, rel ...
... Your job is to make a poster of your selected topic. -The poster should be kid-friendly as to say an intelligent 8-10 year old would be able to understand it yet make sure that all information communicated is true to the text. - Finally, you may not use English, do the best you can, ask friends, rel ...
Unit 3 * Molecular Genetics
... Bases are always bound to their complementary base.Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine, and Cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds with Guanine. ...
... Bases are always bound to their complementary base.Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine, and Cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds with Guanine. ...
DNA/Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... What type of bond attaches a new amino acid to a polypeptide chain? By what process does a tRNA molecule attach onto mRNA during translation? ...
... What type of bond attaches a new amino acid to a polypeptide chain? By what process does a tRNA molecule attach onto mRNA during translation? ...
Chapter 22
... Retroposons of the viral superfamily are transposons that mobilize via an RNA that does not form an infectious particle. Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposi ...
... Retroposons of the viral superfamily are transposons that mobilize via an RNA that does not form an infectious particle. Some retroposons directly resemble retroviruses in their use of LTRs, whereas others do not have LTRs. Other elements can be found that were generated by an RNA-mediated transposi ...
11/11/15 - cloudfront.net
... If you need to make up a quiz due to an absence… come see me Tues or Thurs during PLC Flip it over when you are finished and hang on to it ...
... If you need to make up a quiz due to an absence… come see me Tues or Thurs during PLC Flip it over when you are finished and hang on to it ...
Structures of the bacteriophage Sf6 terminase large subunit reveal a
... reminiscent of those of RNases H and topoisomerases. Structures of gp2-CTD in the absence and presence of catalytic ligand Mg2+ at 1.9 and 2.1 Å resolution reveal an open and closed conformation for the active site, representing an catalytically inactive and active state respectively. Upon binding o ...
... reminiscent of those of RNases H and topoisomerases. Structures of gp2-CTD in the absence and presence of catalytic ligand Mg2+ at 1.9 and 2.1 Å resolution reveal an open and closed conformation for the active site, representing an catalytically inactive and active state respectively. Upon binding o ...
DNA REVIEW SHEET (answer in COMPLETE sentences on another
... List the purines. List the pyrimidines. Describe the hydrogen bonding between the various nitrogen bases. What molecules make up the backbone of the DNA molecule? What does the term semiconservative mean? What about antiparallel? Describe the function of each enzyme associated with DNA: helicase, DN ...
... List the purines. List the pyrimidines. Describe the hydrogen bonding between the various nitrogen bases. What molecules make up the backbone of the DNA molecule? What does the term semiconservative mean? What about antiparallel? Describe the function of each enzyme associated with DNA: helicase, DN ...
DNA Replication, Translation, Transcription, & Protein
... up by one of the students in my 5th block. ...
... up by one of the students in my 5th block. ...
Genetics Introduction:
... tRNA transfers amino acids from cytoplasms pool to a ribosome Ribosome adds each AA carried by tRNA to the growing end of the polypeptide chain In the triplet code, 3 consecutive bases specify an AA, creating 4 3 (64) possible code words The genetic instructions for a PP chain are written in DNA as ...
... tRNA transfers amino acids from cytoplasms pool to a ribosome Ribosome adds each AA carried by tRNA to the growing end of the polypeptide chain In the triplet code, 3 consecutive bases specify an AA, creating 4 3 (64) possible code words The genetic instructions for a PP chain are written in DNA as ...
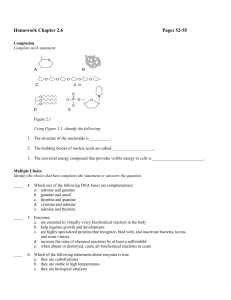
Homework Chapter 2.6 Pages 52-55 Completion Complete each
... c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
... c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
Genetics Exam 3
... ________________________________ Traits that show up in both sexes but are expressed differently. ______________________ __________An organism composed of two or more genetically different cell types. ________________________________ A chromosomal mutation in which there is a change in position of c ...
... ________________________________ Traits that show up in both sexes but are expressed differently. ______________________ __________An organism composed of two or more genetically different cell types. ________________________________ A chromosomal mutation in which there is a change in position of c ...
DNA
... All cells have the same set of genes Different kinds of cells use different combinations of genes ...
... All cells have the same set of genes Different kinds of cells use different combinations of genes ...
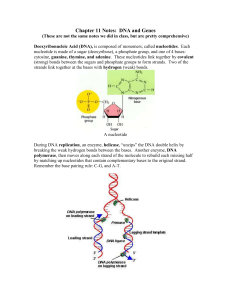
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” the DNA double helix by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase, then moves along each strand of the molecule to rebuild each missing half by matching up nucleotides that contain complementary bases to t ...
... During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” the DNA double helix by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase, then moves along each strand of the molecule to rebuild each missing half by matching up nucleotides that contain complementary bases to t ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.