THE CENTRAL DOGMA THE CENTRAL DOGMA
... Even the simplest proteins can assume many different conformations. ...
... Even the simplest proteins can assume many different conformations. ...
(1) Identify the secondary structure described in each of the
... (16) Ingestion of methanol is a medical emergency. It is often treated by the administration of ethanol, which prevents the dangerous effects of methanol metabolism. In the body, methanol is oxidized to formaldehyde (methanal), a toxic molecule that cannot be further oxidized and that damages protei ...
... (16) Ingestion of methanol is a medical emergency. It is often treated by the administration of ethanol, which prevents the dangerous effects of methanol metabolism. In the body, methanol is oxidized to formaldehyde (methanal), a toxic molecule that cannot be further oxidized and that damages protei ...
Organic compounds
... The basic building blocks are amino acids (a.a.) A structural building block of many organism Enzymes are proteins ...
... The basic building blocks are amino acids (a.a.) A structural building block of many organism Enzymes are proteins ...
Document
... Of course, the vast majority of the oxygen is found in water. Water is essential for life. It is what all chemical reactions in the ...
... Of course, the vast majority of the oxygen is found in water. Water is essential for life. It is what all chemical reactions in the ...
2-BuildingBlocks
... 3. Ionic, hydrogen and Van der Waals bonds are critical for interactions of proteins and other molecules. These non-covalent bonds involve the AA side chains. Selecting from those listed in the box, which type(s) of amino acids would: A. form ionic bonds with negatively charged DNA. _________ B. fo ...
... 3. Ionic, hydrogen and Van der Waals bonds are critical for interactions of proteins and other molecules. These non-covalent bonds involve the AA side chains. Selecting from those listed in the box, which type(s) of amino acids would: A. form ionic bonds with negatively charged DNA. _________ B. fo ...
Organic compounds
... and fabrics such as nylon and rayon. One of the most important synthetic polymers we use everyday is plastics, which are used in products from kitchen utensils to rocket engines. ...
... and fabrics such as nylon and rayon. One of the most important synthetic polymers we use everyday is plastics, which are used in products from kitchen utensils to rocket engines. ...
chemistryandmacromolecules3
... • Fats—solid at room temperature • Oils—liquid at room temperature • They have very little polarity and are extremely hydrophobic. Triglycerides consist of: • Three fatty acids— nonpolar hydrocarbon chain attached to a polar carboxyl (—COOH) (carboxylic acid) • One glycerol—an alcohol with 3 hydroxy ...
... • Fats—solid at room temperature • Oils—liquid at room temperature • They have very little polarity and are extremely hydrophobic. Triglycerides consist of: • Three fatty acids— nonpolar hydrocarbon chain attached to a polar carboxyl (—COOH) (carboxylic acid) • One glycerol—an alcohol with 3 hydroxy ...
Protein interactions are essential for many biological functions to occur. ... Erika Lacy: Cell Biology & Neuroscience
... Fluorescent Probes for Detecting Protein Interactions in Bacteria Protein interactions are essential for many biological functions to occur. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) assay is a complementation-based technique used to study protein interactions. One benefit of this approach is ...
... Fluorescent Probes for Detecting Protein Interactions in Bacteria Protein interactions are essential for many biological functions to occur. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) assay is a complementation-based technique used to study protein interactions. One benefit of this approach is ...
Chapter 5
... • Polymers of AA – 20 AA, all varied in their “R” groups – 9 essential AA can not be made by the body ...
... • Polymers of AA – 20 AA, all varied in their “R” groups – 9 essential AA can not be made by the body ...
File
... Background: Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), an enzyme is found in cells from nearly all organisms, catalyzes the interconversion of lactate and pyruvate. Although this protein has a highly conserved sequence, it is known to have several non-conserved amino acids that vary between species. Research has ...
... Background: Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), an enzyme is found in cells from nearly all organisms, catalyzes the interconversion of lactate and pyruvate. Although this protein has a highly conserved sequence, it is known to have several non-conserved amino acids that vary between species. Research has ...
Introduction to Protein Science Architecture, Function
... 3.Sensitive position in the active site Ex) Gln-> Arg substitution, Malate dehydrogenase -> ...
... 3.Sensitive position in the active site Ex) Gln-> Arg substitution, Malate dehydrogenase -> ...
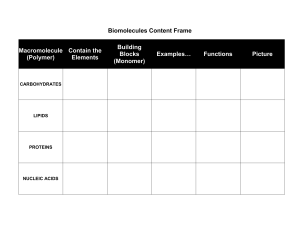
4 Classes of Large Biological Molecules Carbohydrates Lipids
... The 3rd –OH group is attached to a phosphate group (- charge) Show ambivalent properties toward water Steroids Have C skeletons consisting of 4 rings, only variation come in functional groups Cholesterol: precursor from which many other steroids are made ...
... The 3rd –OH group is attached to a phosphate group (- charge) Show ambivalent properties toward water Steroids Have C skeletons consisting of 4 rings, only variation come in functional groups Cholesterol: precursor from which many other steroids are made ...
Macromolecules 9-3
... i. Made of chains of amino acids 1. 20 different amino acids combining in infinite ways 2. 2.43 x 10 ^ 18 combinations! (20x19x18x17…1) 3. Sequence of the amino acid determines the shape of the protein 4. The shape of the protein determines the function of the protein! c. Four Levels of Protein Str ...
... i. Made of chains of amino acids 1. 20 different amino acids combining in infinite ways 2. 2.43 x 10 ^ 18 combinations! (20x19x18x17…1) 3. Sequence of the amino acid determines the shape of the protein 4. The shape of the protein determines the function of the protein! c. Four Levels of Protein Str ...
Topic 4: Biochemistry and Marcomolecules
... Removal of an H2O molecule covalently bonds the monomers. ...
... Removal of an H2O molecule covalently bonds the monomers. ...
Biochemistry Jeopardy
... Proteins have four levels of structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary (The most ...
... Proteins have four levels of structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary (The most ...
CHEM523 Final Exam
... Answer the following questions. Each question is worth 4 points. You have 3 hours to complete this exam. 1) Below are seven amino acids. Indicate all characteristics that apply to each amino acid by writing the appropriate letter(s) in the blanks provided. Note: Each entry may have more than one let ...
... Answer the following questions. Each question is worth 4 points. You have 3 hours to complete this exam. 1) Below are seven amino acids. Indicate all characteristics that apply to each amino acid by writing the appropriate letter(s) in the blanks provided. Note: Each entry may have more than one let ...
Macromolecules
... Structural Proteins and Functional Proteins • Some proteins are structural and provide support in hair, horns, spider webs, etc. ...
... Structural Proteins and Functional Proteins • Some proteins are structural and provide support in hair, horns, spider webs, etc. ...
UNIT 2: BIOCHEMISTRY/ENZYMES
... How do we get these macromolecules? • When we eat, large organic food molecules such as proteins and starches must initially be broken down to enter cells • Proteins amino acids • Starches simple sugars • These nutrients can now enter the cell and be used as building blocks of compounds needed ...
... How do we get these macromolecules? • When we eat, large organic food molecules such as proteins and starches must initially be broken down to enter cells • Proteins amino acids • Starches simple sugars • These nutrients can now enter the cell and be used as building blocks of compounds needed ...
biomolecule notes
... f. Examples: Triglycerides = butter, waxes = waterproof coatings, steroids = testosterone & cholesterol ...
... f. Examples: Triglycerides = butter, waxes = waterproof coatings, steroids = testosterone & cholesterol ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.