Information Sheet - HJ Baker & Bro., Inc.
... Every farm is different. Different cows, different management practices, different forages, different temperature zones ... different. For many of these farms H.J. Baker’s original PRO-LAK® By-pass Protein Concentrate - backed with over 20 years of research - is just what they need. The approach and ...
... Every farm is different. Different cows, different management practices, different forages, different temperature zones ... different. For many of these farms H.J. Baker’s original PRO-LAK® By-pass Protein Concentrate - backed with over 20 years of research - is just what they need. The approach and ...
Ch 3 The Molecules of Cells
... Chemically active Used in all biological processes e.g. antibodies, enzymes, proteinbased hormones ...
... Chemically active Used in all biological processes e.g. antibodies, enzymes, proteinbased hormones ...
1 Name Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Chemical Level of
... 25. The basic make-up of an organic compound are the carbons making the ___________________________. When hydrogens are attached to this, you can refer to that compound as a _________________________. Attached to these basic units are _______________________________ which confers characteristic chem ...
... 25. The basic make-up of an organic compound are the carbons making the ___________________________. When hydrogens are attached to this, you can refer to that compound as a _________________________. Attached to these basic units are _______________________________ which confers characteristic chem ...
Amino Acid Uptake for the Synthesis of Secretory Protein by the
... Cell-free translation: A precursor prolein synthesis : S}'nlhesis of secretory milk proteins: Epithelial cells in the mammary gland proliferate extensively during pregnancy and synthesize large amounts of mammary specific proteins, «-LA and casein-during gestation and lactation. Milk protein mRNAs h ...
... Cell-free translation: A precursor prolein synthesis : S}'nlhesis of secretory milk proteins: Epithelial cells in the mammary gland proliferate extensively during pregnancy and synthesize large amounts of mammary specific proteins, «-LA and casein-during gestation and lactation. Milk protein mRNAs h ...
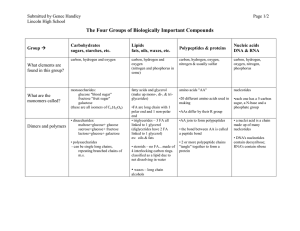
The Four Groups of Biologically Important Compounds
... lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
... lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
lect3
... 1. Primary: amino acid sequence 2. Secondary: describes chain’s orientation in space; e.g., alpha helix, beta sheet ...
... 1. Primary: amino acid sequence 2. Secondary: describes chain’s orientation in space; e.g., alpha helix, beta sheet ...
No Slide Title
... variety of structures enabling it to perform all the functions necessary for the maintenance of life. 3) A ____________ multicellular organism consists of more than one cell. In advanced animals and plants these are arranged into tissues giving a division of labour. 4) _________ Variation in cell st ...
... variety of structures enabling it to perform all the functions necessary for the maintenance of life. 3) A ____________ multicellular organism consists of more than one cell. In advanced animals and plants these are arranged into tissues giving a division of labour. 4) _________ Variation in cell st ...
Document
... Under physiological conditions of solvent and temperature, each protein folds spontaneously into one 3D conformation, called the native conformation. This conformation is usually the most stable thermodynamically, and Usually only the native conformation is functional. ...
... Under physiological conditions of solvent and temperature, each protein folds spontaneously into one 3D conformation, called the native conformation. This conformation is usually the most stable thermodynamically, and Usually only the native conformation is functional. ...
Proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids
... There are many different types of steroids. They are all lipids. Their functions vary. Some common steroids are: ...
... There are many different types of steroids. They are all lipids. Their functions vary. Some common steroids are: ...
Chymotrypsin
... • Chymotrypsin is one of the serine proteases. • Chymotrypsin is selective for peptide bonds with aromatic or large hydrophobic side chains, such as Tyr, Trp, Phe and Met, which are on the carboxyl side of this bond. It can also catalyze the hydrolysis of easter bond. • The main catalytic driving fo ...
... • Chymotrypsin is one of the serine proteases. • Chymotrypsin is selective for peptide bonds with aromatic or large hydrophobic side chains, such as Tyr, Trp, Phe and Met, which are on the carboxyl side of this bond. It can also catalyze the hydrolysis of easter bond. • The main catalytic driving fo ...
workshops: absences: examinations: textbook
... Thick and thin protein filaments, myosin, actin, tropomyosin and the troponin complex. Muscle contraction involves thick and thin filaments sliding past each other. Myosin forms thick filaments, hydrolyses ATP and reversibly binds actin. Structure of myosin and actin. Dissociation of ADP from myosin ...
... Thick and thin protein filaments, myosin, actin, tropomyosin and the troponin complex. Muscle contraction involves thick and thin filaments sliding past each other. Myosin forms thick filaments, hydrolyses ATP and reversibly binds actin. Structure of myosin and actin. Dissociation of ADP from myosin ...
Open questions - in brief: Beyond -omics, missing organisms
... There has been a recent proliferation of publications that describe the identification of intracellular cytosol-based multi-protein complexes in various organisms that can act as functional modules for diverse biochemical activities. The method of choice is generally a form of affinity purification ...
... There has been a recent proliferation of publications that describe the identification of intracellular cytosol-based multi-protein complexes in various organisms that can act as functional modules for diverse biochemical activities. The method of choice is generally a form of affinity purification ...
AP European History (Sem 1), Unit 03, Lesson 04
... The chemical interactions of the R groups of the amino acids allow proteins to rearrange spontaneously to form tertiary and quaternary structures. The order in which the amino acids are linked determines the structure and the function of that protein. Although amino acids B and I are distant in ...
... The chemical interactions of the R groups of the amino acids allow proteins to rearrange spontaneously to form tertiary and quaternary structures. The order in which the amino acids are linked determines the structure and the function of that protein. Although amino acids B and I are distant in ...
Whittier Union High School District
... 20. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Eukaryotic Cells have a nucleus and many organelles, prokaryotic cells do not. 21. Give an example of a prokaryotic cell: Bacteria 22. Give at least two examples of eukaryotic cells: Plant cells and animal cells 23. What is a virus ...
... 20. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Eukaryotic Cells have a nucleus and many organelles, prokaryotic cells do not. 21. Give an example of a prokaryotic cell: Bacteria 22. Give at least two examples of eukaryotic cells: Plant cells and animal cells 23. What is a virus ...
File - Biology
... functions carried out by carbohydrates are that they are used as the main source of energy in organisms, and they are used for structural purposes. If you didn’t already know, carbohydrates are sugar or starch. Simple sugars made of one carbohydrate are called monosaccharides. Complex sugars (starch ...
... functions carried out by carbohydrates are that they are used as the main source of energy in organisms, and they are used for structural purposes. If you didn’t already know, carbohydrates are sugar or starch. Simple sugars made of one carbohydrate are called monosaccharides. Complex sugars (starch ...
Amino acids
... and the host animal access to a rich source of energy. Another important structural polysaccharide is chitin, used in the exoskeletons of arthropods (including insects, spiders, and ...
... and the host animal access to a rich source of energy. Another important structural polysaccharide is chitin, used in the exoskeletons of arthropods (including insects, spiders, and ...
Digestion processes
... Major food groups • Carbohydrates = sugars = saccharides • Lipids = fats • Proteins • nucleic acids Carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acids (but not fats) are long chains of smaller subunits, which are monomers. The combinations are polymers. Polymers in which the order of monomers provides info ...
... Major food groups • Carbohydrates = sugars = saccharides • Lipids = fats • Proteins • nucleic acids Carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acids (but not fats) are long chains of smaller subunits, which are monomers. The combinations are polymers. Polymers in which the order of monomers provides info ...
Enzyme
... are summarized below: Hydrogen bond between neighboring backbone segments. Hydrogen bonds of side chains with each other or with backbone atoms. Ionic attractions between side chain groups or salt bridge. Hydrophobic interactions between side chain groups. Covalent sulfur-sulfur bonds. ...
... are summarized below: Hydrogen bond between neighboring backbone segments. Hydrogen bonds of side chains with each other or with backbone atoms. Ionic attractions between side chain groups or salt bridge. Hydrophobic interactions between side chain groups. Covalent sulfur-sulfur bonds. ...
Document
... d. Complex carbohydrates are found in fruits, vegetables, beans, & grains. i. Dietary fiber (roughage) is indigestible complex carbohydrates but good because it helps keep good cholesterol levels & may reduce risk of cancers. 4. Proteins COOa. made of amino acids: 20+ (R-CH-NH3+; R= side chain/ spec ...
... d. Complex carbohydrates are found in fruits, vegetables, beans, & grains. i. Dietary fiber (roughage) is indigestible complex carbohydrates but good because it helps keep good cholesterol levels & may reduce risk of cancers. 4. Proteins COOa. made of amino acids: 20+ (R-CH-NH3+; R= side chain/ spec ...
Discovery Research and Cell Culture
... of things, e.g. within blood (for carrying molecules and for clotting), for digestion (enzymes are proteins), for movement (actin and myosin in muscle), etc. One other major role of proteins is that of "structural proteins", i.e. those proteins that contribute to and sustain the integrity of the hum ...
... of things, e.g. within blood (for carrying molecules and for clotting), for digestion (enzymes are proteins), for movement (actin and myosin in muscle), etc. One other major role of proteins is that of "structural proteins", i.e. those proteins that contribute to and sustain the integrity of the hum ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.