Learning Guide for Chapter 16
... What are the two ways in which epoxides may be formed? 1) alkene + peroxy acid --> epoxide 2) halohydrin + base --> epoxide Epoxidation of alkenes What do peroxyacids look like? O R ...
... What are the two ways in which epoxides may be formed? 1) alkene + peroxy acid --> epoxide 2) halohydrin + base --> epoxide Epoxidation of alkenes What do peroxyacids look like? O R ...
Catalytic, Enantioselective Alkylations of N,O- and
... provide complementary deprotection procedures. For example, acetal l b with a 2,6dimethyl-4-methoxybenzenesulfonyl (Mds) 7 group reacts with enol silane 4a in the presence of 5 mol% 2 to yield 87% of compound 5d (94% ee, entry 4). It is noteworthy that the nature of the leaving group in substrate lc ...
... provide complementary deprotection procedures. For example, acetal l b with a 2,6dimethyl-4-methoxybenzenesulfonyl (Mds) 7 group reacts with enol silane 4a in the presence of 5 mol% 2 to yield 87% of compound 5d (94% ee, entry 4). It is noteworthy that the nature of the leaving group in substrate lc ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
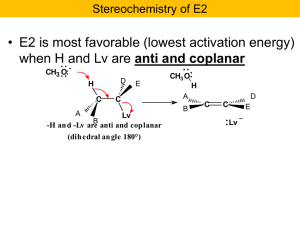
... C=C π bond as the bromide ion (Br:-) leaves from Cα with its bonding electron pair. The designation E2 stands for "elimination (E) with a bimolecular (2) transition state." The E2 transition state is bimolecular because it contains both the base and the haloalkane substrate (Figure 9.06). The rate l ...
... C=C π bond as the bromide ion (Br:-) leaves from Cα with its bonding electron pair. The designation E2 stands for "elimination (E) with a bimolecular (2) transition state." The E2 transition state is bimolecular because it contains both the base and the haloalkane substrate (Figure 9.06). The rate l ...
New Phenylglycine-Derived Primary Amine Organocatalysts for the
... anticipated by us that introducing sterically more demanding side chains through cyclohexylglycine or tert-leucine (amino alcohols 16–17) would enhance the enantioselectivity even further, a hypothesis obviously invalidated by experiment. Clearly, the presence of an aromatic moiety is crucial. Among ...
... anticipated by us that introducing sterically more demanding side chains through cyclohexylglycine or tert-leucine (amino alcohols 16–17) would enhance the enantioselectivity even further, a hypothesis obviously invalidated by experiment. Clearly, the presence of an aromatic moiety is crucial. Among ...
the suzuki-miyaura reaction and boron reagents – mechanism
... (3) Miyaura, N.; Yamada, K.; Suzuki, A. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 3437. (4) Miyaura, N.; Suzuki, A. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1979, 866. (5) Miyaura, N.; Yamada, K.; Suginome, H.; Suzuki, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 972. (6) Miyaura, N.; Suzuki, A. J. Organomet. Chem. 1981, 213, C53. ...
... (3) Miyaura, N.; Yamada, K.; Suzuki, A. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 3437. (4) Miyaura, N.; Suzuki, A. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1979, 866. (5) Miyaura, N.; Yamada, K.; Suginome, H.; Suzuki, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 972. (6) Miyaura, N.; Suzuki, A. J. Organomet. Chem. 1981, 213, C53. ...
4.9 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen Halides
... by positively charged carbon because the s orbital can overlap with the empty 2p orbital of positively charged carbon ...
... by positively charged carbon because the s orbital can overlap with the empty 2p orbital of positively charged carbon ...
Reaction Rates
... reactions because the molecules collide in unfavorable orientations. A carbon atom does not contact an oxygen atom at the instant of impact, so the molecules simply rebound. When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transfe ...
... reactions because the molecules collide in unfavorable orientations. A carbon atom does not contact an oxygen atom at the instant of impact, so the molecules simply rebound. When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transfe ...
Notes 10
... CLASSIFYING REACTIONS Reactions are conveniently classified as substitutions, additions, eliminations and rearrangements. These terms describe the overall process, simply comparing the structure of starting materials and products. They do not indicate anything about the pathway (“mechanism”) by whi ...
... CLASSIFYING REACTIONS Reactions are conveniently classified as substitutions, additions, eliminations and rearrangements. These terms describe the overall process, simply comparing the structure of starting materials and products. They do not indicate anything about the pathway (“mechanism”) by whi ...
Organic 331
... 5. Viscosity (resistance to flow) increases with chain length 4.8 Sigma Bonds and Bond Rotation Ethane has free rotation about the C-C (σ bond). ...
... 5. Viscosity (resistance to flow) increases with chain length 4.8 Sigma Bonds and Bond Rotation Ethane has free rotation about the C-C (σ bond). ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
... Task: convert to a staggered structure wherein H and Br are anti and predict product. We will convert to a Newman and see what we get… Ph ...
... Task: convert to a staggered structure wherein H and Br are anti and predict product. We will convert to a Newman and see what we get… Ph ...
Chapter 21: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH3. Nitrogen
... Electron-donating substituents (-CH3, -OH, -OCH3) make the substituted aniline more basic than aniline itself (the pKa of the substituted anilinium ion is higher than 4.6) Electron-withdrawing substituents (-Cl, -NO2) make the substituted aniline less basic than aniline itself (the pKa of the substi ...
... Electron-donating substituents (-CH3, -OH, -OCH3) make the substituted aniline more basic than aniline itself (the pKa of the substituted anilinium ion is higher than 4.6) Electron-withdrawing substituents (-Cl, -NO2) make the substituted aniline less basic than aniline itself (the pKa of the substi ...
13_lecture_ppt
... Preparation of aldehydes and ketones • Principal means of preparation is oxidation of the corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
... Preparation of aldehydes and ketones • Principal means of preparation is oxidation of the corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
Organic Chemistry - UCR Chemistry
... organic chemists commonly refer to this mechanism as "unimolecular nucleophilic substitution". The term substitution indicates that one group (N) has taken the place of (substituted) another group (X). The term nucleophilic signifies that the new group N participates in the reaction as a nucleophile ...
... organic chemists commonly refer to this mechanism as "unimolecular nucleophilic substitution". The term substitution indicates that one group (N) has taken the place of (substituted) another group (X). The term nucleophilic signifies that the new group N participates in the reaction as a nucleophile ...
Some uses of mischmetall in organic synthesis
... Results and discussion Mischmetall as a coreductant in samarium(II) catalysed reactions Since its introduction in synthetic organic chemistry in 1977,1 samarium diiodide has become one of the most popular reagents. However, its cost could be considered as a major drawback, potentially limiting the d ...
... Results and discussion Mischmetall as a coreductant in samarium(II) catalysed reactions Since its introduction in synthetic organic chemistry in 1977,1 samarium diiodide has become one of the most popular reagents. However, its cost could be considered as a major drawback, potentially limiting the d ...
lecture 7 reductive eliminations
... • A troublesome feature of these reactions is that minor changes in the structure of the substrate, the complex, or in impurities present in the reagents of solvents can sometimes be enough to change the rate, and even the predominant mechanism of a given reaction. ...
... • A troublesome feature of these reactions is that minor changes in the structure of the substrate, the complex, or in impurities present in the reagents of solvents can sometimes be enough to change the rate, and even the predominant mechanism of a given reaction. ...
7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
... • Oxidizing reagents other than ozone also cleave alkenes • Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) can produce carboxylic acids and carbon dioxide if H’s are present on C=C O ...
... • Oxidizing reagents other than ozone also cleave alkenes • Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) can produce carboxylic acids and carbon dioxide if H’s are present on C=C O ...
Direct organocatalytic enantioselective a-aminomethylation
... has also led to development of several amino acid catalyzed stereoselective reactions.14 List reported the first one-pot three-component Mannich reaction between in situ generated imines and unmodified ketones as donors.15 This initial report led to the development of several novel Mannich-type reac ...
... has also led to development of several amino acid catalyzed stereoselective reactions.14 List reported the first one-pot three-component Mannich reaction between in situ generated imines and unmodified ketones as donors.15 This initial report led to the development of several novel Mannich-type reac ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.