Aldehydes and Ketones
... • The sp2 hybridized C–H proton of an aldehyde is highly deshielded and absorbs far downfield at 9–10 ppm. • Splitting occurs with protons on the α carbon, but the coupling constant is often very small (J = 1–3 Hz). • Protons on the α carbon to the carbonyl group absorb at ...
... • The sp2 hybridized C–H proton of an aldehyde is highly deshielded and absorbs far downfield at 9–10 ppm. • Splitting occurs with protons on the α carbon, but the coupling constant is often very small (J = 1–3 Hz). • Protons on the α carbon to the carbonyl group absorb at ...
Chapter Seven - U of L Class Index
... H Carbocation rearrangments are often promoted by the presence of Lewis Acids. In this case, the intermediates are said to be “carbocation-like” if not carbocations. ...
... H Carbocation rearrangments are often promoted by the presence of Lewis Acids. In this case, the intermediates are said to be “carbocation-like” if not carbocations. ...
chemical kinetics
... react simultaneously is very small. Hence, reactions with the molecularity three are very rare and slow to proceed. It is, therefore, evident that complex reactions involving more than three molecules in the stoichiometric equation must take place in more than one step. KClO3 + 6FeSO4 + 3H2SO4 → KCl ...
... react simultaneously is very small. Hence, reactions with the molecularity three are very rare and slow to proceed. It is, therefore, evident that complex reactions involving more than three molecules in the stoichiometric equation must take place in more than one step. KClO3 + 6FeSO4 + 3H2SO4 → KCl ...
Homogeneous Catalysis
... NO2 and ClNO are formed in this reaction should therefore be directly proportional to the concentrations of both ClNO2 and NO. Rate = k(ClNO2)(NO) The collision theory model suggests that the rate of any step in a reaction is proportional to the concentrations of the reagents consumed in that step. ...
... NO2 and ClNO are formed in this reaction should therefore be directly proportional to the concentrations of both ClNO2 and NO. Rate = k(ClNO2)(NO) The collision theory model suggests that the rate of any step in a reaction is proportional to the concentrations of the reagents consumed in that step. ...
Pincer Complexes. Applications in Catalysis
... of these complexes have shown activity in the dehydrogenation of alkanes to alkenes. However, the extremely low reaction rates and the low turnover numbers or the instability of the employed catalysts under the reaction conditions16 has limited the use of these species. In 1976 Moulton and Shaw repo ...
... of these complexes have shown activity in the dehydrogenation of alkanes to alkenes. However, the extremely low reaction rates and the low turnover numbers or the instability of the employed catalysts under the reaction conditions16 has limited the use of these species. In 1976 Moulton and Shaw repo ...
interaction of alcohols with alkalies under autogeneous pressure
... The tendency for the increased yield of sodium carbonate is also evident when the quantity of sodium hydroxide in the reaction mixture is enhanced (Table II). Very often the yield of sodium carbonate is enhanced at the cost of sodium acetate (Table I, Experiments 6 and 7). It is therefore necessary ...
... The tendency for the increased yield of sodium carbonate is also evident when the quantity of sodium hydroxide in the reaction mixture is enhanced (Table II). Very often the yield of sodium carbonate is enhanced at the cost of sodium acetate (Table I, Experiments 6 and 7). It is therefore necessary ...
Phenol - Macmillan Academy
... Electron pair donation takes place from a p orbital on oxygen It increases the electron density of the delocalised system It makes substitution much easier compared to benzene The electron density is the greatest at the 2,4 and 6 positions Substitution takes place at the 2,4 and 6 positions Phenol r ...
... Electron pair donation takes place from a p orbital on oxygen It increases the electron density of the delocalised system It makes substitution much easier compared to benzene The electron density is the greatest at the 2,4 and 6 positions Substitution takes place at the 2,4 and 6 positions Phenol r ...
Chapter 1 Organoaluminum Reagents for Selective Organic
... 1.3. Beckmann Rearrangement Using Organoaluminum Reagent The Beckmann rearrangement is the skeletal rearrangement of ketoximes in the presence of certain acids under aqueous conditions to give amides or lactams. Reexamination of this reaction using organoaluminum reagents under aprotic conditions le ...
... 1.3. Beckmann Rearrangement Using Organoaluminum Reagent The Beckmann rearrangement is the skeletal rearrangement of ketoximes in the presence of certain acids under aqueous conditions to give amides or lactams. Reexamination of this reaction using organoaluminum reagents under aprotic conditions le ...
Nucleophilic Additions to Carbonyl Group
... converts into a product. Reaction mechanisms are the key to your understanding of organic chemistry. Knowing the mechanism of a reaction allows you to generalize your knowledge about organic chemistry and to predict the outcome of a new reaction with ...
... converts into a product. Reaction mechanisms are the key to your understanding of organic chemistry. Knowing the mechanism of a reaction allows you to generalize your knowledge about organic chemistry and to predict the outcome of a new reaction with ...
Catalytic Functionalization of Methyl Group on Silicon: Iridium
... demonstrated recently in C(sp3)−H silylation and borylation. See refs 4k and 15. (18) Double borylated products were not observed at all under the conditions using an excess amount of 3 (4 equiv). When the borylation of 3b was carried out with 2.2 equiv of 1 in cyclooctane at 110 °C for 12 h, the do ...
... demonstrated recently in C(sp3)−H silylation and borylation. See refs 4k and 15. (18) Double borylated products were not observed at all under the conditions using an excess amount of 3 (4 equiv). When the borylation of 3b was carried out with 2.2 equiv of 1 in cyclooctane at 110 °C for 12 h, the do ...
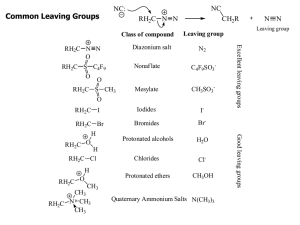
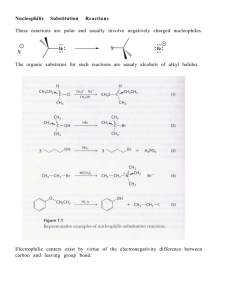
Chem 314 Preorganic Evaluation
... only weak base/nucleophiles (usually the same molecule: H-B: = H-Nu:) will be used in these reactions, usually it is the solvent molecule (H2O, ROH or RCO2H in this book) the solvent is usually a polar, protic solvent that is capable of stabilizing charged intermediates the only synthetically useful ...
... only weak base/nucleophiles (usually the same molecule: H-B: = H-Nu:) will be used in these reactions, usually it is the solvent molecule (H2O, ROH or RCO2H in this book) the solvent is usually a polar, protic solvent that is capable of stabilizing charged intermediates the only synthetically useful ...
13-Elimination Reactions
... isomer of an alkene. Regioselective elimination reactions, on the other hand, produce several different isomers, but give one isomer in greater quantity than the others. Whether a reaction is regiospecific or regioselective depends on whether the reaction prefers to eliminate only one particular β h ...
... isomer of an alkene. Regioselective elimination reactions, on the other hand, produce several different isomers, but give one isomer in greater quantity than the others. Whether a reaction is regiospecific or regioselective depends on whether the reaction prefers to eliminate only one particular β h ...
T_AllylCF3paperBM[5]
... to control fluorinated compounds transformations very effectively. CF3-substituted carbocations are very promising but still rare type of fluorinated species exhibited high electrophilicity and selectivity.3 The present work is a continuation of our investigations on electrophilic activation of alke ...
... to control fluorinated compounds transformations very effectively. CF3-substituted carbocations are very promising but still rare type of fluorinated species exhibited high electrophilicity and selectivity.3 The present work is a continuation of our investigations on electrophilic activation of alke ...
Asymmetric Catalytic Aldol
... • Over 30 have been identified to date • Type I aldolases are primarily found in animals and plants and activate the donor by forming a schiff base as an intermediate. • Type II aldolases are found in bacteria and fungi and contain a Zn2+ cofactor in the active site. • In both types of aldolases the ...
... • Over 30 have been identified to date • Type I aldolases are primarily found in animals and plants and activate the donor by forming a schiff base as an intermediate. • Type II aldolases are found in bacteria and fungi and contain a Zn2+ cofactor in the active site. • In both types of aldolases the ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.


















![T_AllylCF3paperBM[5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003584459_1-3decab572f7fca68901a941affab18ea-300x300.png)