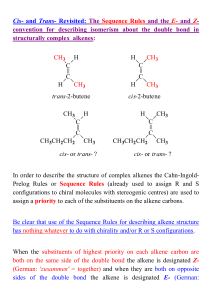
Lecture 1: Key Concepts in Stereoselective Synthesis
... Overall, the reactions are exothermic but nearly ergoneutral. The electronic effect on this reaction is almost purely a result of kinetics, not thermodynamics. Factors, as the equilibrium constants, for these additions are similar (entries 2 vs. 1, 3 vs. 1). In contrast, steric properties of the ami ...
... Overall, the reactions are exothermic but nearly ergoneutral. The electronic effect on this reaction is almost purely a result of kinetics, not thermodynamics. Factors, as the equilibrium constants, for these additions are similar (entries 2 vs. 1, 3 vs. 1). In contrast, steric properties of the ami ...
Organic Chemistry
... Crossed Enolate Reactions using LDA • Equilibrium among enolate anions is established when the ketone is in slight excess, a condition under which it is possible for proton-transfer reactions to occur between an enolate and an a-hydrogen of an unreacted ketone. Thus, equilibrium is established betw ...
... Crossed Enolate Reactions using LDA • Equilibrium among enolate anions is established when the ketone is in slight excess, a condition under which it is possible for proton-transfer reactions to occur between an enolate and an a-hydrogen of an unreacted ketone. Thus, equilibrium is established betw ...
Theoretical studies of systems of biochemical interest containing Fe
... and Cu(II). This fact involves that enzymes active sites are designed to cope with the remarkably different coordination preferences for these two ions. Although the Cu(III) oxidation state is generally considered to be unreachable due to the highly positive Cu(III)/Cu(II) redox potentials that resu ...
... and Cu(II). This fact involves that enzymes active sites are designed to cope with the remarkably different coordination preferences for these two ions. Although the Cu(III) oxidation state is generally considered to be unreachable due to the highly positive Cu(III)/Cu(II) redox potentials that resu ...
Organic Chemistry Introduction
... Nomenclature Disubstituted Benzene • Relative positions on a benzene ring – ortho- (o) on adjacent carbons (1,2) – meta- (m) separated by one carbon (1,3) – para- (p) separated by two carbons (1,4) ...
... Nomenclature Disubstituted Benzene • Relative positions on a benzene ring – ortho- (o) on adjacent carbons (1,2) – meta- (m) separated by one carbon (1,3) – para- (p) separated by two carbons (1,4) ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation by Reductive
... Titanium(II) bis(tetrahydrofuran) 1, generated by the treatm ent of TiCl4 in TH F with two equivalents of n-butyllithium at -7 8 °C, has been found to form carbon-carbon bonds with a variety of organic substrates by reductive coupling. Diphenylacetylene is dimerized to ex clusively (E,E)-1,2,3,4-te ...
... Titanium(II) bis(tetrahydrofuran) 1, generated by the treatm ent of TiCl4 in TH F with two equivalents of n-butyllithium at -7 8 °C, has been found to form carbon-carbon bonds with a variety of organic substrates by reductive coupling. Diphenylacetylene is dimerized to ex clusively (E,E)-1,2,3,4-te ...
C - Deans Community High School
... Reacting hydrogen with ethene to form ethane would be an example of this type of reaction. ...
... Reacting hydrogen with ethene to form ethane would be an example of this type of reaction. ...
Alkenes 3 - ChemWeb (UCC)
... This reaction illustrated above is called a 1,2- or -elimination to indicate that the groups being eliminated are located on adjacent atoms in the starting material as compared to a 1,1- or -elimination where both are located on the same carbon atom This, in itself, tells you nothing about the act ...
... This reaction illustrated above is called a 1,2- or -elimination to indicate that the groups being eliminated are located on adjacent atoms in the starting material as compared to a 1,1- or -elimination where both are located on the same carbon atom This, in itself, tells you nothing about the act ...
6 Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
... The orbitals containing a pair of electrons are not capable of combination. In fact, half-filled orbitals on one atom have a tendency to combine with half-filled orbitals on other atom, and the resulting orbital acquires a pair of electrons of opposite spins. (2) The atoms with valence or bonding or ...
... The orbitals containing a pair of electrons are not capable of combination. In fact, half-filled orbitals on one atom have a tendency to combine with half-filled orbitals on other atom, and the resulting orbital acquires a pair of electrons of opposite spins. (2) The atoms with valence or bonding or ...
Rutgers...Ch17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... more electronegative element (bad) since it has more bonds than the previous structure (good) and also carbon now has a full octet (good). This type of stabilization is called resonance stabilization. The oxygen atom is said to be resonance donating, or pi donating since it is donating electron dens ...
... more electronegative element (bad) since it has more bonds than the previous structure (good) and also carbon now has a full octet (good). This type of stabilization is called resonance stabilization. The oxygen atom is said to be resonance donating, or pi donating since it is donating electron dens ...
Chapter 18 – Carbonyl Compounds II (Last Chapter we mostly talk
... Nu directly to the carbonyl carbon. This type of addition, however, isn’t the only way that Nu can add, when a molecule contains a carbonyl group). (It can also undergo something called conjugate addition or also called 1,4 addition) ...
... Nu directly to the carbonyl carbon. This type of addition, however, isn’t the only way that Nu can add, when a molecule contains a carbonyl group). (It can also undergo something called conjugate addition or also called 1,4 addition) ...
A family of intracules, a conjecture and the electron correlation... z* Peter M. W. Gill,* Deborah L. Crittenden,w
... been the single greatest challenge to the progress of quantum chemistry since the subject’s inception in 1927. Models of electron correlation fall into two broad classes. Those in the first class, which include configuration interaction, Møller–Plesset perturbation theory and coupled cluster theory,9 ...
... been the single greatest challenge to the progress of quantum chemistry since the subject’s inception in 1927. Models of electron correlation fall into two broad classes. Those in the first class, which include configuration interaction, Møller–Plesset perturbation theory and coupled cluster theory,9 ...
Answers to Midterm Practice Questions
... c. IR absorption : absorption of electromagnetic radiation (emr) in the infrared range (approx. 4000 – 400 cm–1), causing transition from one vibrational level to a higher vibrational level ( increase in amplitude, but (ideally) not in frequency) d. wavenumber: number of waves per unit length; custo ...
... c. IR absorption : absorption of electromagnetic radiation (emr) in the infrared range (approx. 4000 – 400 cm–1), causing transition from one vibrational level to a higher vibrational level ( increase in amplitude, but (ideally) not in frequency) d. wavenumber: number of waves per unit length; custo ...
Photo-induced metal–ligand bond weakening, potential
... parameters for both of the ligands interacting with the specific metal must be known. Modern molecular orbital methods make it easy to calculate the bonding properties of any type of ligand. For ionic ‘Werner’ complexes where crystal-field theory parameters have been calculated, useful estimations c ...
... parameters for both of the ligands interacting with the specific metal must be known. Modern molecular orbital methods make it easy to calculate the bonding properties of any type of ligand. For ionic ‘Werner’ complexes where crystal-field theory parameters have been calculated, useful estimations c ...
Microsoft Word
... substituents of the chiral sulfur atom: a lone pair of electrons, an oxygen atom and two different carbon ligands. It is well known that sulfoxides participate as neighbouring groups in a number of reactions. Sulfoxide group participation in halohydrin formation from cyclic and simple acyclic olefin ...
... substituents of the chiral sulfur atom: a lone pair of electrons, an oxygen atom and two different carbon ligands. It is well known that sulfoxides participate as neighbouring groups in a number of reactions. Sulfoxide group participation in halohydrin formation from cyclic and simple acyclic olefin ...
Topic 8 notes - A
... b) Elimination of hydrogen halides to make alkenes If haloalkanes are boiled with an ethanolic solution of KOH instead of with an aqueous solution, they will undergo elimination of an HX molecule to give an alkene: R1R2CHR3R4CBr + OH- R1R2C=CR3R4 + Br- + H2O NaOH is not used since it is only spari ...
... b) Elimination of hydrogen halides to make alkenes If haloalkanes are boiled with an ethanolic solution of KOH instead of with an aqueous solution, they will undergo elimination of an HX molecule to give an alkene: R1R2CHR3R4CBr + OH- R1R2C=CR3R4 + Br- + H2O NaOH is not used since it is only spari ...
revised Chemical Kinetics
... of you, and you come to a stop at a red light. You speed up when entering a multilane freeway in light traffic, and then slow down again when you exit the freeway. So the driver who travels 80 miles in 2 hours has an average speed of 40 miles / hour, but the actual speed at any moment of time could ...
... of you, and you come to a stop at a red light. You speed up when entering a multilane freeway in light traffic, and then slow down again when you exit the freeway. So the driver who travels 80 miles in 2 hours has an average speed of 40 miles / hour, but the actual speed at any moment of time could ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.