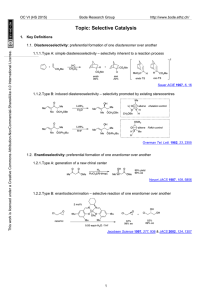
First palladium- and nickel-catalyzed oxidative
... on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involved in the overall process as selective deuteration at the terminal position of the alkene leads to diaster ...
... on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involved in the overall process as selective deuteration at the terminal position of the alkene leads to diaster ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions
... the amount of reaction that has occurred. Then you measure the rate of the reaction with varying amounts of the substance being tested, while all other reaction conditions are held constant. If the reaction rate increases as the concentration of the substance tested increases, it is very likely that ...
... the amount of reaction that has occurred. Then you measure the rate of the reaction with varying amounts of the substance being tested, while all other reaction conditions are held constant. If the reaction rate increases as the concentration of the substance tested increases, it is very likely that ...
M.Sc.Course - Department of Chemistry, IIT Bombay
... checking their purity. Separation of enantiomers and measurements of optical rotation. Studies of electrophilic/nucleophilic substitution reactions, redox reactions. CH 223 Structure and Stereochemistry Frontier molecular orbitals and organic reactions: Introduction to HOMO and LUMO, classification ...
... checking their purity. Separation of enantiomers and measurements of optical rotation. Studies of electrophilic/nucleophilic substitution reactions, redox reactions. CH 223 Structure and Stereochemistry Frontier molecular orbitals and organic reactions: Introduction to HOMO and LUMO, classification ...
Studies toward the Stereoselective Synthesis of the
... plays a pivotal role in this synthetic route as all 4 stereogenic centres present in the 3,7dimethylundecane-1,5,6-triol target are generated by this methodology at three different stages of the proposed synthesis. The epoxy alcohol formed at each stage was subjected to regioselective ring opening f ...
... plays a pivotal role in this synthetic route as all 4 stereogenic centres present in the 3,7dimethylundecane-1,5,6-triol target are generated by this methodology at three different stages of the proposed synthesis. The epoxy alcohol formed at each stage was subjected to regioselective ring opening f ...
A Model For the Calculation of Solvent ... Reaction Rates for Process Design Purposes
... along a bond or a set of contiguous bonds and can be defined in quantum mechanical terms as operators that act on the electronic population matrix. Operators are bondspecific and have weights associated to them, indicating how much a certain bond or chain of bonds contributes to the concentration (o ...
... along a bond or a set of contiguous bonds and can be defined in quantum mechanical terms as operators that act on the electronic population matrix. Operators are bondspecific and have weights associated to them, indicating how much a certain bond or chain of bonds contributes to the concentration (o ...
CHEM 203 Material
... Principle: determining whether the bonded state of a given atom resembles more closely the preceding or the successive noble gas allows one to make important predictions about chemical reactivity: Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of – ...
... Principle: determining whether the bonded state of a given atom resembles more closely the preceding or the successive noble gas allows one to make important predictions about chemical reactivity: Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of – ...
Changing counterion can switch the preference for selective 1,2
... This is especially common for Pd-catalyzed reactions, where the directing group also helps stabilize high oxidation state intermediates. In the example below, the pivanilide group directs ortho-palladation of the aromatic ring. Note that consecutive alkylations/arylations are hallmarks of electrophi ...
... This is especially common for Pd-catalyzed reactions, where the directing group also helps stabilize high oxidation state intermediates. In the example below, the pivanilide group directs ortho-palladation of the aromatic ring. Note that consecutive alkylations/arylations are hallmarks of electrophi ...
PHENOL - Gneet's
... The above reaction is laboratory method for preparation of phenol 2. Hydrolysis of diazonium salt ...
... The above reaction is laboratory method for preparation of phenol 2. Hydrolysis of diazonium salt ...
Document
... exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
... exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
Chapter 5 | Molecular Orbitals
... separate regions with opposite signs of the wave function. When two orbitals overlap, and the overlapping regions have the same sign, the sum of the two orbitals has an increased electron probability in the overlap region. When two regions of opposite sign overlap, the combination has a decreased el ...
... separate regions with opposite signs of the wave function. When two orbitals overlap, and the overlapping regions have the same sign, the sum of the two orbitals has an increased electron probability in the overlap region. When two regions of opposite sign overlap, the combination has a decreased el ...
Cerium(IV) Ammonium Nitrate as a Catalyst in
... José Carlos Menéndez was born in Madrid (1960) and obtained degrees in Pharmacy from Universidad Complutense at Madrid, UCM (1982) and Chemistry from UNED (1985), followed by a Ph.D. in Pharmacy from UCM in 1988, under the supervision of Dr. Mónica M. Söllhuber. In August 1988, he joined the gro ...
... José Carlos Menéndez was born in Madrid (1960) and obtained degrees in Pharmacy from Universidad Complutense at Madrid, UCM (1982) and Chemistry from UNED (1985), followed by a Ph.D. in Pharmacy from UCM in 1988, under the supervision of Dr. Mónica M. Söllhuber. In August 1988, he joined the gro ...
Aromatic heterocycles 1: structures and reactions
... Benzene is aromatic because it has six electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. We know it is aromatic because it is exceptionally stable and it has a ring current and hence large chemical shifts in the proton NMR spectrum as well as a special chemistry involving substitution rather than addition wi ...
... Benzene is aromatic because it has six electrons in a cyclic conjugated system. We know it is aromatic because it is exceptionally stable and it has a ring current and hence large chemical shifts in the proton NMR spectrum as well as a special chemistry involving substitution rather than addition wi ...
Aromatic Hydrocarbon Tutorial
... intermolecular interactions with H2O and other polar compounds, aromatic hydrocarbons are considered to be insoluble in these media. Remember, water is a polar (H-O-H) substance that forms an ordered medium characterized by a high degree of intermolecular H-bonding. To dissolve in water, a “solute” ...
... intermolecular interactions with H2O and other polar compounds, aromatic hydrocarbons are considered to be insoluble in these media. Remember, water is a polar (H-O-H) substance that forms an ordered medium characterized by a high degree of intermolecular H-bonding. To dissolve in water, a “solute” ...
Document
... exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
... exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
Development of New Synthetic Routes to Organoboronates by Catalytic Allylic Substitution and
... in organoboronate chemistry, in particular for transition metal catalyzed coupling reactions.131-132,188 These reagents are air- and thermostable species, which are usually easier to handle and purify, than other organoboronates. Recently, Batey and co-workers133-134 described the synthesis of a new ...
... in organoboronate chemistry, in particular for transition metal catalyzed coupling reactions.131-132,188 These reagents are air- and thermostable species, which are usually easier to handle and purify, than other organoboronates. Recently, Batey and co-workers133-134 described the synthesis of a new ...
View/Open
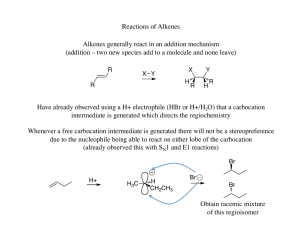
... isomers yield the same product—butane—but the heat of reaction is different in each case. On conversion to butane, 1-butene liberates the most heat (127 kJ mol-1), followed by cis-2-butene (120 kJ mol-1), with trans-2-butene producing the least heat (115 kJ mol-1). These data indicate that the trans ...
... isomers yield the same product—butane—but the heat of reaction is different in each case. On conversion to butane, 1-butene liberates the most heat (127 kJ mol-1), followed by cis-2-butene (120 kJ mol-1), with trans-2-butene producing the least heat (115 kJ mol-1). These data indicate that the trans ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.