PowerPoint 演示文稿
... in his early work, to test the theory. Studies of aliphatic substitutions and eliminations, often with his long-time collaborator E. D. Hughes, led to I ncorporation into the standard language of chemistry of such words as nucleophile, electrophile, inductive and mesomeric (resonance) effects, and s ...
... in his early work, to test the theory. Studies of aliphatic substitutions and eliminations, often with his long-time collaborator E. D. Hughes, led to I ncorporation into the standard language of chemistry of such words as nucleophile, electrophile, inductive and mesomeric (resonance) effects, and s ...
BSA - Sigma
... BSA (N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide) is one of the most commonly used silylating reagents. Its reactivity is similar to that of BSTFA, readily silylating a wide range of acidic functional groups such as non-sterically hindered alcohols, amides, amines, amino acids, carboxylic acids, and enols. It ...
... BSA (N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide) is one of the most commonly used silylating reagents. Its reactivity is similar to that of BSTFA, readily silylating a wide range of acidic functional groups such as non-sterically hindered alcohols, amides, amines, amino acids, carboxylic acids, and enols. It ...
New insights into the mechanism of sorbitol transformation
... cleavage reactions. The former can take place at the end of the carbon chain over aldehyde or carboxylic acid group (decarbonylation and decarboxylation) [11–14] or in the middle of the carbon chain (retro-aldol reaction) [15] along with dehydrogenation, hydrogenation, and water –gas shift (WGS) rea ...
... cleavage reactions. The former can take place at the end of the carbon chain over aldehyde or carboxylic acid group (decarbonylation and decarboxylation) [11–14] or in the middle of the carbon chain (retro-aldol reaction) [15] along with dehydrogenation, hydrogenation, and water –gas shift (WGS) rea ...
Chemical Reactivity and Biological Activity of Diketene
... reaction, which results in an amide bond in the NBP-diketene adduct. The lability of the amide bond as opposed to the amine bonds formed by β-propiolactone and β-butyrolactone could be one of the differential factors responsible for the lack of carcinogenicity of diketene. (v) Ab initio calculations ...
... reaction, which results in an amide bond in the NBP-diketene adduct. The lability of the amide bond as opposed to the amine bonds formed by β-propiolactone and β-butyrolactone could be one of the differential factors responsible for the lack of carcinogenicity of diketene. (v) Ab initio calculations ...
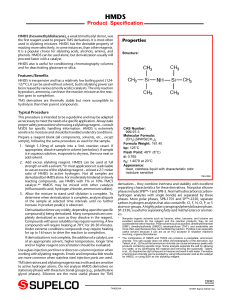
HMDS - Sigma
... increase in product peak(s) is observed. Derivatization times vary widely, depending upon the specific compound(s) being derivatized. Many compounds are completely derivatized as soon as they dissolve in the reagent. Compounds with poor solubility may require warming. A few compounds will require he ...
... increase in product peak(s) is observed. Derivatization times vary widely, depending upon the specific compound(s) being derivatized. Many compounds are completely derivatized as soon as they dissolve in the reagent. Compounds with poor solubility may require warming. A few compounds will require he ...
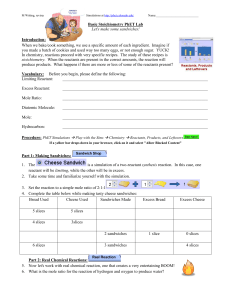
Basic Stoichometry
... Imagine if you made a batch of cookies and used way too many eggs, or not enough sugar. YUCK! In chemistry, reactions proceed with very specific recipes. The study of these recipes is stoichiometry. When the reactants are present in the correct amounts, the reaction will produce products. What happe ...
... Imagine if you made a batch of cookies and used way too many eggs, or not enough sugar. YUCK! In chemistry, reactions proceed with very specific recipes. The study of these recipes is stoichiometry. When the reactants are present in the correct amounts, the reaction will produce products. What happe ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, UNIVERSITY OF JYVÄSKYLÄ
... modern description of chemical bonding is based on quantum theory and the atomic shell structure, which easily rationalize why bonding is typically far simpler for s- and p-block elements than for their d- and f-block counterparts. It was also long thought that chemical bonding and covalent bonding ...
... modern description of chemical bonding is based on quantum theory and the atomic shell structure, which easily rationalize why bonding is typically far simpler for s- and p-block elements than for their d- and f-block counterparts. It was also long thought that chemical bonding and covalent bonding ...
Lokshin2011
... 1. By the methods of IR, UV-Vis spectroscopy and quantum chemistry, the possibility of obtaining photochromic systems based on cymantrene derivatives containing mono- and bifunctional n-donor and p-donor substituents was studied. 2. When irradiated by a mercury lamp, the CO molecule is abstracted fr ...
... 1. By the methods of IR, UV-Vis spectroscopy and quantum chemistry, the possibility of obtaining photochromic systems based on cymantrene derivatives containing mono- and bifunctional n-donor and p-donor substituents was studied. 2. When irradiated by a mercury lamp, the CO molecule is abstracted fr ...
Mock Exam One
... a.) LiAlH4 and a Ketone b.) CH3CH2MgBr and an Aldehyde c.) 2-butene and Hg(OAc)2, H2O followed by NaBH4 d.) All of these. 3.) Which of the following terms best describes the reactive nature of the Grignard ...
... a.) LiAlH4 and a Ketone b.) CH3CH2MgBr and an Aldehyde c.) 2-butene and Hg(OAc)2, H2O followed by NaBH4 d.) All of these. 3.) Which of the following terms best describes the reactive nature of the Grignard ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
Alkyl Halides SN and E reactions
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
... 3. Consider the nature of the solvent: For SN1 reactions, the solvent affects the rate only if it influences the stability of the charged transition state, i.e., the C+. The Nu:- is not involved in the rate determining step so solvent effects on the Nu:- do not affect the rate of SN1 reactions. ...
Chapter 12
... amine adduct with BF3 . Since the enthalpy of adduct formation is least favorable with BF3, however, it is concluded that the loss in BX double-bond character upon rehybridization to form an adduct is greater with BF3 than in the other tri halides. From this we can conclude that the double-bond cha ...
... amine adduct with BF3 . Since the enthalpy of adduct formation is least favorable with BF3, however, it is concluded that the loss in BX double-bond character upon rehybridization to form an adduct is greater with BF3 than in the other tri halides. From this we can conclude that the double-bond cha ...
Palladium and Ruthenium Catalyzed Reactions By Bryan Jaksic
... activity of commonly used precatalysts with the newly synthesized precatalyst, Pd(η5-C5H5)(η3-1Ph-C3H4), for Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Sonogashira reactions are important as they provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within impor ...
... activity of commonly used precatalysts with the newly synthesized precatalyst, Pd(η5-C5H5)(η3-1Ph-C3H4), for Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Sonogashira reactions are important as they provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within impor ...
52 - University of Strathclyde
... a synergic bimetallic-induced reaction.21 Interestingly, as mentioned above, Robinson recently reported a more conventional two-step metathetical methodology involving generation of an anionic dicarbene by C4-lithiation of IPr15 followed by transmetallation with the zinc alkyl ZnEt2 which led to the ...
... a synergic bimetallic-induced reaction.21 Interestingly, as mentioned above, Robinson recently reported a more conventional two-step metathetical methodology involving generation of an anionic dicarbene by C4-lithiation of IPr15 followed by transmetallation with the zinc alkyl ZnEt2 which led to the ...
PDF File
... and stored at -20 °C (11). Protein concentration was determined using the calculated extinction coefficient at 280 nm: 9200 M-1 cm-1 (13). Enzyme concentration was expressed as concentration of 17 kDa subunits. Reactions of H122 Mutants with Alcohols. Reactions of H122 mutants and ATP were performed ...
... and stored at -20 °C (11). Protein concentration was determined using the calculated extinction coefficient at 280 nm: 9200 M-1 cm-1 (13). Enzyme concentration was expressed as concentration of 17 kDa subunits. Reactions of H122 Mutants with Alcohols. Reactions of H122 mutants and ATP were performed ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.