rate
... Basic Idea: As a rule, an increase in temperature * increases the rate of both endothermic and exothermic reactions. However, endothermic reactions are increased a greater extent Reason: An increase in temperature, indicates that more energy has been added to the reacting species. This increase in e ...
... Basic Idea: As a rule, an increase in temperature * increases the rate of both endothermic and exothermic reactions. However, endothermic reactions are increased a greater extent Reason: An increase in temperature, indicates that more energy has been added to the reacting species. This increase in e ...
CHEM 203 Topics Discussed on Nov. 20 Principle: protonation of
... CHEM 203 Topics Discussed on Nov. 20 Principle: protonation of alcohols transforms the OH group into an incipient molecule of H2O, which is the conjugate base of a strong Bronsted acid, H3O+ (pKa ≈ –2). So, H2O can function as a leaving group in SN2/SN1 or E2/E1 reactions (cf. the case of ethers; no ...
... CHEM 203 Topics Discussed on Nov. 20 Principle: protonation of alcohols transforms the OH group into an incipient molecule of H2O, which is the conjugate base of a strong Bronsted acid, H3O+ (pKa ≈ –2). So, H2O can function as a leaving group in SN2/SN1 or E2/E1 reactions (cf. the case of ethers; no ...
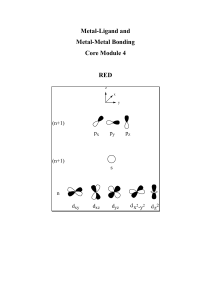
Metal-Ligand and Metal-Metal Bonding Lecture Notes
... 1. Radius (Covalent/ionic) :- Increases from right to left and down a group. 2. Electropositivity:- electropositive character increases from right to left and down a group. The trends observed in 1 and 2 are a result of the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) that is a consequence of shielding and penet ...
... 1. Radius (Covalent/ionic) :- Increases from right to left and down a group. 2. Electropositivity:- electropositive character increases from right to left and down a group. The trends observed in 1 and 2 are a result of the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) that is a consequence of shielding and penet ...
Step 1
... Primary aromatic amines such as Phenylamine do not form basic solutions because the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen delocalise with the ring of electrons in the benzene ring. This means the N is less able to accept protons (or donate an electron pair) as the electron change density aroun ...
... Primary aromatic amines such as Phenylamine do not form basic solutions because the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen delocalise with the ring of electrons in the benzene ring. This means the N is less able to accept protons (or donate an electron pair) as the electron change density aroun ...
Chem 150 Unit 4 - Chemical Properties I Chemical Reactions
... within and between molecules that results in the formation of new molecules. • This process involves the making and breaking of covalent bonds. • An important concept in these processes is that all of the atoms present before a reaction are also present after the reaction ...
... within and between molecules that results in the formation of new molecules. • This process involves the making and breaking of covalent bonds. • An important concept in these processes is that all of the atoms present before a reaction are also present after the reaction ...
Wittig Reaction
... the liquid out by applying pressure inside the pipette (using a stream of air). Finally, during the isolation steps, it is quite possible that some product remained dissolved in one of the many solvents used. This yield may turn out to be irrelevant though because the sample did not appear to be Tra ...
... the liquid out by applying pressure inside the pipette (using a stream of air). Finally, during the isolation steps, it is quite possible that some product remained dissolved in one of the many solvents used. This yield may turn out to be irrelevant though because the sample did not appear to be Tra ...
Novel amine-catalysed hydroalkoxylation reactions of
... The importance of b-hydroxycarbonyl compounds and their protected alkoxy analogues in natural product chemistry1 and organic synthesis in general2 is difficult to overstate. While the former class of compounds is readily prepared via (inter alia) the aldol reaction, the direct synthesis of b-alkoxyc ...
... The importance of b-hydroxycarbonyl compounds and their protected alkoxy analogues in natural product chemistry1 and organic synthesis in general2 is difficult to overstate. While the former class of compounds is readily prepared via (inter alia) the aldol reaction, the direct synthesis of b-alkoxyc ...
45. kinetics ch 12
... The rate of a reaction is the positive quantity that expresses how the concentration of a reactant or product changes with time. The rates of reactions span an enormous range. From those that are complete within seconds to those that take thousands or even millions of years. ...
... The rate of a reaction is the positive quantity that expresses how the concentration of a reactant or product changes with time. The rates of reactions span an enormous range. From those that are complete within seconds to those that take thousands or even millions of years. ...
Oxidation of Cyclohexanol
... much material used. The flask will become significantly warm because of the exothermic reaction. Swirl the flask containing the reaction mixture frequently for a full 20 minutes, also in the fume hood. During this time the reaction mixture should cool back to room temperature. Wet a piece of a potas ...
... much material used. The flask will become significantly warm because of the exothermic reaction. Swirl the flask containing the reaction mixture frequently for a full 20 minutes, also in the fume hood. During this time the reaction mixture should cool back to room temperature. Wet a piece of a potas ...
diazonium salt
... periods of time. Loss of nitrogen from an aryl diazonium ion generates an unstable aryl cation and is much slower than loss of nitrogen from an alkyl diazonium ion. Stability is due to: interaction with the aromatic electron system (8-center, 10-electron bonding system and 5 resonance structures) ...
... periods of time. Loss of nitrogen from an aryl diazonium ion generates an unstable aryl cation and is much slower than loss of nitrogen from an alkyl diazonium ion. Stability is due to: interaction with the aromatic electron system (8-center, 10-electron bonding system and 5 resonance structures) ...
Review
... Disubstituted cyclohexanes: cis/trans-isomerism; comparison of stability (the fewer are the axial substituents, the more stable is the disubstituted cyclohexane. Fused rings (cis and trans decalins) ...
... Disubstituted cyclohexanes: cis/trans-isomerism; comparison of stability (the fewer are the axial substituents, the more stable is the disubstituted cyclohexane. Fused rings (cis and trans decalins) ...
the importance of electron transfer mechanism in
... low-lying electronic states that results from the near degeneracy of 4s and 3d orbitals. This situation provides unique opportunity to study roles of electronic energies and configuration on reactivities. Very recently, the electronic state selective reaction rates have been determined for ground an ...
... low-lying electronic states that results from the near degeneracy of 4s and 3d orbitals. This situation provides unique opportunity to study roles of electronic energies and configuration on reactivities. Very recently, the electronic state selective reaction rates have been determined for ground an ...
EXPERIMENT 3: The Grignard Reaction: Synthesis of
... formations, is most important in anabolic organic synthesis. The various reactions involved in the creation of large molecules from simple starting materials are quite limited in number. One of the most fundamental carbon forming bond reactions is the Grignard reaction. The Grignard reaction involve ...
... formations, is most important in anabolic organic synthesis. The various reactions involved in the creation of large molecules from simple starting materials are quite limited in number. One of the most fundamental carbon forming bond reactions is the Grignard reaction. The Grignard reaction involve ...
Solvent free permanganate oxidations
... oxidants such as ruthenium tetroxide18 or chromium(VI),18 the experimental simplicity of this procedure may make it the approach of choice. When the a-carbons are tertiary, the product is a dione, formed presumably by dehydration of the corresponding diol as in Scheme 6. Addition of alumina to the s ...
... oxidants such as ruthenium tetroxide18 or chromium(VI),18 the experimental simplicity of this procedure may make it the approach of choice. When the a-carbons are tertiary, the product is a dione, formed presumably by dehydration of the corresponding diol as in Scheme 6. Addition of alumina to the s ...
The origin and status of the Arrhenius equation
... course, reflect the role of the solvent in the reaction process. For truly elementary processes, i.e., bimolecular reactions in the gas phase, reservations about the Arrhenius eouation were not &dent until much later,eren though hoth ilk main theories of himolecular reactions (collision theorv and t ...
... course, reflect the role of the solvent in the reaction process. For truly elementary processes, i.e., bimolecular reactions in the gas phase, reservations about the Arrhenius eouation were not &dent until much later,eren though hoth ilk main theories of himolecular reactions (collision theorv and t ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.