Alkenes - MsReenChemistry
... to give an alkyl halide, the hydrogen adds to the carbon of the alkene that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, and the halogen to the carbon of the alkene with the fewer ...
... to give an alkyl halide, the hydrogen adds to the carbon of the alkene that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, and the halogen to the carbon of the alkene with the fewer ...
AT 25 °C - University of Bath
... Hence, at 450 °C, 108.24 kJ is evolved for each mole of the equation i.e 108.24 kJ is evolved per mole of nitrogen which reacts. Since, for a gas, volume ∝ number of moles, the 1:3 mixture is in the stoichiometric amount. At 0 °C and 1 atm pressure, 1 mole occupies 22.4 dm3. Thus, the total amount o ...
... Hence, at 450 °C, 108.24 kJ is evolved for each mole of the equation i.e 108.24 kJ is evolved per mole of nitrogen which reacts. Since, for a gas, volume ∝ number of moles, the 1:3 mixture is in the stoichiometric amount. At 0 °C and 1 atm pressure, 1 mole occupies 22.4 dm3. Thus, the total amount o ...
M. Sc. in Industrial Chemistry Centre for Applied Chemistry Syllabus
... exactly solvable system, particle in a box, harmonic oscillator and hydrogen atom, shapes of the atomic orbitals, orbital angular momenta, tunnelling. Approximate methods of quantum mechanics, vibrational principle, perturbation theory up to second order in energy, applications, Born interpretation, ...
... exactly solvable system, particle in a box, harmonic oscillator and hydrogen atom, shapes of the atomic orbitals, orbital angular momenta, tunnelling. Approximate methods of quantum mechanics, vibrational principle, perturbation theory up to second order in energy, applications, Born interpretation, ...
Substitution Rxns-a-Sn2-12-quesx
... L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected mechanism. In this new pathway, called the roundabout mechanism, chloride bumps into the methyl group and spins the entire methyl iodide molecu ...
... L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected mechanism. In this new pathway, called the roundabout mechanism, chloride bumps into the methyl group and spins the entire methyl iodide molecu ...
Assignment 30 STRUCTURE OF MOLECULES AND MULTI
... form four C-H bonds. The problem is that such an overlap would result in two different ‘types’ of C-H bond (one C(2s) - H(1s) overlap and three C(2p) – H(1s) overlaps) with the three C(2p) – H(1s) overlaps producing C-H bonds mutually perpendicular to each other. Neither of these attributes is obser ...
... form four C-H bonds. The problem is that such an overlap would result in two different ‘types’ of C-H bond (one C(2s) - H(1s) overlap and three C(2p) – H(1s) overlaps) with the three C(2p) – H(1s) overlaps producing C-H bonds mutually perpendicular to each other. Neither of these attributes is obser ...
Aromatic Compounds
... Apply the principles of MOT • σ bonds form the basic framework of the molecule. • The π electrons are placed in MO obeying the following rules. (i) There are as many MO as carbon atoms in the system. (ii) There is always an orbital of lowest energy which is single and can accommodate 2π electrons. ...
... Apply the principles of MOT • σ bonds form the basic framework of the molecule. • The π electrons are placed in MO obeying the following rules. (i) There are as many MO as carbon atoms in the system. (ii) There is always an orbital of lowest energy which is single and can accommodate 2π electrons. ...
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... dehydration, an E1 reaction. In this experiment, a mixture of concentrated phosphoric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is used to prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol via an E1 reaction. The mechanism of this E1 reaction involves three steps. First, is the rapid (and reversible) protonation of t ...
... dehydration, an E1 reaction. In this experiment, a mixture of concentrated phosphoric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is used to prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol via an E1 reaction. The mechanism of this E1 reaction involves three steps. First, is the rapid (and reversible) protonation of t ...
Date - Chaminade University`s syllabus repository
... Identify and classify organic molecules according to their functional groups Carry out functional group inter-conversions of the classes of compounds studied Illustrate the mechanism of each of the functional group inter-conversions identifying intermediates and transition states where appropr ...
... Identify and classify organic molecules according to their functional groups Carry out functional group inter-conversions of the classes of compounds studied Illustrate the mechanism of each of the functional group inter-conversions identifying intermediates and transition states where appropr ...
Lectures p block elements 3 hypervalency
... For PCl2F3 one observes that in the fluorine NMR spectra taken at room temperature there is only one kind of fluorine’s but when measured at -143°C one gets two sets of peaks (a doublet of a doublet for the two axial fluorine’s and a doublet of a triplet for the equatorial fluorine at -143 °C). This ...
... For PCl2F3 one observes that in the fluorine NMR spectra taken at room temperature there is only one kind of fluorine’s but when measured at -143°C one gets two sets of peaks (a doublet of a doublet for the two axial fluorine’s and a doublet of a triplet for the equatorial fluorine at -143 °C). This ...
1 Intro / Review : Chemical Kinetics
... Enduring understanding 4.B: Elementary reactions are mediated by collisions between molecules. Only collisions having sufficient energy and proper relative orientation of reactants lead to products. Enduring understanding 4.C: Many reactions proceed via a series of elementary reactions. Essential kn ...
... Enduring understanding 4.B: Elementary reactions are mediated by collisions between molecules. Only collisions having sufficient energy and proper relative orientation of reactants lead to products. Enduring understanding 4.C: Many reactions proceed via a series of elementary reactions. Essential kn ...
Chapter 10: Alkyl Halides
... Allylic Bromination with NBS is analogous to the radical reaction with an alkane, a halogen and uv light (Ch. 5). The NBS can be thought of as producing a Br radical. The Br radical removes a hydrogen, leaving an allylic radical and forming HBr. This allylic radical reacts with Br2 (which is formed ...
... Allylic Bromination with NBS is analogous to the radical reaction with an alkane, a halogen and uv light (Ch. 5). The NBS can be thought of as producing a Br radical. The Br radical removes a hydrogen, leaving an allylic radical and forming HBr. This allylic radical reacts with Br2 (which is formed ...
Polysulfane Antitumor Agents from o
... Various heterocycles may be expected to arise from the reaction of o-benzyne with cyclic S8. B3LYP/6-31G(d) calculations are used to predict the stability of possible ortho-fused heterocycles, o-C6H4Sx (where x ) 1-8). Lowenergy conformers of the rings containing up to 8 sulfurs were identified by a ...
... Various heterocycles may be expected to arise from the reaction of o-benzyne with cyclic S8. B3LYP/6-31G(d) calculations are used to predict the stability of possible ortho-fused heterocycles, o-C6H4Sx (where x ) 1-8). Lowenergy conformers of the rings containing up to 8 sulfurs were identified by a ...
Chemistry 250A -- Exam #3 Answer Key -
... to be anti to the leaving group. Thus, unlike the E2 case, both isomeric products can be efficiently produced. The second product, with the isopropyl group on the double bond, contains a more highly substituted double bond and thus is more stable than the first product and, to the extent that the tr ...
... to be anti to the leaving group. Thus, unlike the E2 case, both isomeric products can be efficiently produced. The second product, with the isopropyl group on the double bond, contains a more highly substituted double bond and thus is more stable than the first product and, to the extent that the tr ...
Efficient and catalyst-free condensation of acid chlorides and
... Full conversion of benzoyl chloride and methanol into methyl benzoate is possible using a residence time of 300 sec, a reaction temperature of 80°C and as little as 1.3 equivalents of MeOH. At lower residence times, traces of benzoyl chloride were detected in the reaction mixture, even if the stoich ...
... Full conversion of benzoyl chloride and methanol into methyl benzoate is possible using a residence time of 300 sec, a reaction temperature of 80°C and as little as 1.3 equivalents of MeOH. At lower residence times, traces of benzoyl chloride were detected in the reaction mixture, even if the stoich ...
Thermochem Practice Test
... a) that is exothermic, b) that has delta Suniv > 0, c) that has delta Ssys < 0, d) that has delta Ssurr > 0 2. Name the first law of thermodynamics. 3. Name the second law of thermodynamics. 4. Name the third law of thermodynamics 5. For a particular chemical reaction delta H = 5.5 kJ and delta S = ...
... a) that is exothermic, b) that has delta Suniv > 0, c) that has delta Ssys < 0, d) that has delta Ssurr > 0 2. Name the first law of thermodynamics. 3. Name the second law of thermodynamics. 4. Name the third law of thermodynamics 5. For a particular chemical reaction delta H = 5.5 kJ and delta S = ...
Notes Set 1
... have either H+ ions and water in them or OH- ions and water in them. These are the half reactions that will take place in either acidic or basic solutions. It should be stressed that These are only half of the reaction that will take place. They are all reduction reactions. We have seen that reducti ...
... have either H+ ions and water in them or OH- ions and water in them. These are the half reactions that will take place in either acidic or basic solutions. It should be stressed that These are only half of the reaction that will take place. They are all reduction reactions. We have seen that reducti ...
Results
... Conformation D is sufficiently destabilized so only A, B and C are expected to show decarbonylation reaction The following 3 families of mechanisms may be anticipated A: Unimolecular Internal SN2 type reactionmechanism (SNi) with alactone formation B: Unimolecular Internal Addition/elimination mecha ...
... Conformation D is sufficiently destabilized so only A, B and C are expected to show decarbonylation reaction The following 3 families of mechanisms may be anticipated A: Unimolecular Internal SN2 type reactionmechanism (SNi) with alactone formation B: Unimolecular Internal Addition/elimination mecha ...
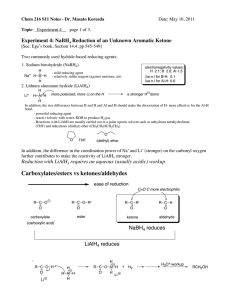
Carboxylates/esters vs ketones/aldehydes
... The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Because of this, usually at least one mol. equivalents of NaBH4 are used for the reaction in a prot ...
... The mechanism of the NaBH4 reduction in a protic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, and water is known to be quite complex since NaBH4 reacts with the solvent, e.g., NaBH4 + C2H5OH → NaBH3(OC2H5) + H2 Because of this, usually at least one mol. equivalents of NaBH4 are used for the reaction in a prot ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.