Reaction Kinetics. The Bromination of Acetone
... Determination of the B constant: The constant B of equation [10] is determined by measuring the absorbance of at least three solutions of known bromine concentration. At room temperature, prepare one solution by pipetting 10.0 ml of stock 0.02 M Br2 into a clean 125-ml Erlenmeyer flask. Add 10.0 ml ...
... Determination of the B constant: The constant B of equation [10] is determined by measuring the absorbance of at least three solutions of known bromine concentration. At room temperature, prepare one solution by pipetting 10.0 ml of stock 0.02 M Br2 into a clean 125-ml Erlenmeyer flask. Add 10.0 ml ...
Organic Chemistry Introduction
... Step through highest energy point is rate-limiting (k1 in forward direction) ...
... Step through highest energy point is rate-limiting (k1 in forward direction) ...
Document
... – Combination of concentrations that allow Q = K – Infinite number of possible equilibrium positions • Le Châtelier’s principle – System at equilibrium (Q = K) when upset by disturbance (Q ≠ K) will shift to offset stress • System said to “shift to right” when forward reaction is dominant (Q < K) • ...
... – Combination of concentrations that allow Q = K – Infinite number of possible equilibrium positions • Le Châtelier’s principle – System at equilibrium (Q = K) when upset by disturbance (Q ≠ K) will shift to offset stress • System said to “shift to right” when forward reaction is dominant (Q < K) • ...
AP Chemistry
... and the bonds broken in the combustion of C2H6 and C2H2. In the combustion of 1 mol of C2H6 we break 1 CC bond and 6 C-H bonds. We make 4 C=O bonds and 6 H-O bonds. In the combustion of 1 mol of C2H2 we break 1 C-C bond, 2 C-C bonds, and 2 C-H bonds. We make 4 C=O bonds and 2 H-O bonds. If you ...
... and the bonds broken in the combustion of C2H6 and C2H2. In the combustion of 1 mol of C2H6 we break 1 CC bond and 6 C-H bonds. We make 4 C=O bonds and 6 H-O bonds. In the combustion of 1 mol of C2H2 we break 1 C-C bond, 2 C-C bonds, and 2 C-H bonds. We make 4 C=O bonds and 2 H-O bonds. If you ...
Ch 6 Lecture 2
... 1) Stabilize negative charge: I- > Br- > Cl- > F2) Polarizability (size/charge) of I- allows it to readily handle (-) 3) F is a very poor leaving group: (high bond strength, low polarizability) 4) Other good leaving groups: Sulfates and Sulfonates O ...
... 1) Stabilize negative charge: I- > Br- > Cl- > F2) Polarizability (size/charge) of I- allows it to readily handle (-) 3) F is a very poor leaving group: (high bond strength, low polarizability) 4) Other good leaving groups: Sulfates and Sulfonates O ...
Microwave-Enhanced Sulphated Zirconia and SZ/MCM
... reactions, one may mention the use of silica gel [11], zeolite NaY [12], alumina [13], copper sulphatesupported polymer [14], montmorillonite [15], alumina-supported phosphomolybdic acid [16] and acid resins [17]. Microwave (MW) irradiation, an unconventional energy source, has been used for a varie ...
... reactions, one may mention the use of silica gel [11], zeolite NaY [12], alumina [13], copper sulphatesupported polymer [14], montmorillonite [15], alumina-supported phosphomolybdic acid [16] and acid resins [17]. Microwave (MW) irradiation, an unconventional energy source, has been used for a varie ...
MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
... undergoes chemistry Point of the catalyst that facilitates strong interaction with reactant Number of molecules reacting per active site per second ...
... undergoes chemistry Point of the catalyst that facilitates strong interaction with reactant Number of molecules reacting per active site per second ...
Substitution and Elimination Reactions . 7.1. Definitions.
... Brstart off with (S)-2-bromobutane, and if the incoming nucleophile has the same CIP priority as the leaving group, then the product has the absolute (R) configuration. We call this the Walden inversion. (Don't confuse this inversion with the lone pair inversion that occurs so easily in amines.) It ...
... Brstart off with (S)-2-bromobutane, and if the incoming nucleophile has the same CIP priority as the leaving group, then the product has the absolute (R) configuration. We call this the Walden inversion. (Don't confuse this inversion with the lone pair inversion that occurs so easily in amines.) It ...
Handbook for the Lab Course Organic Chemistry I
... will be returned. In the last week there will be a list on the whiteboard in front of 329 where the students have to sign up for a special duty which has to be carried out at the last day of the lab course. The students come at the scheduled and hand over their equipment. All equipment is placed on ...
... will be returned. In the last week there will be a list on the whiteboard in front of 329 where the students have to sign up for a special duty which has to be carried out at the last day of the lab course. The students come at the scheduled and hand over their equipment. All equipment is placed on ...
- Wiley Online Library
... resonance cavity (green squares) as extracted from the temporal shifts in the higher-order cavity modes. All measurements were carried out at [PTA] = 2.53 m. See the Experimental Section for details. ...
... resonance cavity (green squares) as extracted from the temporal shifts in the higher-order cavity modes. All measurements were carried out at [PTA] = 2.53 m. See the Experimental Section for details. ...
Topic 5 - Chemical Reactions
... Matter can be described using both chemical and physical properties. Elements are the simplest form of matter that has a unique set of properties. A compound is a substance that contains two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion. 4. Chemical formulas are used to represent compou ...
... Matter can be described using both chemical and physical properties. Elements are the simplest form of matter that has a unique set of properties. A compound is a substance that contains two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion. 4. Chemical formulas are used to represent compou ...
Chem 30CL - Lecture 1c - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... substrates and well controlled conditions • The Lipitor synthesis requires halohydrin dehalogenase, nitrilase, aldolase • The reduction of benzil using cryptococcus macerans leads to the formation of (R,R)-hydrobenzoin (dl:meso=95:5, 99 % e.e.) ...
... substrates and well controlled conditions • The Lipitor synthesis requires halohydrin dehalogenase, nitrilase, aldolase • The reduction of benzil using cryptococcus macerans leads to the formation of (R,R)-hydrobenzoin (dl:meso=95:5, 99 % e.e.) ...
KIMIA ORGANIK FISIK
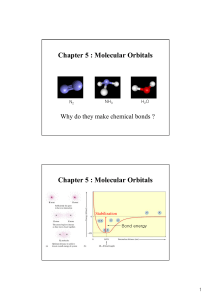
... • Combination of n atomic orbitals gives n MOs. • MOs are arranged in order of increasing energy. • MO filling is governed by the same rules as for atomic orbitals: • Aufbau principle: fill beginning with LUMO • Pauli exclusion principle: no more than 2e- in a MO • Hund’s rule: when two or more MOs ...
... • Combination of n atomic orbitals gives n MOs. • MOs are arranged in order of increasing energy. • MO filling is governed by the same rules as for atomic orbitals: • Aufbau principle: fill beginning with LUMO • Pauli exclusion principle: no more than 2e- in a MO • Hund’s rule: when two or more MOs ...
PDF Full-text
... mechanical operators, one-electron density or one-electron Hamiltonian. They allow molecules to be classified based on an invariance property according to two pictorial rules, linear transformations, applied to the VIF pictures. The number of doubly, singly, and unoccupied valence orbitals or the nu ...
... mechanical operators, one-electron density or one-electron Hamiltonian. They allow molecules to be classified based on an invariance property according to two pictorial rules, linear transformations, applied to the VIF pictures. The number of doubly, singly, and unoccupied valence orbitals or the nu ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.




![[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015878975_1-55791b331e05591620375059b6f74bac-300x300.png)