Lectures 15, 16 and 17
... • The (S)-CBS reagent delivers H:- from the front side of the C=O. This generally affords the R alcohol as the major product. • The (R)-CBS reagent delivers H:- from the back side of the C=O. This generally affords the S alcohol as the major product. ...
... • The (S)-CBS reagent delivers H:- from the front side of the C=O. This generally affords the R alcohol as the major product. • The (R)-CBS reagent delivers H:- from the back side of the C=O. This generally affords the S alcohol as the major product. ...
Contents - Personal WWW Pages
... We will look at three systems as case studies showing how catalysts are developed, how mechanisms can be probed and the origin of selectivity. In order to make sense of catalytic reactions we need a basis on which to approach them. A set of rules have been developed, which when coupled with a knowle ...
... We will look at three systems as case studies showing how catalysts are developed, how mechanisms can be probed and the origin of selectivity. In order to make sense of catalytic reactions we need a basis on which to approach them. A set of rules have been developed, which when coupled with a knowle ...
Remodeling of the natural product fumagillol
... Further optimization using La(OTf)3 and Zn(OTf)2 catalysts was next pursued. The transformations were robust and did not require inert atmosphere, nor special precautions for anhydrous solvent. Other nonpolar solvents provided similar regioselectivity, though toluene proved to be optimal, in which c ...
... Further optimization using La(OTf)3 and Zn(OTf)2 catalysts was next pursued. The transformations were robust and did not require inert atmosphere, nor special precautions for anhydrous solvent. Other nonpolar solvents provided similar regioselectivity, though toluene proved to be optimal, in which c ...
Organic Chemistry I (CHEM 2010 and 2012)
... Attendance and Expectations: Students are expected to attend every lecture in its entirety. Students are expected to read and study the material to be discussed prior to the lecture. This includes working in-chapter and end-of-chapter problems and exercises in the text. Students should review the ma ...
... Attendance and Expectations: Students are expected to attend every lecture in its entirety. Students are expected to read and study the material to be discussed prior to the lecture. This includes working in-chapter and end-of-chapter problems and exercises in the text. Students should review the ma ...
Year 1 Foundation course, section B2
... Year 1 Foundation course, section B2; Structure and reactivity of specific functional groups Alkanes - the most basic of all organic compounds, composed of only C and H, with no functional groups. General formulae CnH2n+2 (unless cyclic in which case it is CnH2n). Alkanes are generally quite unreac ...
... Year 1 Foundation course, section B2; Structure and reactivity of specific functional groups Alkanes - the most basic of all organic compounds, composed of only C and H, with no functional groups. General formulae CnH2n+2 (unless cyclic in which case it is CnH2n). Alkanes are generally quite unreac ...
Haloalkanes
... The Environmental problems associated with CFC Because of the lack of reactivity and insolubility in water, there is no natural process for removing CFC. In fact they drift up into the stratosphere (the upper atmosphere), where they receive sufficient ultraviolet Light to cause photolysis. The chlor ...
... The Environmental problems associated with CFC Because of the lack of reactivity and insolubility in water, there is no natural process for removing CFC. In fact they drift up into the stratosphere (the upper atmosphere), where they receive sufficient ultraviolet Light to cause photolysis. The chlor ...
Copper-Catalyzed Hydroalkylation of Terminal Alkynes
... turnover-limiting step of the catalytic cycle. As previously pointed out alkyl triflates can be transformed into alkyl fluorides23 or alkanes20 under reaction conditions that are remarkably similar to the conditions used in the hydroalkylation reaction. In that light, the selectivity of the hydroalkyl ...
... turnover-limiting step of the catalytic cycle. As previously pointed out alkyl triflates can be transformed into alkyl fluorides23 or alkanes20 under reaction conditions that are remarkably similar to the conditions used in the hydroalkylation reaction. In that light, the selectivity of the hydroalkyl ...
main types and mechanisms of the reactions in organic chemistry
... elimination is formed. Product of reaction is secondary propanol (propan-2-ol). In hydration reaction proton attaches in accordance with Markovnikov’s rule – to the carbon atom with more hydrogen atoms, as electron dencity shifts to this atom because of positive inductive effect of СН3-group. Beside ...
... elimination is formed. Product of reaction is secondary propanol (propan-2-ol). In hydration reaction proton attaches in accordance with Markovnikov’s rule – to the carbon atom with more hydrogen atoms, as electron dencity shifts to this atom because of positive inductive effect of СН3-group. Beside ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... 1) Monobromination of toluene gives 3 products. Draw the entire mechanism for the formation of one product and draw the other two. ...
... 1) Monobromination of toluene gives 3 products. Draw the entire mechanism for the formation of one product and draw the other two. ...
Assigning Hybridization: A Tutorial
... by overlap of one sp orbital on each carbon atom. The 2py orbitals (green) overlap to form one π bond (green tape; perpendicular to the plane of your computer screen), and the 2pz orbitals (green) overlap to form another π bond (orange tape; parallel to the plane of your computer screen), perpendicu ...
... by overlap of one sp orbital on each carbon atom. The 2py orbitals (green) overlap to form one π bond (green tape; perpendicular to the plane of your computer screen), and the 2pz orbitals (green) overlap to form another π bond (orange tape; parallel to the plane of your computer screen), perpendicu ...
Chapter in Zumdahl: Chapter #12 Kinetics (2
... define entropy and how it relates to spontaneity. calculate the entropy change that occurs during an: (a) a phase change (b) the formation of a compound from it’s elements determine the sign and magnitude of the entropy change for a given chemical or physical change and how it relates to the r ...
... define entropy and how it relates to spontaneity. calculate the entropy change that occurs during an: (a) a phase change (b) the formation of a compound from it’s elements determine the sign and magnitude of the entropy change for a given chemical or physical change and how it relates to the r ...
BHR - A Brief History - Process Intensification Network
... Just ahead of the “dead zone” allowing predictable scale-up. ...
... Just ahead of the “dead zone” allowing predictable scale-up. ...
I 1 Chemical Reaction Cross Sections I and Rate Constants
... Equation (2) is often called the rate law for the reaction. In this case it is a second-order rate law. I n general, rate constants depend on the temperature. Furthermore, the rate of a reaction does not necessarily vary with the concentrations of the reactants raised to the powers given by the stoi ...
... Equation (2) is often called the rate law for the reaction. In this case it is a second-order rate law. I n general, rate constants depend on the temperature. Furthermore, the rate of a reaction does not necessarily vary with the concentrations of the reactants raised to the powers given by the stoi ...
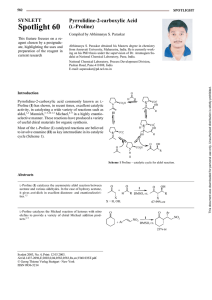
Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic Acid (l
... from Amravati University, Maharastra, India. He is currently working on his PhD thesis under the supervision of Dr. Arumugum Sudalai at National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India. ...
... from Amravati University, Maharastra, India. He is currently working on his PhD thesis under the supervision of Dr. Arumugum Sudalai at National Chemical Laboratory, Pune, India. ...
Get cached
... The I R spectra of Cr°(CN—R) and Ni°(CN—R) could provide further criteria to test the validity of the V B and M O models. Since both complexes are highly symmetric (octahedral and tetrahedral configurations) they should exhibit only one N C stretching frequency unless back donation lowers the symmet ...
... The I R spectra of Cr°(CN—R) and Ni°(CN—R) could provide further criteria to test the validity of the V B and M O models. Since both complexes are highly symmetric (octahedral and tetrahedral configurations) they should exhibit only one N C stretching frequency unless back donation lowers the symmet ...
Sodium Borohydride Reduction of Vanillin
... perfume ingredient. Most vanillin is now synthesized using lignin derived from wood pulp. Lignin is a complex polymer that gives rigidity to trees and other woody plants. After cellulose, lignin is the second most abundant organic material on earth. Reduction Reactions In chemistry, reduction refers ...
... perfume ingredient. Most vanillin is now synthesized using lignin derived from wood pulp. Lignin is a complex polymer that gives rigidity to trees and other woody plants. After cellulose, lignin is the second most abundant organic material on earth. Reduction Reactions In chemistry, reduction refers ...
Advanced Chemistry
... 7) When the concentration of B in the reaction below is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. 2 A(g) + B(g) 2 C(g) The most probable explanation for this observation is that (A) The order of the reaction with respect to substa ...
... 7) When the concentration of B in the reaction below is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. 2 A(g) + B(g) 2 C(g) The most probable explanation for this observation is that (A) The order of the reaction with respect to substa ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.