The aim of this exercise is to study the acid... prepare a buffer solution. General Sciences Sample
... Study of a Pharmacological Hydrogen Peroxide Solution A pharmacological hydrogen peroxide solution (S0), used as an antiseptic and as hairs’ colorizing agent, is labeled 30V. This indication represents the maximum volume of 30 L of oxygen gas (measured under normal conditions where Vm = 22.4 L.mol-1 ...
... Study of a Pharmacological Hydrogen Peroxide Solution A pharmacological hydrogen peroxide solution (S0), used as an antiseptic and as hairs’ colorizing agent, is labeled 30V. This indication represents the maximum volume of 30 L of oxygen gas (measured under normal conditions where Vm = 22.4 L.mol-1 ...
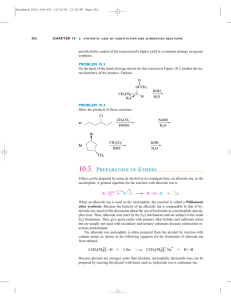
Reaction of orthoesters with alcohols in the presence of acidic
... also. As O-acetylation with orthoester is not hitherto a known reaction, we were curious to explore this to find out whether such a transformation could be useful as a synthetic methodology and the results are summarized in Table I. Thus the reaction of alcohols and orthoester with various acid cata ...
... also. As O-acetylation with orthoester is not hitherto a known reaction, we were curious to explore this to find out whether such a transformation could be useful as a synthetic methodology and the results are summarized in Table I. Thus the reaction of alcohols and orthoester with various acid cata ...
Ethers and Epoxides - faculty at Chemeketa
... Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether Thiols (R–S–H) and sulfides (R–S–R) are sulfur (for oxygen) analogs of alcohols and ethers ...
... Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether Thiols (R–S–H) and sulfides (R–S–R) are sulfur (for oxygen) analogs of alcohols and ethers ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether Thiols (R–S–H) and sulfides (R–S–R) are sulfur (for oxygen) analogs of alcohols and ethers ...
... Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether Thiols (R–S–H) and sulfides (R–S–R) are sulfur (for oxygen) analogs of alcohols and ethers ...
syntheses, structures, and their interconversion
... not. The latter turned out to be the case, as small amounts of K2[HgSe2]·H2O (4) emerged from the experiment upon addition of 0.5 vol% of water to the reaction mixture. Complete absence of water, or other volume ratios than 995 : 5 led to no or lower yields. For us, such hydrate compounds are partic ...
... not. The latter turned out to be the case, as small amounts of K2[HgSe2]·H2O (4) emerged from the experiment upon addition of 0.5 vol% of water to the reaction mixture. Complete absence of water, or other volume ratios than 995 : 5 led to no or lower yields. For us, such hydrate compounds are partic ...
Homo-coupling of terminal alkynes on a noble metal surface
... are rendered with the same colour code. The characteristic outline, the smooth connection via the thinner waist, as well as the slightly brighter benzene rings compared to the waist, all agree well with the simulation. We furthermore analysed the small regular dimer patch depicted in Fig. 3c. With ...
... are rendered with the same colour code. The characteristic outline, the smooth connection via the thinner waist, as well as the slightly brighter benzene rings compared to the waist, all agree well with the simulation. We furthermore analysed the small regular dimer patch depicted in Fig. 3c. With ...
Section 2 Simple Molecular Orbital Theory
... two of the four hybrids are directed away from all other valence orbitals and hence can not form bonds. In all such qualitative mo analyses, the final results (i.e., how many mos there are of any given symmetry) will not depend on whether one thinks of the interactions involving atomic or hybrid orb ...
... two of the four hybrids are directed away from all other valence orbitals and hence can not form bonds. In all such qualitative mo analyses, the final results (i.e., how many mos there are of any given symmetry) will not depend on whether one thinks of the interactions involving atomic or hybrid orb ...
PPT file
... Because electrophilic addition to a carbonyl group is reactantfavoured, whenever we see a gem-diol (two –OH groups on one carbon) or a carbon atom with a –OH group and a halogen attached, we expect it to collapse to a carbonyl group: H O C ...
... Because electrophilic addition to a carbonyl group is reactantfavoured, whenever we see a gem-diol (two –OH groups on one carbon) or a carbon atom with a –OH group and a halogen attached, we expect it to collapse to a carbonyl group: H O C ...
Chapter 14 Enzyme Characteristics
... • Participates in the reaction, but original structure regenerated during catalytic cycle • Tightly bound, sometimes covalently, does not dissociate during course of reaction. ...
... • Participates in the reaction, but original structure regenerated during catalytic cycle • Tightly bound, sometimes covalently, does not dissociate during course of reaction. ...
Synthesis of [RuCl2(NO)2(THF)] and its Double CN BondForming
... oxide at transition-metal centers have received considerably less attention.[1–3] For example, the migratory insertion of NO into metal–alkyl or metal–aryl bonds has been observed in only a handful of metal complexes,[3] despite the analogous reaction of CO dominating its organometallic chemistry an ...
... oxide at transition-metal centers have received considerably less attention.[1–3] For example, the migratory insertion of NO into metal–alkyl or metal–aryl bonds has been observed in only a handful of metal complexes,[3] despite the analogous reaction of CO dominating its organometallic chemistry an ...
PDF Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics
... 2. They must collide with enough energy to overcome an energy barrier to reaction called the activation energy. 3. They must collide in an orientation that allows the necessary bond‐breaking and forming needed to transform the reactants to the products. ...
... 2. They must collide with enough energy to overcome an energy barrier to reaction called the activation energy. 3. They must collide in an orientation that allows the necessary bond‐breaking and forming needed to transform the reactants to the products. ...
Barton Deoxygenation
... The radical can react with multiple bonds in an intramolecular fashion to yield cyclized radical intermediates. The two ends of the multiple bond constitute two possible sites of reaction. If the radical in the resulting intermediate ends up outside of the ring, the attack is termed "exo"; if it end ...
... The radical can react with multiple bonds in an intramolecular fashion to yield cyclized radical intermediates. The two ends of the multiple bond constitute two possible sites of reaction. If the radical in the resulting intermediate ends up outside of the ring, the attack is termed "exo"; if it end ...
Microbial Production of D
... of FeSO4- 7H20, 10 mg of MnSO4 4-6H20, and 500 mg of yeast extract in 1,000 ml of tap water (pH 6.5). Medium and cultivation. A basal medium for cultivation consisting of 10 g of glucose, 2 g of maleate, 3 g of (NH4)2SO4, 10.5 g of KH2PO4, 250 mg of MgSO4. 7H20, 10 mg of FeSO4 7H20, 10 mg of MnSO4 4 ...
... of FeSO4- 7H20, 10 mg of MnSO4 4-6H20, and 500 mg of yeast extract in 1,000 ml of tap water (pH 6.5). Medium and cultivation. A basal medium for cultivation consisting of 10 g of glucose, 2 g of maleate, 3 g of (NH4)2SO4, 10.5 g of KH2PO4, 250 mg of MgSO4. 7H20, 10 mg of FeSO4 7H20, 10 mg of MnSO4 4 ...
CHEM120 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WORKSHEET 1
... Be able to determine which of two groups is the better base and be able to predict whether a substitution reaction will occur or not. If a reaction can occur, you must be able to predict the product. ...
... Be able to determine which of two groups is the better base and be able to predict whether a substitution reaction will occur or not. If a reaction can occur, you must be able to predict the product. ...
16.2: Structure and Bonding in Ethers and Epoxides
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. ...
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.











![Synthesis of [RuCl2(NO)2(THF)] and its Double CN BondForming](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001773792_1-763ad0089529123821e01ed17077bbf2-300x300.png)