Exam 4 - Chemistry Courses
... than the initial total pressure. D. The equilibrium partial pressure of BrCl(g) will be greater than 2.00 atm. E. The reaction will go to completion since there are equal amounts of Br2(g) and Cl2(g). ...
... than the initial total pressure. D. The equilibrium partial pressure of BrCl(g) will be greater than 2.00 atm. E. The reaction will go to completion since there are equal amounts of Br2(g) and Cl2(g). ...
conversion of the OH group into a better leaving group, and
... • The mechanism of ether cleavage is SN1 or SN2, depending on the identity of R. • When 2° or 3° alkyl groups are bonded to the ether oxygen, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN1 mechanism involving a carbocation. With methyl or 1° R groups, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN2 mechanism. Example: In the ...
... • The mechanism of ether cleavage is SN1 or SN2, depending on the identity of R. • When 2° or 3° alkyl groups are bonded to the ether oxygen, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN1 mechanism involving a carbocation. With methyl or 1° R groups, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN2 mechanism. Example: In the ...
Density Functional Study of Molecular Orbitals of Ferrocene and
... bond angles and dihedral angles of these two compounds. The optimized bond length of C-C double and single bonds in ferrocene rings fall in the range 1.36-1.83°A, and cobaltocene 1.36-1.96°A at DFT/ B3LYP, levels through 6-31G (d) basis set. There are two types of C-C bonds involved in these species ...
... bond angles and dihedral angles of these two compounds. The optimized bond length of C-C double and single bonds in ferrocene rings fall in the range 1.36-1.83°A, and cobaltocene 1.36-1.96°A at DFT/ B3LYP, levels through 6-31G (d) basis set. There are two types of C-C bonds involved in these species ...
ppt
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. H3C ...
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. H3C ...
A-level Chemistry Question paper Unit 04 - Kinetics, Equilibria
... The compound (CH3)3CBr reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide as shown in the folfollowing equation. ...
... The compound (CH3)3CBr reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide as shown in the folfollowing equation. ...
Faculteit der Natuurwetenschappen, Wiskunde en Informatica
... A new approach towards the right-hand side of Solanoeclepin A (figure 3) is under investigation. The key step in the synthesis of the tricyclic core of the natural product is a [2+2] photocycloaddition. A challenging part of this approach is to obtain enantiomerically pure β-hydroxy-ketones (17, fig ...
... A new approach towards the right-hand side of Solanoeclepin A (figure 3) is under investigation. The key step in the synthesis of the tricyclic core of the natural product is a [2+2] photocycloaddition. A challenging part of this approach is to obtain enantiomerically pure β-hydroxy-ketones (17, fig ...
3.2 Synthesis Part 1 Notes - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... In the previous two addition reactions, there were the possibilities of two isomeric products forming depending on which of the carbon atoms in the C = C was attacked first by the electrophile ( H+ ). ...
... In the previous two addition reactions, there were the possibilities of two isomeric products forming depending on which of the carbon atoms in the C = C was attacked first by the electrophile ( H+ ). ...
Ethers and Epoxides - Delaware State University
... signal at 3.4 In epoxides, these H’s absorb at 2.5 to 3.5 in their 1H NMR spectra Carbon NMR: C’s in ethers exhibit a downfield shift to 50 to 80 ...
... signal at 3.4 In epoxides, these H’s absorb at 2.5 to 3.5 in their 1H NMR spectra Carbon NMR: C’s in ethers exhibit a downfield shift to 50 to 80 ...
Zn mediated regioselective Barbier reaction of propargylic bromides
... alcohols but unsubstituted propargyl halides always gave the corresponding propargylic alcohols with high selectivity [9]. It was reported recently that allenic alcohols were obtained with high selectivity by indium-mediated coupling of propargylic halides with aldehydes in aqueous media [7]. The zi ...
... alcohols but unsubstituted propargyl halides always gave the corresponding propargylic alcohols with high selectivity [9]. It was reported recently that allenic alcohols were obtained with high selectivity by indium-mediated coupling of propargylic halides with aldehydes in aqueous media [7]. The zi ...
fference: mechanistic How phenyl makes a di insights into the ruthenium( )-catalysed
... to the degree of hindrance around the double bond making coordination of the vinyl group to the metal difficult. However, this methodology can potentially be used as a selective system for internal and 1,1- and 1,2-disubstituted allylic alcohols, which should render it of interest to, for example, nat ...
... to the degree of hindrance around the double bond making coordination of the vinyl group to the metal difficult. However, this methodology can potentially be used as a selective system for internal and 1,1- and 1,2-disubstituted allylic alcohols, which should render it of interest to, for example, nat ...
Methodology for the olefination of aldehydes and ketones via the Meyer-Schuster reaction
... Phosphorus ylides are prepared before the reaction or in-situ and precautions must be taken due to their sensitivity to moisture and air. The carbanion of the ylide is the characteristic component that allows for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon. The ylides have been found to demonstrate ...
... Phosphorus ylides are prepared before the reaction or in-situ and precautions must be taken due to their sensitivity to moisture and air. The carbanion of the ylide is the characteristic component that allows for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon. The ylides have been found to demonstrate ...
Document
... molecular weight and surface area, and (3) dipole moments. Except for neopentane, these compounds have similar molecular weights. Neopentane is the lightest, and it is a compact spherical structure that minimizes van der Waals attractions. Neopentane is the lowest-boiling compound. Neither n-hexane ...
... molecular weight and surface area, and (3) dipole moments. Except for neopentane, these compounds have similar molecular weights. Neopentane is the lightest, and it is a compact spherical structure that minimizes van der Waals attractions. Neopentane is the lowest-boiling compound. Neither n-hexane ...
Get Reprint - McMaster Chemistry
... alcohol, the proton transfer step is slower than that for complex formation is consistent with the small but clearly primary deuterium kinetic isotope effects that these two alcohols exhibit in their reactions with 1.17 The magnitudes of the Arrhenius activation energies indicate that the transition ...
... alcohol, the proton transfer step is slower than that for complex formation is consistent with the small but clearly primary deuterium kinetic isotope effects that these two alcohols exhibit in their reactions with 1.17 The magnitudes of the Arrhenius activation energies indicate that the transition ...
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH)
... cannot occur by an E1 mechanism involving a carbocation intermediate. Therefore, 1° alcohols undergo dehydration following an E2 mechanism. ...
... cannot occur by an E1 mechanism involving a carbocation intermediate. Therefore, 1° alcohols undergo dehydration following an E2 mechanism. ...
110A Exam 1 Review Sheet-Fall Semester 2016 Review Session
... 4. Be able to list the usual valences of H, O, N, S, P, F, Cl, Br, I, and C, and to know examples of cases where carbon’s valence is not four. 5. Be able to list and apply a set of rules of evaluating resonance structures and gauging their relative contributions to the overall electronic structure o ...
... 4. Be able to list the usual valences of H, O, N, S, P, F, Cl, Br, I, and C, and to know examples of cases where carbon’s valence is not four. 5. Be able to list and apply a set of rules of evaluating resonance structures and gauging their relative contributions to the overall electronic structure o ...
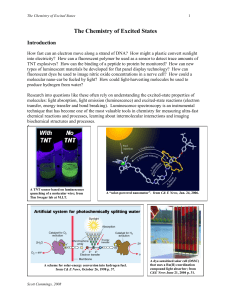
The Chemistry of Excited States
... by electrons and the lowest-energy “unoccupied” orbitals having no electrons. Of these, the transition requiring the lowest-energy photon corresponds to a transition of an electron from the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) to the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO). The HOMO-LUMO ene ...
... by electrons and the lowest-energy “unoccupied” orbitals having no electrons. Of these, the transition requiring the lowest-energy photon corresponds to a transition of an electron from the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) to the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO). The HOMO-LUMO ene ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.