Microsoft Word
... coupling reaction between a carbonyl compound and an alkylnitro compound bearing αhydrogen, the overall transformation enables the formation of a C-C bond with the concomitant generation of a new difunctional group, namely the optically active βnitroalcohol function in presence of a chiral catalyst. ...
... coupling reaction between a carbonyl compound and an alkylnitro compound bearing αhydrogen, the overall transformation enables the formation of a C-C bond with the concomitant generation of a new difunctional group, namely the optically active βnitroalcohol function in presence of a chiral catalyst. ...
Condensed Matter 2
... thermodynamics and kinetics to the study of the physical properties of gases, liquids and solids on both microscopic and macroscopic scales. There will be particular emphasis on the properties of liquids and solutions. This course provides a bridge between the elementary study of condensed matte ...
... thermodynamics and kinetics to the study of the physical properties of gases, liquids and solids on both microscopic and macroscopic scales. There will be particular emphasis on the properties of liquids and solutions. This course provides a bridge between the elementary study of condensed matte ...
Document
... Primary bromoalkanes and iodoalkanes can be prepared by the reaction with HBr and HI. Chloroalkanes cannot be prepared by this method because Cl- is too poor a nucleophile. ...
... Primary bromoalkanes and iodoalkanes can be prepared by the reaction with HBr and HI. Chloroalkanes cannot be prepared by this method because Cl- is too poor a nucleophile. ...
Effect of nucleophile on reaction
... • Normally ethers are stable under most conditions • They are commonly used as solvents • But with strong protic acids or Lewis acids they can be cleaved O ...
... • Normally ethers are stable under most conditions • They are commonly used as solvents • But with strong protic acids or Lewis acids they can be cleaved O ...
cycloadditions with singlet oxygen
... was not the main cause of selectivity since the tert-butyl group at R3 did not increase syn / anti selectivity (entry 2).21 Entries 3 and 4 seemed to support a stepwise mechanism. With R1=OMe, the electron-rich olefin was farther from the directing hydroxyl group and a decreased selectivity was obs ...
... was not the main cause of selectivity since the tert-butyl group at R3 did not increase syn / anti selectivity (entry 2).21 Entries 3 and 4 seemed to support a stepwise mechanism. With R1=OMe, the electron-rich olefin was farther from the directing hydroxyl group and a decreased selectivity was obs ...
...detail
... of zero, first and second order reactions; consecutive, reversible first order and side reactions. Arrhenius equation and activation energy. Concept of steady state with reference to hydrogenbromine chain reaction (thermal). (10 lectures) 5. Properties of Ionic Solutions I Ostwald’s dilution law; pH ...
... of zero, first and second order reactions; consecutive, reversible first order and side reactions. Arrhenius equation and activation energy. Concept of steady state with reference to hydrogenbromine chain reaction (thermal). (10 lectures) 5. Properties of Ionic Solutions I Ostwald’s dilution law; pH ...
Chemistry in Action: Question paper - A
... (iii) State how barium sulfate can be used in medicine. Explain why this use is possible, given that solutions containing barium ions are poisonous. Use ............................................................................................................................ Explanation .......... ...
... (iii) State how barium sulfate can be used in medicine. Explain why this use is possible, given that solutions containing barium ions are poisonous. Use ............................................................................................................................ Explanation .......... ...
Chapter 14
... and especially DO NOT distill these solvents that have been kept after long periods of time ...
... and especially DO NOT distill these solvents that have been kept after long periods of time ...
Effect of nature and surface density of oxygen species on product
... However, in the calculations performed for non-flow reactor, the total number of species of each type is fixed from the beginning. This means that not only oxygen and hydrocarbon concentrations, but also the initial (at zero time) distribution of active sites determine the amount of oxidant and redu ...
... However, in the calculations performed for non-flow reactor, the total number of species of each type is fixed from the beginning. This means that not only oxygen and hydrocarbon concentrations, but also the initial (at zero time) distribution of active sites determine the amount of oxidant and redu ...
12-Nucleophilic Reactions
... Due to the nucleophile reacting in a backside attack to the electrophilic carbon ...
... Due to the nucleophile reacting in a backside attack to the electrophilic carbon ...
Mechanism of Autoxidative Degradation of Cellulose
... In aqueous solutions, molecular oxygen is a fairly good oxidizing agent. During the reaction, oxygen may be reduced to water by one-electron transfer in four successive stages giving rise to intermediate products, namely, superoxide (HOO/O2ˉ), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl radicals (HO). The ...
... In aqueous solutions, molecular oxygen is a fairly good oxidizing agent. During the reaction, oxygen may be reduced to water by one-electron transfer in four successive stages giving rise to intermediate products, namely, superoxide (HOO/O2ˉ), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl radicals (HO). The ...
Molecular Structure and Orbitals - Blackboard
... – Usually atomic orbitals are half-filled before bonding – Spins of the electrons are paired once bond is formed • Overlapping orbitals are on adjacent atoms and are either – Standard atomic orbitals (s, p, d, f) – Hybridized atomic orbitals made by combining individual atomic orbitals. • Each bonde ...
... – Usually atomic orbitals are half-filled before bonding – Spins of the electrons are paired once bond is formed • Overlapping orbitals are on adjacent atoms and are either – Standard atomic orbitals (s, p, d, f) – Hybridized atomic orbitals made by combining individual atomic orbitals. • Each bonde ...
Chapter 10
... Atomic p orbital is higher in energy than sp3 (less s character) and the overlap for p orbitals is much less to form π bond ...
... Atomic p orbital is higher in energy than sp3 (less s character) and the overlap for p orbitals is much less to form π bond ...
Reactions of Alcohols - John Carroll University
... • Glycols can be oxidatively cleaved by periodic acid (HIO4) to form the corresponding ketones and aldehydes. • This cleavage can be combined with the hydroxylation of alkenes by osmium tetroxide or cold potassium permanganate to form the glycol and the cleavage of the glycol with periodic acid. • S ...
... • Glycols can be oxidatively cleaved by periodic acid (HIO4) to form the corresponding ketones and aldehydes. • This cleavage can be combined with the hydroxylation of alkenes by osmium tetroxide or cold potassium permanganate to form the glycol and the cleavage of the glycol with periodic acid. • S ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 10 – Alkyl Halides II Chem 2310 I
... Only 2o alkyl halides commonly undergo rearrangements. 3 o alkyl halides are already as stable as they can be, and 1o carbocations are not commonly formed. ...
... Only 2o alkyl halides commonly undergo rearrangements. 3 o alkyl halides are already as stable as they can be, and 1o carbocations are not commonly formed. ...
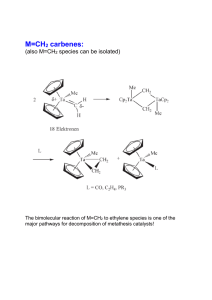
Steric protection of alkylidene is not needed:
... - X should NOT be O (dimer formation) but NR with large R group - other substituents should be electron-withdrawing (important for alkene coordination) ...
... - X should NOT be O (dimer formation) but NR with large R group - other substituents should be electron-withdrawing (important for alkene coordination) ...
Final Exam Review Sheet Chemistry 110a/1998
... thermodynamic control, using an arrow-pushing mechanism and a potential energy diagram analysis of any relevant intermediates. 8. Explain how the Diels-Alder reaction can be used to construct six-membered rings, using an arrow-pushing mechanism and a HOMO-LUMO orbital correlation to explain how the ...
... thermodynamic control, using an arrow-pushing mechanism and a potential energy diagram analysis of any relevant intermediates. 8. Explain how the Diels-Alder reaction can be used to construct six-membered rings, using an arrow-pushing mechanism and a HOMO-LUMO orbital correlation to explain how the ...
Acyl Anions Derived from Enol Ethers
... The normal disconnection pattern of a carboxylic acid with a Grignard reagent and carbon dioxide as SEs (path a) and a disconnection leading to a carboxyl synthon with an "unnatural" negative charge (path b). Cyanide ion can act as an SE of a negatively charged carboxyl synthon. Its reaction with R ...
... The normal disconnection pattern of a carboxylic acid with a Grignard reagent and carbon dioxide as SEs (path a) and a disconnection leading to a carboxyl synthon with an "unnatural" negative charge (path b). Cyanide ion can act as an SE of a negatively charged carboxyl synthon. Its reaction with R ...
reaction rate - davis.k12.ut.us
... particles must have to form the activated complex and lead to a reaction is called the activation energy. • High activation energy means that few collisions have the required energy and the reaction rate is slow. ...
... particles must have to form the activated complex and lead to a reaction is called the activation energy. • High activation energy means that few collisions have the required energy and the reaction rate is slow. ...
IB2 SL CHEMISTRY Name: …………………………… Topic 10
... Secondary halogenoalkanes can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions by both SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. The mechanism showing the formation of the transition state in the reaction between 2-bromobutane and potassium hydroxide can be represented as follows. CH 2 CH 3 H ...
... Secondary halogenoalkanes can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions by both SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. The mechanism showing the formation of the transition state in the reaction between 2-bromobutane and potassium hydroxide can be represented as follows. CH 2 CH 3 H ...
New process of low-temperature methanol synthesis from CO/CO2
... dual-catalysis, the mechanism of methanol synthesis reaction maybe changes, and the activity energy of the rate-determining step gets lower, leading to easy progress of the synthesis reaction. For the same type of alcohol, higher carbon alcohol has lower catalytic activity, as shown in the cases of ...
... dual-catalysis, the mechanism of methanol synthesis reaction maybe changes, and the activity energy of the rate-determining step gets lower, leading to easy progress of the synthesis reaction. For the same type of alcohol, higher carbon alcohol has lower catalytic activity, as shown in the cases of ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.