Kinetic study on carbonation of crude Li2CO3 with CO2
... Abstract−Investigations were conducted to purify crude Li2CO3 via direct carbonation with CO2-water solutions at atmospheric pressure. The experiments were carried out in a slurry bubble column reactor with 0.05 m inner diameter and 1.0 m height. Parameters that may affect the dissolution of Li2CO3 ...
... Abstract−Investigations were conducted to purify crude Li2CO3 via direct carbonation with CO2-water solutions at atmospheric pressure. The experiments were carried out in a slurry bubble column reactor with 0.05 m inner diameter and 1.0 m height. Parameters that may affect the dissolution of Li2CO3 ...
Air-Stable Trialkylphosphonium Salts
... focusing on the phosphonium salts of P(n-Bu)3 and P(t-Bu)3. We show that [(n-Bu)3PH]BF4 and [(t-Bu)3PH]BF4 are stable to oxygen and to moisture and that they can be stored in air for long periods of time (>4 months) without any detectable deterioration. Furthermore, we demonstrate that these phospho ...
... focusing on the phosphonium salts of P(n-Bu)3 and P(t-Bu)3. We show that [(n-Bu)3PH]BF4 and [(t-Bu)3PH]BF4 are stable to oxygen and to moisture and that they can be stored in air for long periods of time (>4 months) without any detectable deterioration. Furthermore, we demonstrate that these phospho ...
Kinetics
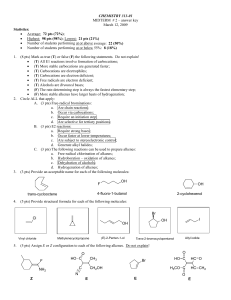
... CH3CH2I + OH- CH3CH2OH + IThe reaction is first order with respect to both ethyl iodide and hydroxide ion, and the overall-rate expression for the reaction is as follows: rate = k[CH3CH2I][OH-] What would you do in the laboratory to obtain data to confirm the order in the rate expression for eithe ...
... CH3CH2I + OH- CH3CH2OH + IThe reaction is first order with respect to both ethyl iodide and hydroxide ion, and the overall-rate expression for the reaction is as follows: rate = k[CH3CH2I][OH-] What would you do in the laboratory to obtain data to confirm the order in the rate expression for eithe ...
Chapter 19, part II Notes
... simultaneously in both directions. •Products are being formed and are also being used to form reactants. ...
... simultaneously in both directions. •Products are being formed and are also being used to form reactants. ...
HCN Synthesis from Methane and Ammonia: Mechanisms of Pt
... results from the frequency calculations at the DZP level. The level of theory applied cannot be expected to yield as accurate thermochemical data as reported for the 3d transition metal series,16,17 because relativistic effects18-21 are substantial for platinum, and the pseudopotential used only cov ...
... results from the frequency calculations at the DZP level. The level of theory applied cannot be expected to yield as accurate thermochemical data as reported for the 3d transition metal series,16,17 because relativistic effects18-21 are substantial for platinum, and the pseudopotential used only cov ...
C - Glow Blogs
... Reacting hydrogen with ethene to form ethane would be an example of this type of reaction. ...
... Reacting hydrogen with ethene to form ethane would be an example of this type of reaction. ...
Alcohols and Carbonyls test
... Reacting hydrogen with ethene to form ethane would be an example of this type of reaction. ...
... Reacting hydrogen with ethene to form ethane would be an example of this type of reaction. ...
Abstract
... D2O (due to NH2) in addition to preence of singlet of two protons at 7.61 ppm ( S-CH2). The El-Mass spectra of compound (VI) shows prominent molecular ion peak and the fragmentation pattern are characterized by loss of NH-NH2 to produce the base peak. The new derivatives of quinoline was obtained wh ...
... D2O (due to NH2) in addition to preence of singlet of two protons at 7.61 ppm ( S-CH2). The El-Mass spectra of compound (VI) shows prominent molecular ion peak and the fragmentation pattern are characterized by loss of NH-NH2 to produce the base peak. The new derivatives of quinoline was obtained wh ...
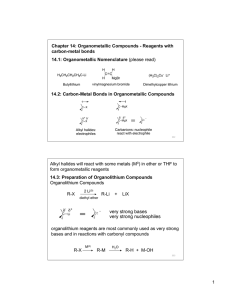
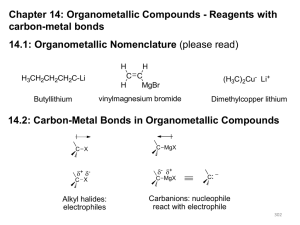
Organometallic Compounds - Reagents
... synthesis by reasoning backward from the the target molecule to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ulti ...
... synthesis by reasoning backward from the the target molecule to a starting compound using known and reliable reactions. “it is a problem solving technique for transforming the structure of a synthetic target molecule (TM) to a sequence of progressively simpler structures along the pathway which ulti ...
3.10 aromatic chemistry
... Kathleen Lonsdale used X – Ray diffraction to confirm the ring type structure. It did however throw up new problems: Ø The structure was shown to be planar Ø It was found that all the C-C bond lengths were equal in length and in between C – C and C = C bond lengths C – C 0.153nm cyclohexane C = C 0. ...
... Kathleen Lonsdale used X – Ray diffraction to confirm the ring type structure. It did however throw up new problems: Ø The structure was shown to be planar Ø It was found that all the C-C bond lengths were equal in length and in between C – C and C = C bond lengths C – C 0.153nm cyclohexane C = C 0. ...
An Overview of Carbonyl Compound Chemistry
... carbon cation character. Like a typical carbon cation, two possible reactions can occur around the carbonyl carbon. The first is simply an addition reaction in which a nucleophile is added to the carbonyl to form a new covalent bond (termed AdN , addition nucleophilic). The second is a β-elimination ...
... carbon cation character. Like a typical carbon cation, two possible reactions can occur around the carbonyl carbon. The first is simply an addition reaction in which a nucleophile is added to the carbonyl to form a new covalent bond (termed AdN , addition nucleophilic). The second is a β-elimination ...
Hydrogen bonding
... The reaction is very slow with primary chlorides, and may occur by heating them with ZnCl2 for several hours. Since this reaction occurs by SN2 mechanism, the order of reactivity is: ...
... The reaction is very slow with primary chlorides, and may occur by heating them with ZnCl2 for several hours. Since this reaction occurs by SN2 mechanism, the order of reactivity is: ...
Chapter 8 I. Nucleophilic Substitution
... Physicist Roland Wester and his team in Matthias Weidemüller's group at the University of Freiburg, in Germany, in collaboration with William L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected m ...
... Physicist Roland Wester and his team in Matthias Weidemüller's group at the University of Freiburg, in Germany, in collaboration with William L. Hase's group at Texas Tech University, provide direct evidence for this mechanism in the gas phase. However, they also detected an additional, unexpected m ...
M_ScOrganic_Chemistr..
... 5. Compendium of Organic Synthetic Methods, Vol. I and III, Harrison and Harrison. 6. The Logic of Chemical Synthesis, E. J. Corey and X-M. Cheng, John Wiley 1998 7. Classics in Total Synthesis; K.C. Nicolaou and E.J. Sorensen, VCH;1996. 8. Classics in Total Synthesis II: More Targets, Strategies, M ...
... 5. Compendium of Organic Synthetic Methods, Vol. I and III, Harrison and Harrison. 6. The Logic of Chemical Synthesis, E. J. Corey and X-M. Cheng, John Wiley 1998 7. Classics in Total Synthesis; K.C. Nicolaou and E.J. Sorensen, VCH;1996. 8. Classics in Total Synthesis II: More Targets, Strategies, M ...
98 pts
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
General Sciences Sample First Exercise Propanoic Acid Solution
... Study of a Pharmacological Hydrogen Peroxide Solution A pharmacological hydrogen peroxide solution (S0), used as an antiseptic and as hairs’ colorizing agent, is labeled 30V. This indication represents the maximum volume of 30 L of oxygen gas (measured under normal conditions where Vm = 22.4 L.mol-1 ...
... Study of a Pharmacological Hydrogen Peroxide Solution A pharmacological hydrogen peroxide solution (S0), used as an antiseptic and as hairs’ colorizing agent, is labeled 30V. This indication represents the maximum volume of 30 L of oxygen gas (measured under normal conditions where Vm = 22.4 L.mol-1 ...
Metal Carbenes
... Carbenes are both thermodynamically and kinetically unstable therefore forming very strong metal-carbene bonds disfavoring dissociation e.g. just as pramagnetic triplet :CH2 can dimerize to form diamagnetic H2C=CH2, it also binds to a triplet LnM fragment to give a diamagnetic LnM=CH2 complex. ...
... Carbenes are both thermodynamically and kinetically unstable therefore forming very strong metal-carbene bonds disfavoring dissociation e.g. just as pramagnetic triplet :CH2 can dimerize to form diamagnetic H2C=CH2, it also binds to a triplet LnM fragment to give a diamagnetic LnM=CH2 complex. ...
Woodward–Hoffmann rules

The Woodward–Hoffmann rules, devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann, are a set of rules in organic chemistry predicting the barrier heights of pericyclic reactions based upon conservation of orbital symmetry. The Woodward–Hoffmann rules can be applied to understand electrocyclic reactions, cycloadditions (including cheletropic reactions), sigmatropic reactions, and group transfer reactions. Reactions are classified as allowed if the electronic barrier is low, and forbidden if the barrier is high. Forbidden reactions can still take place but require significantly more energy.The Woodward–Hoffmann rules were first formulated to explain the striking stereospecificity of electrocyclic reactions under thermal and photochemical control. Thermolysis of the substituted cyclobutene trans-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (1) gave only one diastereomer, the (E,E)-3,4-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene (2) as shown below; the (Z,Z) and the (E,Z) diastereomers were not detected in the reaction. Similarly, thermolysis of cis-1,2,3,4-tetramethylcyclobutene (3) gave only the (E,Z) diastereomer (4).Due to their elegance and simplicity, the Woodward–Hoffmann rules are credited with first exemplifying the power of molecular orbital theory to experimental chemists. Hoffmann was awarded the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work, shared with Kenichi Fukui who developed a similar model using frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory; because Woodward had died two years before, he was not eligible to win what would have been his second Nobel Prize for Chemistry.